
The following foods increase oxidative stress in your body: Sugar – Sugar increases oxidative stress in multiples ways (see my previous article about liver function). Sugar is a carbohydrate. Some people think of it as an “easy energy source.”
What is the best supplement for oxidative stress?
- Almonds
- Sunflower Seeds
- Strawberries
- Broccoli
- Bell Peppers
What are some foods that reduce stress?
The 10 Best Foods to Help Fight Stress
- Herbal Tea Helps Promote Feelings of Warmth and Calmness. ...
- Dark Chocolate Offers an Antioxidant-Rich Indulgence. ...
- Whole Grains Provide a Mood-Boosting Way to Carbo-Load. ...
- Avocados Offer Stress-Busting Omega-3 Fatty Acids. ...
- Fish Can Boost Your Heart Health While Fending Off Stress. ...
- Warm Milk Can Help You Get a Good Night’s Sleep, Aiding Stress Management. ...
How do you reduce oxidative stress?
These are some ideas for daily stress remedies:
- Exercise
- Meditation
- Talking with a friend
- Enjoying nature
- Journaling
- Watching a funny show
- Taking a walk.
How to counteract oxidative stress?
Some of the best ways to prevent oxidative stress include:
- Change your diet to a healthier one
- Indulge in an active lifestyle
- Consume some more antioxidants
- Keep your health in check
- Quit smoking
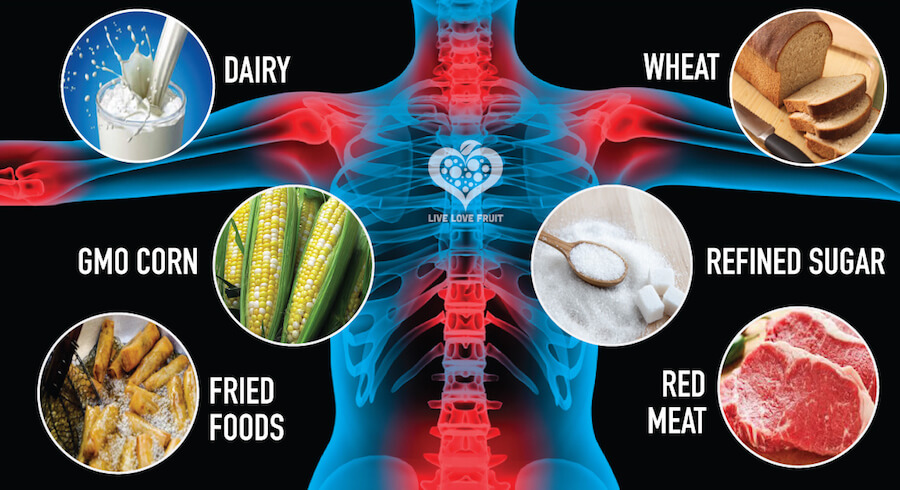
What food increases oxidative stress?
Diets, especially high-fat or high-carbohydrate diets, have been shown to be associated with oxidative stress by elevating the levels of protein carbonylation and lipid peroxidation products while reducing the antioxidant defense status [1].
What food reduces oxidative stress?
Managing and preventing oxidative stressberries.cherries.citrus fruits.prunes.dark leafy greens.broccoli.carrots.tomatoes.More items...
What food reduces oxidative stress and inflammation?
High intake of fruit and vegetables is related to low oxidative stress and inflammation in a group of patients with type 2 diabetes - PMC.
How do you fix oxidative stress?
Making the following lifestyle changes may help prevent oxidative stress:Quit smoking, if you smoke. ... Include more antioxidant-rich foods in your diet. ... Limit alcohol use. ... Lower your stress levels. ... Protect your skin. ... Get physical. ... Get enough sleep. ... Try antioxidant supplements.
Do eggs cause oxidative stress?
We consistently found that the inclusion of whole eggs does not adversely affect the inflammatory status but reduces the oxidative stress, even with dietary cholesterol present, supporting eggs as an abundant source of antioxidants.
Does vitamin D reduce oxidative stress?
Vitamin D adequacy leads to less oxidative stress and improves mitochondrial and endocrine functions, reducing the risks of disorders, such as autoimmunity, infections, metabolic derangements, and impairment of DNA repair; all of this aids a healthy, graceful aging process.
How do you know if you have oxidative stress?
There are a few signs that can indicate oxidative stress in the body or excessive inflammation, such as:Chronic fatigue.Digestive disorders (Acid reflux, constipation, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, etc.)Memory loss and lack of concentration.Joint pain and inflammation.Premature aging.Headaches and sensitivity to noise.More items...•
Which vitamin protects against oxidative stress?
Vitamin E (i.e., α-tocopherol) and Vitamin C (i.e., ascorbic acid) are antioxidants that are thought to have a protective effect by either reducing or preventing oxidative damage.
What vitamin protects the body from oxidative damage?
Vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene, often referred to as "antioxidant vitamins," have been suggested to limit oxidative damage in humans, thereby lowering the risk of certain chronic diseases.
Can you reverse oxidative stress?
Once you've eliminated your exposure to these triggers, you can help your body reverse the effects of oxidative stress by take anti-oxidant supplements* (even before you start taking folate), such as: Vitamin C – immune support, anti-histamine and antioxidant all in one; best absorbed in the liposomal form.
Does coffee cause oxidative stress?
Caffeine has been reported as a protective substance against cellular damage with beneficial antioxidant effects [8–10]. Intake of caffeine is associated with reduced levels of biomarkers of oxidative stress [11–15].
Does fasting reduce oxidative stress?
Fasting and caloric restriction have been associated with reduced incidence of chronic diseases and cancers. These effects have been attributed to reduced oxidative stress.
Can you reverse oxidative stress damage?
Once you've eliminated your exposure to these triggers, you can help your body reverse the effects of oxidative stress by take anti-oxidant supplements* (even before you start taking folate), such as: Vitamin C – immune support, anti-histamine and antioxidant all in one; best absorbed in the liposomal form.
What vitamins reduce oxidative stress?
Vitamin E (i.e., α-tocopherol) and Vitamin C (i.e., ascorbic acid) are antioxidants that are thought to have a protective effect by either reducing or preventing oxidative damage.
What is the most powerful antioxidant?
As mentioned above, a-tocopherol is well recognized and accepted as the nature's most effective lipid-soluble, chain-breaking antioxidant, protecting cellular membranes from being attacked by lipid peroxyl radicals. Vitamin E prevents the propagation of lipid peroxyl radicals in cellular membranes.
What Is Oxidative Stress?
Oxidative stress is something that happens inside our cells. Remember: our bodies are made up of trillions of cells. It’s hard to imagine, but it’s true! And inside each and every cell (except red blood cells) is a tiny “engine” called a mitochondrion. The mitochondria create the energy our bodies use to function, to be awake, to sleep, to digest, to think, to breathe – everything!
How to reverse oxidative stress?
Once you’ve eliminated your exposure to these triggers, you can help your body reverse the effects of oxidative stress by take anti-oxidant supplements * (even before you start taking folate), such as: Vitamin C – immune support, anti- histamine and antioxidant all in one; best absorbed in the liposomal form.
Why is oxidative stress a paradox?
It is like a “snowball effect.” In an effort to protect us from stress and infection, oxidative stress increases , which ends up damaging our cells and slowing down processes further.
What happens when your body is overwhelmed by oxidative stress?
When our bodies are overwhelmed by oxidative stress and/or inflammation, they perpetuate that pattern and things get worse. It is like a “snowball effect.”. In an effort to protect us from stress and infection, oxidative stress increases, which ends up damaging our cells and slowing down processes further.
What happens when you don't have enough anti-oxidants in your cells?
And if we don’t have enough “anti-oxidants” in our cells, then that exhaust can damage our mitochondria, causing decreased energy production and overall function.
Is oxidative stress a protection mechanism?
Similar to inflammation, oxidative stress is one of our body’s protection mechanisms. Without it, we would be in trouble. Thankfully, when our bodies are healthy, they also produce natural anti-oxidative stress mechanisms, to balance things out.
Can oxidative stress change?
So, people tend to accept it as something they can’t change. And people often tell me they don’t want to learn about something if they can’t do something about it. But you CAN do something about oxidative stress. Similar to inflammation, oxidative stress is one of our body’s protection mechanisms.
How to prevent oxidative stress?
One method of preventing oxidative stress is to ensure that you’re obtaining enough antioxidants in your diet. Eating five servings per day of a variety of fruits and vegetables is the best way to provide your body what it needs to produce antioxidants. Examples of fruits and vegetables include: berries. cherries.
What is oxidative stress?
Overview. Oxidative stress is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body. Free radicals are oxygen-containing molecules with an uneven number of electrons. The uneven number allows them to easily react with other molecules. Free radicals can cause large chain chemical reactions in your body because they react so easily ...
How does oxidative stress affect the body?
Oxidative stress can cause damage to many of your tissues, which can lead to a number of diseases over time. While you can’t completely avoid exposure to free radicals, you can make lifestyle choices regarding diet, exercise, and environment to help keep your body in balance, and prevent damage and disease.
What are the causes of aging?
inflammatory conditions. high blood pressure, which is also known as hypertension. heart disease. neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. cancer. Oxidative stress also contributes to aging.
How can we reduce free radicals?
Be environmentally conscious. Environmentally friendly initiatives like carpooling help reduce free radical production for you and your community.
What is the best way to reduce oxidative stress?
A regular, moderate exercise routine. This has been associated with higher natural antioxidant levels and decreased damage caused by oxidative stress. Regular exercise has been linked with a longer lifespan, fewer effects of aging, and decreased risk of cancer and disease.
What happens when free radicals are present?
When there are more free radicals present than can be kept in balance by antioxidants, the free radicals can start doing damage to fatty tissue, DNA, and proteins in your body. Proteins, lipids, and DNA make up a large part of your body, so that damage can lead to a vast number of diseases over time.
Why are antioxidants weak?
However, the protective system of antioxidants may be weak because of sickness, aging, small amounts of antioxidants in food, and poor intake. Factors that boost the creation of free radicals in the body can be internal, or external.
What happens when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants?
However, when there’s an imbalance between free radical action and antioxidant action, oxidative stress may take place. When the share of free radicals in the body escalates remarkably and, due to their excessive activity, will instead begin to assault and damage the body’s own cells. These injured cells, in turn, create new free radicals.
What is the disproportion between antioxidants and free radicals?
Oxidative stress is a disproportion between antioxidants and free radicals (known as reactive oxygen species (ROS)) in your body. Free radicals are chemical compounds developed by oxidation, for instance, as by-products of metabolism.
How do antioxidants help the body?
Above all, antioxidants stimulate, and significantly increase the body defenses against pathogens and boost the immune system. In conclusion, They help to eliminate harmful toxic substances, inhibit and prevent the onset and development of many dangerous diseases, and contribute to the treatment of almost all chronic diseases.
Why are antioxidants called free radical scavengers?
So, because of that antioxidants are sometimes also called “free-radical scavengers.”. The sources of antioxidants can be natural or artificial. Your body also generates some antioxidants, known as endogenous antioxidants. Antioxidants that originate outer the body are named exogenous.
What are unsteady radicals?
These radicals are exceptionally unsteady atoms that have electrons accessible to respond with different natural substrates, for example DNA, proteins and lipids. Free radicals include:
Why do we have free radicals?
Your body generates free radicals as a response to environmental and other forces, as the body processes food and responds to the environment. Therefore, it is absolutely ordinary to have some free radicals in your body.
What is the cause of oxidative stress?
Oxidative stress is a phenomenon caused by an imbalance between production and accumulation of oxygen reactive species (ROS) in cells and tissues and the ability of a biological system to detoxify these reactive products.
How does oxidative stress affect cancer?
Cancer onset in humans is a complex process, which requires both cellular and molecular alterations mediated by endogenous and/or exogenous triggers. It is already well known that oxidative DNA damage is one of those stimuli responsible for cancer development [14, 15, 22]. Cancer can be driven and/or promoted by chromosomal abnormalities and oncogene activation determined by oxidative stress. Hydrolyzed DNA bases are common by-products of DNA oxidation and are considered one of the most relevant events in chemical carcinogenesis [14, 22]. The formation of such kind of adducts impairs normal cell growth by altering the physiological transcriptomic profile and causing gene mutations. Oxidative stress can also cause a variegated amount of modifications against DNA structure, for example, base and sugar lesions, DNA-protein cross-links, strand breaks, and base-free sites. For instance, tobacco smoking, environmental pollutants, and chronic inflammation are sources of oxidative DNA damage that could contribute to tumor onset [14, 17, 29]. Oxidative stress resulting from lifestyle reasons can also play an important role in cancer development, as suggested by the strong correlation between dietary fat consumption (a factor that exposes the organism at greater risk of lipid peroxidation) and death rates from different types of cancer [16, 21].
Which compounds can acquire a prooxidant behavior?
6.2. Polyphenols. Under conditions like high concentrations, high pH, and the presence of redox-active metals, phenolic compounds can acquire a prooxidant behavior [157, 158], mainly based on the generation of an aroxyl radical or a labile complex with a metal cation exerting redox activity.
What are the causes of free radicals?
Free radicals are generated from both endogenous and exogenous sources. Immune cell activation, inflammation, ischemia, infection, cancer, excessive exercise, mental stress, and aging are all responsible for endogenous free radical production. Exogenous free radical production can occur as a result from exposure to environmental pollutants, heavy metals (Cd, Hg, Pb, Fe, and As), certain drugs (cyclosporine, tacrolimus, gentamycin, and bleomycin), chemical solvents, cooking (smoked meat, used oil, and fat), cigarette smoke, alcohol, and radiations [15–25]. When these exogenous compounds penetrate the body, they are degraded or metabolized, and free radicals are generated as by-products.
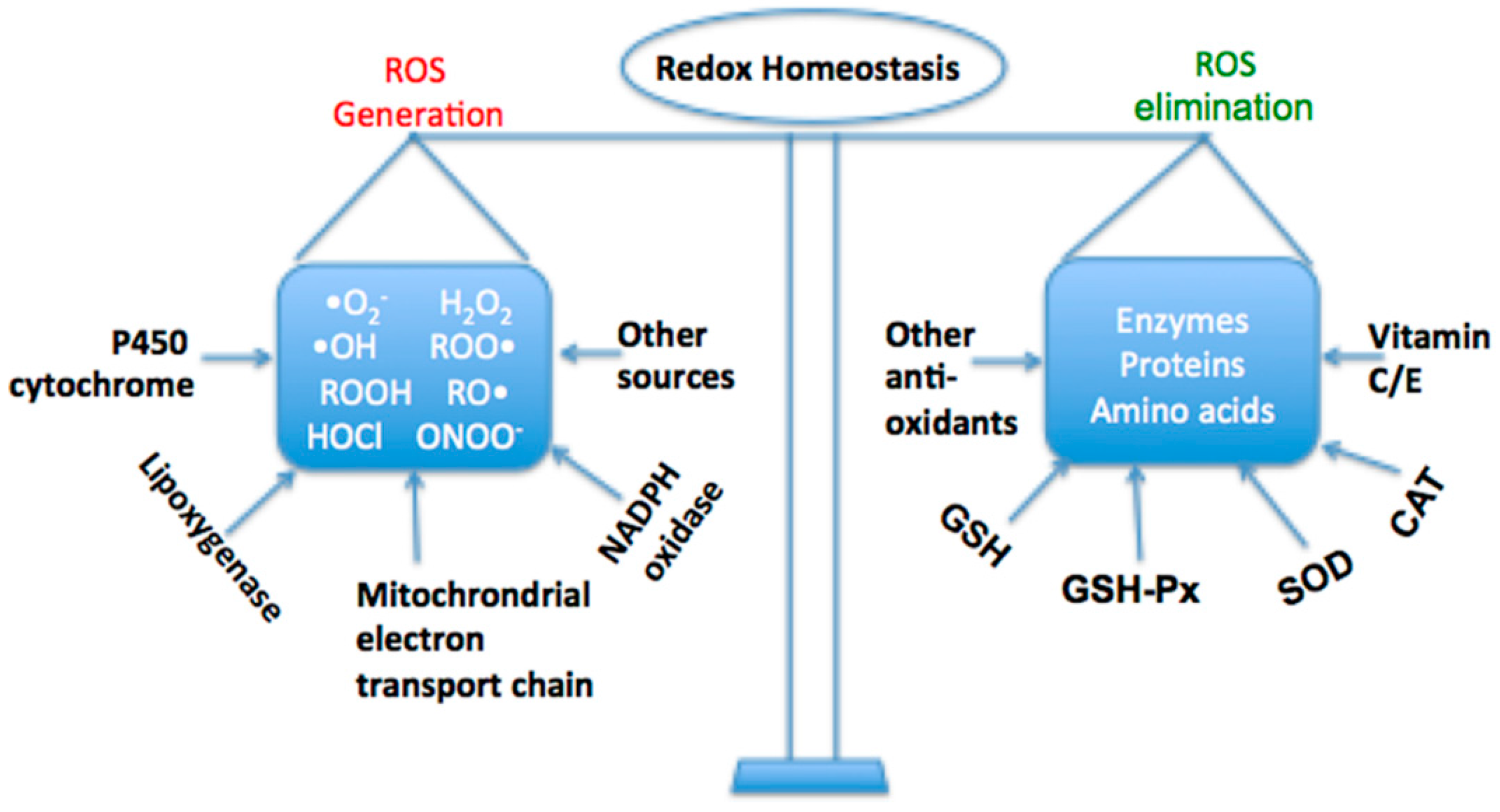
What are the two types of reactions that produce ROS?
ROS production basically relies on enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Enzymatic reactions able to generate ROS are those involved in respiratory chain, prostaglandin synthesis, phagocytosis, and cytochrome P450 system [10–20]. Superoxide radical (O2•−) is generated by NADPH oxidase, xanthine oxidase, and peroxidases. Once formed, it is involved in several reactions that in turn generate hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical (OH•), peroxynitrite (ONOO−), hypochlorous acid (HOCl), and so on. H2O2(a nonradical) is produced by multiple oxidase enzymes, that is, amino acid oxidase and xanthine oxidase. Hydroxyl radical (OH•), the most reactive among all the free radical species in vivo, is generated by reaction of O2•−with H2O2, with Fe2+or Cu+as a reaction catalyst (Fenton reaction) [12–19]. Nitric oxide radical (NO•), which plays some important physiological roles, is synthesized from arginine-to-citrulline oxidation by nitric oxide synthase (NOS) [12–19].
What are the reactive oxygen species?
Superoxide radicals (O2•−), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl radicals (•OH), and singlet oxygen (1O2) are commonly defined reactive oxygen species (ROS); they are generated as metabolic by-products by biological systems [1, 2]. Processes, like protein phosphorylation, activation of several transcriptional factors, apoptosis, immunity, and differentiation, are all dependent on a proper ROS production and presence inside cells that need to be kept at a low level [3]. When ROS production increases, they start showing harmful effects on important cellular structures like proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids [4]. A large body of evidences shows that oxidative stress can be responsible, with different degrees of importance, in the onset and/or progression of several diseases (i.e., cancer, diabetes, metabolic disorders, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular diseases) [5].
Is oxidative stress a neurodegenerative disease?
Oxidative stress has been linked to several neurological diseases (i.e., Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), multiple sclerosis, depression, and memory loss) [32–35]. In AD, several experimental and clinical researches showed that oxidative damage plays a pivotal role in neuron loss and progression to dementia [34]. β-amyloid, a toxic peptide often found present in AD patients' brain, is produced by free radical action and it is known to be at least in part responsible for neurodegeneration observed during AD onset and progression [35].
What would happen if we didn't have enough antioxidants?
Without enough antioxidants we would age more quickly and be more prone to neurodegenerative diseases. According to the USDA Database for the Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) of Selected Foods, Release 2, “The development of various chronic and degenerative diseases, such as heart disease, and neuronal degeneration such as Alzheimer’s ...
What are antioxidants?
Antioxidants are extremely important for fighting oxidative stress and diminishing free radical damage to our cells and DNA. Without enough antioxidants we would age more quickly and be more prone to neurodegenerative diseases.
What is the root cause of disease?
Oxidative stress is one of the fundamental root causes of disease that is within your grasp to reverse and prevent. When there is an imbalance in the production of free radicals from the metabolism of energy from the air you breathe, oxidative stress is the result.
Do herbs have more antioxidants than food?
From these lists we can see that herbs contain way more antioxidant potential or higher ORAC scores than food. It’s no wonder traditional cultures the world over have a long history of herbal medicine use! So go ahead and add more of these high-ORAC foods and herbs into your daily diet. The more the better; and you will start repairing from the inside out and can feel better and more vibrant soon.
Overview
- Oxidative stress is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body. Free radic…
Antioxidants are molecules that can donate an electron to a free radical without making themselves unstable. This causes the free radical to stabilize and become less reactive.
Effects of oxidative stress on the body
- Oxidation is a normal and necessary process that takes place in your body. Oxidative stress, on …
When there are more free radicals present than can be kept in balance by antioxidants, the free radicals can start doing damage to fatty tissue, DNA, and proteins in your body. Proteins, lipids, and DNA make up a large part of your body, so that damage can lead to a vast number of disea… - •diabetes
•atherosclerosis, or the hardening of the blood vessels
What are the risk factors?
- Everyone produces some free radicals naturally in their body through processes like exercise or …
You may also be exposed to free radicals in the environment. Some sources include: - •ozone
•certain pesticides and cleaners
Managing and preventing oxidative stress
- It’s impossible to completely avoid free radical exposure and oxidative stress. However, there ar…
One method of preventing oxidative stress is to ensure that you’re obtaining enough antioxidants in your diet. Eating five servings per day of a variety of fruits and vegetables is the best way to provide your body what it needs to produce antioxidants. Examples of fruits and vegetables inclu… - •berries
•cherries
The takeaway
- While free radicals and antioxidants are part of your body’s natural and healthy functioning, oxid…
While you can’t completely avoid exposure to free radicals, you can make lifestyle choices regarding diet, exercise, and environment to help keep your body in balance, and prevent damage and disease.