
How does air travel through the bronchial tubes?
What flows in bronchial tubes? When a person breathes, air comes in through the nose or mouth and then goes into the trachea (windpipe). From there, it passes through the bronchial tubes, which are in the lungs. These tubes let air in and out of your lungs, so you can breathe. The bronchial tubes are sometimes referred to as bronchi or airways.
What are the bronchial tubes?
Normally, the muscles surrounding your bronchial tubes are thin and smooth, and they allow air to flow easily. If you have a respiratory problem, such as asthma, these muscles can contract and...
How does asthma affect the bronchial tubes?
Particle deposition in the small bronchial tubes (generations six through twelve) is strongly influenced by the vortex-dominated secondary flows that are induced by axial curvature of the tubes. In this paper, we employ particle destination maps in conjunction with two-dimensional, finite-time Lyapunov exponent maps to illustrate how the trajectories of finite-mass particles …
What is the pathway of air through the body?
The laminar flow in the small bronchial tubes, characterized by a Reynolds number range of approximately 100 to 1000, is quite complex due to the presence of …

What moves mucus in bronchial tubes?
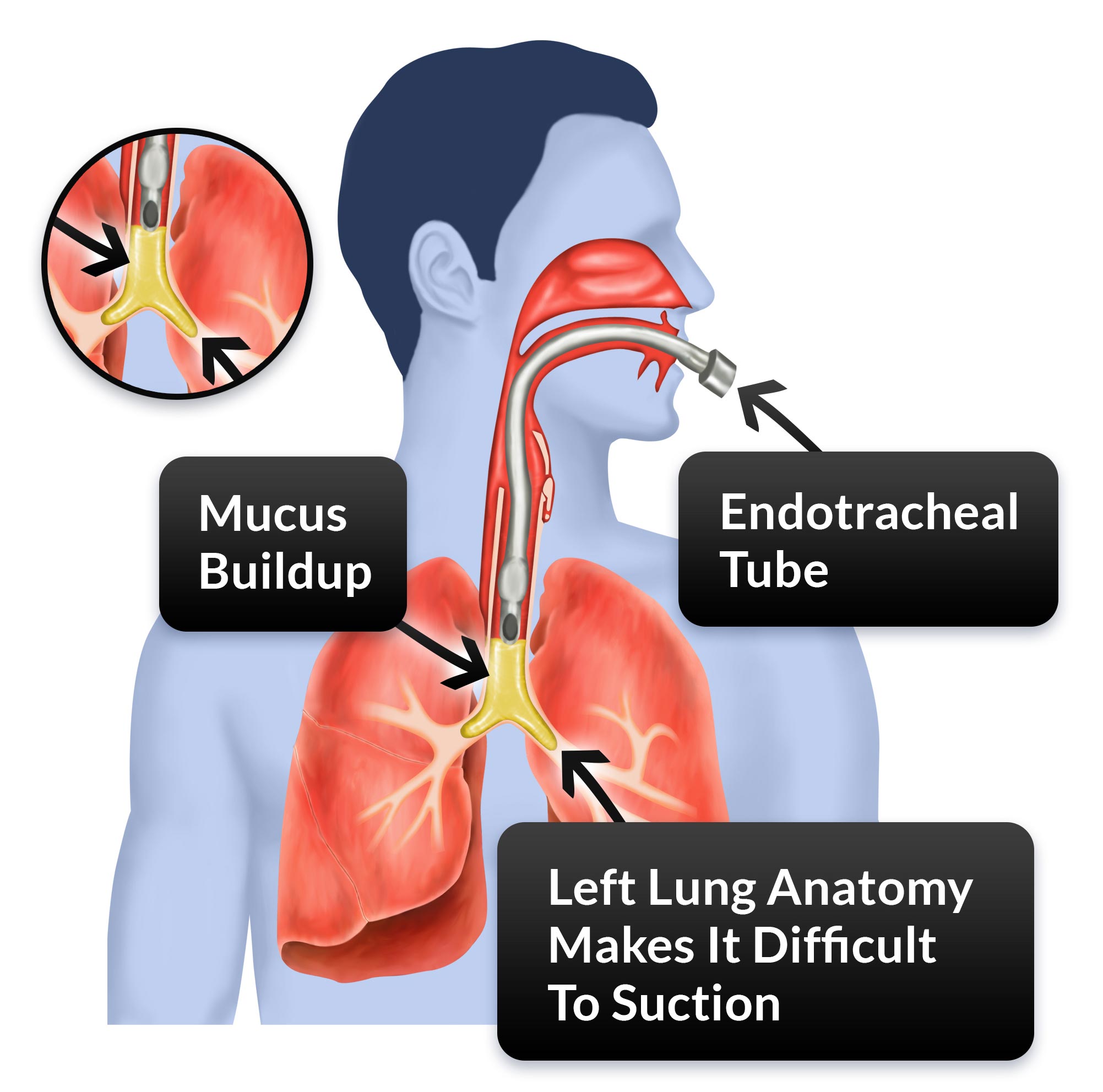
The bronchi are lined with cilia, tiny hairlike structures. The cilia help move mucus (phlegm) and particles out of your lungs. When you cough or swallow, the particles trapped in the mucus move out of your body or into your digestive tract, where your body can dispose of them.Jun 21, 2021
What is the main function of the bronchial tubes?
When a person breathes, air comes in through the nose or mouth and then goes into the trachea (windpipe). From there, it passes through the bronchial tubes, which are in the lungs. These tubes let air in and out of your lungs, so you can breathe.
Does gas exchange occurs in your bronchial tubes?
The smallest branches of the bronchial tubes are called BRONCHIOLES, at the end of which are the air sacs or alveoli. ALVEOLI are the very small air sacs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place.Mar 5, 2021
What gases are added to inhaled air and then exhaled?
They bring oxygen into our bodies (called inspiration, or inhalation) and send carbon dioxide out (called expiration, or exhalation). This exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide is called respiration.
What does bronchial mean?
Listen to pronunciation. (BRON-kee-ul) Having to do with the bronchi, which are the larger air passages of the lungs, including those that lead from the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs and those within the lungs.
Where do the bronchial tubes start?
Breathing starts when you inhale air into your nose or mouth. It travels down the back of your throat and into your windpipe, which is divided into air passages called bronchial tubes.Nov 25, 2021
How does gaseous exchange occur?
Gaseous exchange occurs at the alveoli in the lungs and takes place by diffusion. The alveoli are surrounded by capillaries so oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the air in the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries.
Which is the order of airflow during inhalation?
Pathway of air: nasal cavities (or oral cavity) > pharynx > trachea > primary bronchi (right & left) > secondary bronchi > tertiary bronchi > bronchioles > alveoli (site of gas exchange)
Where does gaseous exchange take place?
the lungsDuring gas exchange oxygen moves from the lungs to the bloodstream. At the same time carbon dioxide passes from the blood to the lungs. This happens in the lungs between the alveoli and a network of tiny blood vessels called capillaries, which are located in the walls of the alveoli.Jul 25, 2020
Where does diffusion meet bulk flow in the respiratory system?
7:159:21Respiratory System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #31 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo it's your alveoli where diffusion meets bulk flow because while you're picking up oxygen.MoreSo it's your alveoli where diffusion meets bulk flow because while you're picking up oxygen.
What tube acts as the trunk of the respiratory tree?
The trachea is the trunk of the tree located in the superior mediastinum. The bronchi are the branches of the tree within the lungs. Both the trachea and bronchi form part of the conducting zone of the respiratory system.Aug 11, 2021
What is alveolar sac?
(al-VEE-oh-ly) Tiny air sacs at the end of the bronchioles (tiny branches of air tubes in the lungs). The alveoli are where the lungs and the blood exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide during the process of breathing in and breathing out.
What is the name of the tube that passes through the lungs?
Benjamin F. Asher, MD. on August 21, 2020. Your bronchial tubes are one of the tubes where air passes through your lungs to get to the area where oxygen enters the bloodstream and waste products are released so they can be breathed out of the body. BSIP / Getty Images.
What are the symptoms of bronchial tubes?
As a result, the changes lead to symptoms such as: Wheezing. Chest tightness. Shortness of breath. Cough. The treatments for changes in the bronchial tubes are both drugs to provide acute symptom relief and drugs designed to prevent asthma symptoms.
Why do you need mucus for asthma?
While your doctor probably often talks about the overproduction of mucus in asthma, you need some mucus to be healthy. The mucus acts as a sticky pad and tries to keep foreign things that should not be in your lungs out.
How does breathing work?
How Breathing Works. When you breathe air in, it passes through your nose or mouth, through the larynx, and into the trachea or windpipe. From your trachea, air splits off into your right and left main bronchial tubes, or right and left main bronchus. As your bronchial tubes continue to branch off and get smaller and smaller, ...
Where do airways end?
Your airways terminate at the air sacs called alveoli, where the exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen takes place. The alveoli are surrounded by a network of blood vessels called capillaries. The capillaries are where oxygen enters the bloodstream to be delivered to the rest of the body and the body gets rid of some waste products such as carbon ...
Where does oxygen travel?
After the oxygen enters the bloodstream in the capillaries, it travels back to the heart where it is distributed to the rest of the body. As oxygen is delivered to cells in the body it is exchanged for carbon dioxide that is then delivered back to the capillaries and ultimately exhaled out of the lungs.
Does asthma damage the bronchial tubes?
Asthma usually does not permanently damage the structure of the bronchial tubes, but other diseases can, such as: However, there are long-term consequences of poorly controlled asthma. While most asthma symptoms are reversible with treatment, chronic inflammation can lead to a process called airway remodeling.
Why do my bronchial tubes constrict?
If you have allergy-induced asthma, your bronchial tubes will constrict when you inhale substances that trigger an allergic reaction.
What is bronchial spasm?
What are bronchial spasms? When you breathe, air travels through your throat and trachea, which is also known as your windpipe. Then it travels into and out of your bronchial tubes. These tubes extend into your lungs and branch into smaller air passages.
What is it called when you wheeze when you catch your breath?
When that happens, it’s called a bronchial spasm, or a bronchospasm. During a bronchial spasm, breathing becomes more difficult. You may find yourself wheezing as you try to catch your breath. In many cases, bronchial spasms are treatable or preventable.
What is the best treatment for acute bronchitis?
For example, a bacterial infection will require antibiotics to treat. If you have chronic bronchitis or emphysema, your doctor will likely pre scribe inhalers and antibiotics.
What are the causes of asthma?
Common allergens include plant pollens, pet dander, and dust. Nonallergic asthma can be triggered by irritants such as air pollution, cigarette or wood-fire smoke, fumes from household cleaning products, or very cold air. Exercise can also trigger an asthma attack in some people.
What tests can be done to check for lung disease?
For example, your doctor may order a chest X-ray or other imaging tests. This can help them assess your lung health and check for signs of infection or structural abnormalities. They may conduct a spirometry test. This measures how much air you can inhale and exhale.
Can bronchial spasms affect exercise?
Bronchial spasms limit your ability to exercise. Over time, this can have far-reaching effects on your fitness and overall health, which depends on your ability to be physically active. Serious bronchial spasms can also limit the amount of oxygen that you inhale.
Why does my bronchial tube swell?
In both cases, the bronchial tubes swell, become narrower, and mucus builds up. When a bronchial tube is inflamed, it becomes harder for air to flow through it.
What are the symptoms of bronchitis?
Most common bronchitis symptoms. The most common symptom is a cough. It often produces mucus. You may also have a mild fever, trouble breathing, chest pressure, and wheezing. Symptoms may be similar to a bacterial infection, pneumonia, allergies, or chemical exposure.
What does it mean when you cough with mucus?
A cough with mucus is a sign of bronchitis. During the doctor's exam, you might have abnormal breath sounds. A chest X-ray, labs, and cultures (blood, respiratory, and viral) may be needed too. —Dr. Chandra Manuelpillai
What causes a cough and a fever?
Bronchitis is a viral infection that causes swelling (inflammation) of the bronchial tubes. The bronchial tubes bring air to the lungs. Bronchitis causes a cough. You may also have a mild fever, wheezing, some difficulty breathing, and chest tightness.
How long does it take for bronchitis to go away?
Bronchitis usually improves within a few weeks. Though a mild cough and some chest discomfort (tightness or shortness of breath) may last a few months. Smokers can take even longer to recover. And sometimes the cough may not completely go away.
How to avoid bronchitis?
Washing hands often with soap and water is the best way to avoid getting a viral infection like bronchitis. Also avoiding cigarette smoke. Always stay up-to-date on immunizations. This includes your annual flu shot and all recommended vaccines for children.
Is it dangerous to have bronchitis?
Bronchitis is not usually dangerous. Unless you have a risk factor, call your doctor or go to urgent care. For serious breathing problems, wheezing, racing heart, dizziness, vomiting, or other similar symptoms, go to the ER.
Causes
- Your bronchial tubes are one of the tubes where air passes through your lungs to get to the area where oxygen enters the bloodstream and waste products are released so they can be breathed out of the body. When you breathe air in, it passes through your nose or mouth, through the larynx, and into the trachea or windpipe. From your trachea, air spli...
Mechanism of action
- After the oxygen enters the blood stream in the capillaries, it travels back to the heart where it is distributed to the rest of the body. As oxygen is delivered to cells in the body it is exchanged for carbon dioxide that is then delivered back to the capillaries and ultimately exhaled out of the lungs.
Symptoms
- Asthma affects the bronchial tubes by causing inflammation that can lead to bronchoconstriction and increased mucus production that impairs the flow of air. As a result, the changes lead to symptoms such as:
Treatment
- The treatments for changes in the bronchial tubes are both drugs to provide acute symptom relief and drugs designed to prevent asthma symptoms. Rescue inhalers are designed to provide acute asthma relief by opening up your airways and increasing airflow. These medications are only taken as needed and use more than twice per week indicates poor asthma control. Preventive m…
Clinical significance
- Asthma usually does not permanently damage the structure of the bronchial tubes, but other diseases can, such as:
Prognosis
- However, there are long-term consequences to poorly controlled asthma. While most asthma symptoms are reversible with treatment, chronic inflammation can lead to a process called airway remodeling. Over many years of poor asthma control, a chronic scarring of the lung can occur and eventually lead to disability. The only way to prevent this from occurring is to get proactive abou…