Foods like bread, couscous or pasta are all usually made from refined grains, or a mixture of whole and refined grains. Foods naturally high in, or with added, sugar cause a rapid increase in insulin production. Products may list sugars under a number of different names, such as sucrose, maltose or dextrose, all of which contain glucose.
- sugary drinks, such as soda, juices, and sports drinks.
- processed foods and baked goods, which often contain trans fats.
- white rice, bread, and pasta.
- breakfast cereals with added sugar.
- yogurts with added sugar.
- honey and maple syrup.
What foods are rich in insulin?
The following can cause blood sugar and insulin levels to spike:
- sugary drinks, such as soda, juices, and sports drinks
- processed foods and baked goods, which often contain trans fats
- white rice, bread, and pasta
- breakfast cereals with added sugar
- yogurts with added sugar
- honey and maple syrup
- flavored, sugary coffee drinks
- french fries
- dried fruit, which often has added sugar
What foods will not raise blood sugar?
Thirteen foods that won't raise blood glucose
- Avocados. Avocados are high in healthful fats, and may help to reduce the risk of metabolic syndrome. ...
- Tuna, halibut, and fish with omega-3 fatty acids. ...
- Garlic. ...
- Sour cherries. ...
- Apple cider vinegar. ...
- Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and chard. ...
- Chia seeds. ...
- Cacao. ...
- Blueberries and blackberries. ...
- Almonds and other nuts. ...
Do nuts raise insulin?
That being said, even freshly ground 100 percent peanuts can raise your blood sugar, too. For those taking insulin, you may find you need a very small bolus of insulin with a serving of peanuts, peanut butter, or other nuts.
How to stop insulin spike?
Natural Ways to Prevent Mealtime Sugar Spikes
- Go for a walk after you eat. Research shows that a 15-minute stroll after dinner can help bring blood sugar down. ...
- Get enough shut-eye. Skimping on sleep, even for one night, makes your body use insulin less efficiently. ...
- See your dentist regularly. ...
- Drink plenty of water. ...
- Watch your stress level. ...
What macronutrients do not cause insulin?
What is the insulin index of food?
How does the body process carbohydrates?
How does insulin affect your body?
Why are people overweight on a low carb diet?
How does the body get energy from food?
Does fiber cause obesity?
See 2 more
What foods dont trigger insulin?
Thirteen foods that won't raise blood glucoseAvocados.Fish.Garlic.Sour cherries.Vinegar.Vegetables.Chia seeds.Cacao.More items...
What triggers an insulin spike?
Carbohydrates (carbs) are what cause blood sugar to rise. When you eat carbs, they are broken down into simple sugars. Those sugars then enter the bloodstream. As your blood sugar levels rise, your pancreas releases a hormone called insulin, which prompts your cells to absorb sugar from the blood.
Do eggs raise insulin levels?
While high protein, virtually no-carb foods like meat and eggs are low on the glycemic index, they measure high on the insulin index. In other words, while the meat and eggs didn't cause a spike in blood sugar the way most carbohydrates do, they do result in a significant rise in insulin.
What foods help control insulin levels?
Fill Your Kitchen With the Following FoodsVeggies.Fruit.Beans.Lentils.Barley, quinoa, oats.Omega-3 fatty fish (sardines, herring, salmon)Sweet potatoes.Water, tea, and other unsweetened beverages.
How do you prevent insulin spikes?
12 Simple Tips to Prevent Blood Sugar SpikesGo low-carb. Carbohydrates (carbs) are what cause blood sugar to rise. ... Eat fewer refined carbs. ... Reduce your sugar intake. ... Keep a healthy weight. ... Exercise more. ... Eat more fiber. ... Drink more water. ... Introduce some vinegar into your diet.More items...
Can a non diabetic have blood sugar spikes?
High blood sugar is the [primary symptom that underlies diabetes], but it can also occur in people who don't have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, either because of stress or trauma, or gradually as a result of certain chronic conditions.
What causes blood sugar spikes without eating?
Coffee—even without sweetener. Some people's blood sugar is extra-sensitive to caffeine. Losing sleep—even just one night of too little sleep can make your body use insulin less well. Skipping breakfast—going without that morning meal can increase blood sugar after both lunch and dinner.
What foods spike glucose levels?
In general, foods that cause blood sugar level to rise the most are those that are high in carbohydrates, which are quickly converted into energy, such as rice, bread, fruits and sugar. Next are foods high in protein, such as meats, fish eggs, milk and dairy products, and oily foods.
White Grains
The food items which contain white grain are generally considered to be refined sources of carbohydrates, such as white bread, pasta, and rice.
Sugar-Sweetened Drinks
There is no doubt that sugar-sweetened drinks will lead to an elevation of blood sugar levels in your body.
Starchy Vegetables
Starchy vegetables such as peas, corn, potatoes, etc contain huge amounts of carbs.
Non-Dairy Milk
Non-dairy milk is said to have been composed of a high amount of sugar, on the other hand, dairy milk is composed of carbs with low GI.
Fruits
Consumption of fruits can also lead to an increase in blood sugar levels, but remember that no one can cut down on fruits entirely.
High-fat meat
High-fat meats such as fatty cuts of pork, beef, and lamb, poultry skin, dark meat chicken, etc should also be avoided by those suffering from type 2 diabetes.
Which foods have the highest insulin levels?
This study and subsequent studies showed that any type of meat (beef, chicken, and pork) produced substantial insulin secretion. "In fact meat protein causes as much insulin release as pure sugar.".
Why does insulin go up?
This means the body has to produce more insulin to keep blood sugar levels healthy. If the pancreas is unable to keep up with the increased demand for insulin, blood sugar levels go up. When this happens, cells can't use all of the excess glucose in the blood. This leads to type 2 diabetes.
What Is Insulin?
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that allows your body to use sugar (glucose) from carbohydrates in the food that you eat for energy or to store glucose for future use. Insulin helps keeps your blood sugar level from getting too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia). The cells in your body need sugar for energy. However, sugar cannot go into most of your cells directly. After you eat food and your blood sugar level rises, cells in your pancreas (known as beta cells) are signaled to release insulin into your bloodstream. Insulin then attaches to and signals cells to absorb sugar from the bloodstream. Insulin is often described as a “key,” which unlocks the cell to allow sugar to enter the cell and be used for energy. If you have more sugar in your body than it needs, insulin helps store the sugar in your liver and releases it when your blood sugar level is low or if you need more sugar, such as in between meals or during physical activity. Therefore, insulin helps balance out blood sugar levels and keeps them in a normal range. As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas secretes more insulin. If your body does not produce enough insulin or your cells are resistant to the effects of insulin, you may develop hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), which can cause long-term complications if the blood sugar levels stay elevated for long periods of time. Insulin Treatment for Diabetes People with type 1 diabetes cannot make insulin because the beta cells in their pancreas are damaged or destroyed. Therefore, these people will need insulin injections to allow their body to process glucose and avoid complications from hyperglycemia. People with type 2 diabetes do not respond well or are resistant to insulin. They may need insulin shots to help them better process Continue reading >>
Why Would Eating Fish Increase Diabetes Risk?
The fact that there are six different ones published recently highlights how open the question remains. One thread of consistency, though, was that fish consumers in the United States tended to be at greater risk for diabetes. If we include Europe, then fish eaters appeared to have a 38% increased risk of diabetes. On a per serving basis, that comes out to be about a 5% increase in risk for every serving of fish one has per week. To put that into perspective, a serving of red meat per day is associated with 19% increase in risk. Just one serving per day of fish would be equivalent to a 35% increase in risk. But why might fish be worse than red meat? Fish intake may increase type 2 diabetes risk by increasing blood sugar levels, as a review of the evidence commissioned by the U.S. government found. The review found that blood sugars increase in diabetics given fish oil. Another possible cause is that omega 3’s appear to cause oxidative stress. A recent study, highlighted in my video, Fish and Diabetes, found that the insulin producing cells in the pancreas don’t appear to work as well in people who eat two or more servings of fish a week. Or it may not be related to omega 3’s at all but rather the environmental contaminants that build up in fish. It all started with Agent Orange. We sprayed 20 million gallons of the stuff on Vietnam, and some of it was contaminated with trace amounts of dioxins. Though the Red Cross estimates that a million Vietnamese were adversely affected, what about all the servicem Continue reading >>
How to lower insulin levels?
1. Follow a Low-Carb Diet Of the three macronutrients — carbs, protein and fat — carbs raise blood sugar and insulin levels the most.For this and other reasons, low-carb diets can be very effective for losing weight and controlling diabetes.
Why are people overweight on a low carb diet?
Due to rising obesity and insulin resistance rates, low-carb and Paleo diets have become a popular approach to the growing population of overweight Americans. As stated by Dr. John McDougall, "Advocates of high-protein diets explain the reason people are fat is not because of the fat they eat, but because of hyperinsulinism and insulin resistance. Insulin encourages fat cells to store fat and prevents the release of fat from these cells. Therefore, high levels of insulin, known as hyperinsulinism, would be expected to promote obesity." One high-protein, low-carb website, emphasizes that carbohydrates are the "root of all evil" when it comes to weight loss and health. Consequently, the majority of calories from a low-carb diet come from meat, which contains protein and fat, but no carbs. Although carbs do make our insulin levels go up, Dr. Micheal Greger points out in the video above that scientists have known for over a half century that protein makes it go up as well. An "Insulin Index of Foods" was published in 1997 which listed 38 foods that produced higher insulin levels. This study and subsequent studies showed that any type of meat (beef, chicken, and pork) produced substantial insulin secretion. "In fact meat protein causes as much insulin release as pure sugar." Meat raised insulin levels higher than a large apple, a cup of oatmeal, a cup and a half of white flour pasta. Below we've highlighted a few points from the Insulin Index: "Some of the protein-rich foods (beef, cheese, eggs) had larger insulin responses per gram than did many of the foods consisting predominately of carbohydrate." "Carbohydrate is not the only stimulus for insulin secretion." Protein-rich foods can also stimulate insulin secretion without increasing blood glucose concentrations. "A low-f Continue reading >>
How to reduce insulin insensitivity?
Making diet changes can reduce insulin insensitivity. This reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes and the health problems that go with it. Contents of this article: Understanding insulin resistance Glucose is a vital source of energy for the body. However, many of the body's cells can't absorb glucose on their own.
How to increase insulin sensitivity?
Here are 25 simple actions you can take that improve insulin sensitivity. #1: Do strength training and other anaerobic activities. Exercise is absolutely critical for improving insulin sensitivity because your muscles and cells are desperate for fuel during and after your workout.
How to help diabetics with food?
Sticking to a diet of diabetic foods is one natural way to help manage your condition and feel as good as possible all day long. If you’re tired of the cycle of eating foods that spike your blood sugar levels, this list will help you avoid those foods and crowd them out with better, more healthy choices. 1. Spinach and Kale Spinach and kale are very similar to each other in terms of how they’re handled by the body and the amount of nutrition they provide. Diabetics can enjoy as much of either one as they care for, and there really isn’t a huge advantage of one over the other. You’ll be getting both Vitamin A and Vitamin C from each, as well as potassium, magnesium, and iron. Baby spinach and baby kale are very much alike in terms of usability, each having their own taste which is their major difference. You can use spinach and kale interchangeably in green smoothie recipes, but kale gets the edge in the snack department because it’s so easy to make kale chips that taste great and won’t leave you filled with regret when you’re done snacking. Eating Nutrient Dense Foods If you’re looking for some of the most nutrient dense foods on the planet you can’t go wrong with spinach and kale. Once for once they provide more vitamins and minerals than just about any other food, including other vegetables and fruit. 2. Beans Beans are a great addition to most any meal because they’ll help to stabilize your blood sugar, rather than have a detrimental effect or no effect at all. Foods like this are important because they can help balance out other foods that aren’t necessarily diabetic-friendly, and they can reduce the amount of insulin needed to bring your levels back to normal. Beans are easy enough to add to a meal, and many recipes call for beans as part of t Continue reading >>
Why do we need to select foods based on their glycemic index?
Selecting foods based on their glycemic index, a system that ranks foods based on their potential effect on your blood sugar levels, helps you to find foods that keep your blood sugar levels low; the lower the GI ranking, the less of an impact on your blood sugar levels.
What is the blood sugar solution?
The Blood Sugar Solution (2012) is a book about reducing the risk of “diabesity,” the continuum from optimal blood sugar balance toward insulin resistance and full-blown diabetes. Food guidelines: Eat natural, unprocessed foods Eat moderate amounts of low-glycemic-load carbs – with stricter limits for the advanced program Avoid dairy and gluten during the program to allow the gut to heal 1 week preparation, 6 weeks program (basic or advanced) Below on this page is a full description of the food recommendations. Preparation | General guidelines | Basic program | Advanced program | Boosting your nutrition | Reintroduction and diet for life. The book has a lot more information in it. Get a copy of The Blood Sugar Solution for more information on the reasons behind the recommendations, hormone regulation, quizzes, supplementation, menus, recipes, resources and more. Also, get The Blood Sugar Solution Cookbook for a detailed list of serving sizes and many more recipes for the Basic Program and the Advanced Program as well as Reintroduction, and a few desserts. Note that this is the original book / basic plan – see also The Blood Sugar Solution 10-Day Detox Diet by the same author for his detox diet. The reasoning behind The Blood Sugar Solution This book encourages the use of functional medicine – asking the question “why?” – not just “what is the right drug for this disease?” The goal is to understand what disturbs the normal function of these systems, and how we can best create optimal function. It states that nearly all people who are overweight (over 70% of adult Americans) already have “pre-diabetes” and have significant risks of disease and death. Managing blood sugar and insulin levels through diet and supplements reduces this risk better than Continue reading >>
What is the cause of glucose in urine?
Diabetes is when the body’s ability to produce or respond to insulin is compromised. This results in abnormal metabolism of carbohydrates. This also causes an increase of glucose levels in urine and in the blood. This disease is a chronic disease that’s fast on the rise.
Why is insulin sensitivity important?
Insulin sensitivity is SO important for fat loss because when you are insulin resistant, the body is much more likely to store the food you eat as fat. Insulin resistance also produces inflammation in the body, causing a whole bunch of health problems that any sane person wouldn’t want to deal with.
What are the fears of fat?
For the past four decades mainstream food recommendations have been dominated by a fear of fat, particularly saturated fat and cholesterol, which if, taken to the extreme can lead us towards more processed, insulinogenic, nutrient poor, low fat foods.
What foods affect blood sugar the most?
Foods containing carbohydrates affect blood sugar the most. Maintaining healthy blood sugar doesn’t mean cutting out this food group altogether though. Instead, avoid those carb-containing foods that digest quickly, taking your blood glucose levels on a hair-raising ride through peaks and valleys. Among the biggest offenders are:
What foods help with glucose?
Carbohydrates with a high fiber content – sometimes called “slow” carbs or "low-glycemic" foods – are better for controlling blood glucose naturally. Fiber actually slows the process of digestion, curbing the release of glucose into the bloodstream and supporting healthy insulin function. Foods high in fiber include: 1 Fresh fruits and vegetables, especially with the skin on 2 Whole grains like oats, millet, quinoa and whole wheat 3 Beans and legumes
How to keep blood sugar steady?
Three squares – featuring a mix of lean protein, fiber-filled carbs and healthy fats – help keep you full and prevent blood sugar spikes. You can even enjoy a snack between meals, like a handful of nuts or a serving of whole-grain crackers with cheese.
Which is better for controlling blood glucose?
Carbohydrates with a high fiber content – sometimes called “slow” carbs or "low-glycemic" foods – are better for controlling blood glucose naturally. Fiber actually slows the process of digestion, curbing the release of glucose into the bloodstream and supporting healthy insulin function. Foods high in fiber include:
What is the function of insulin?
Produced in the pancreas, insulin’s main functions are to facilitate the absorption of glucose into your cells and the storage of excess glucose for future use. If you have prediabetes and diabetes, however, your body either can’t produce enough insulin, or it doesn’t use the hormone properly, resulting in too much circulating glucose in your blood. Monitoring your food choices helps you avoid a rush of glucose your body can’t handle.
What are processed foods?
Baked goods like cookies, cakes and other sugary desserts. Candy. Processed foods with high sugar content, like cereal, granola and granola bars. Refined grains, like white bread, rice, bagels and pasta. Jellies and jams. Fruit-flavored yogurt and sweetened milk.
Does jam affect glucose levels?
Note, though, that dried fruits and fruit juices have a higher concentrated sugar content than a piece of fresh fruit. Also, adding jam or syrup to your whole-grain toast or oatmeal will impact how quickly those foods turn to glucose in your blood.
What foods should diabetics avoid?
The following can cause blood sugar and insulin levels to spike: sugary drinks, such as soda, juices, and sports drinks. processed foods and baked goods, which often contain trans fats. white rice, bread, and pasta.
How to control blood sugar and insulin levels?
By eating a balanced diet, and avoiding foods rich in sugar, simple carbohydrates, and unhealthful fats, a person can better control their blood sugar and insulin levels. Last medically reviewed on May 3, 2019. Diabetes. Type 1.
How does diet help with diabetes?
The diet can play an essential role in managing diabetes. Understanding how certain foods affect insulin and blood sugar levels can help a person make informed choices about what to eat and when. A person with diabetes can eat a balanced, healthful diet without giving up the foods they enjoy .
How to add cacao to diet?
An easy way to add cacao to the diet is by eating dark chocolate, although too much might still cause a spike in blood sugar. Consume dark chocolate in moderation. Dark chocolate contains more cacao than milk chocolate.
Why do people eat whole grain food?
A person can incorporate whole-grain products into meals or snacks to help control blood sugar levels.
Is protein good for diabetics?
Protein content is particularly healthful for people who have diabetes, as it does not impact blood sugar. It is filling and provides essential nutrients to help the body grow and repair. People who have diabetes should try adding fatty fish to the diet on at least one day per week.
Can diabetics eat healthy food?
A person with diabetes can eat a balanced, healthful diet without giving up the foods they enjoy. The important factors in an effective diabetes diet include moderation and careful food choice to maintain healthful blood sugar levels. In this article, we identify some of the best foods for stabilizing insulin and blood sugar levels.
Why is the insulin index important?
For this reason, the insulin index can be a more useful tool when measuring the body’s response to food.
Why is it important to have a lower insulin index?
Foods with lower insulinemic indices are recommended as part of a healthy diet, to help reduce risk of developing metabolic syndromes. The insulin index of pure glucose, for example, is 100, while avocados have an insulin index of 6.
How is insulin measured?
The insulin index is measured by using a portion of the given food, along with a reference food, containing equal amounts of calories, usually 250 calories or 1000kJ (1).
How to reduce insulin release?
Therefore, minimizing the amount of carbohydrates you consume will reduce the amount of insulin eventually released. There are two predominant sources of carbohydrates in the human diet: starch and sugar. Try modifying your diet so that you eat a moderate amount of these foods. Foods that are high in sugar include:
What is the body's hormone that produces glucose?
However, for this process to work successfully, the body requires insulin . Insulin is a hormone made up of beta cells that is produced in the pancreas. Without insulin, the glucose remains in the bloodstream and can cause dangerously high blood sugar levels. Advertisement.
What is the glycemic load of a food?
Using the glycemic load is a great way of creating a list of foods that help stabilize blood sugar.
What is the process of converting carbohydrates into sugar?
When the stomach begins the digestive process , it extracts carbohydrates from consumed foods, and these carbohydrates are then turned into a form of sugar known as glucose. The stomach and small intestine then both absorb this glucose and feed it into the bloodstream, which is how cells absorb energy and keep you moving.
Does glycemic load affect insulin sensitivity?
Luckily, there are other ways to tell which foods increase insulin sensitivity and which don't.
Does minimizing carbohydrates reduce insulin?
Therefore, minimizing the amount of carbohydrates you consume will reduce the amount of insulin eventually released.
Do apples cause insulin?
Apples don't cause insulin release. Image Credit: Yulia Gusterina/iStock/GettyImages. A list of foods that do not cause insulin release would be nearly identical to a list of foods that do not raise blood sugar, as the two processes are directly linked. Insulin is the hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and allows for the absorption ...
What foods do not spike insulin?
Some of the foods that don’t spike insulin include: 1. Raw or Cooked Vegetables. Vegetables are possibly one of the best options and additions when it comes to discussing the list of foods that do not cause insulin release in an unprecedented rate.
What are the best foods to avoid insulin release?
Chia Seeds. Chia seeds are a universal ingredient that does cater to the list of foods that do not cause insulin release. These small seeds are not just high on antioxidants but are loaded with healthy fibers, calcium and even healthy fats and the omega-3 fatty acids.
What is the best way to lower insulin levels?
14. Apple Cider Vinegar. It is the acetic acid in the apple cider vinegar which has beneficial impacts on managing the insulin levels in the body. Experts do suggest that consuming apple cider vinegar after a meal can effectively help in bringing down the levels of the impacts of the carbs that you have eaten.
Why doesn't garlic spike insulin?
The best reason why garlic is often considered one of the best foods that don’t spike insulin is because of the fact that it doesn’t contain any kind of carbohydrates and thus there is no possible reason why it would cause any kind of spikes in the glucose levels.
What vegetables are low carb?
If you are wondering which vegetables to opt for under such circumstances, mushrooms, onions, tomatoes, eggplant, zucchini etc. pan out to be amazing choices.
Why is it important to eat nuts when you are hungry?
These are rich in proteins and have also been found beneficial in reducing the cholesterol levels in the body.
Do avocados help with metabolic syndrome?
All the more, even studies ( R) have found that the consumption of avocados can effectively lower the risks associated with a metabolic syndrome that majority of us complain about. Avocados also have a low glycemic index which further help manage the symptoms associated with the spikes in blood glucose and insulin. 3.
Which leaf type of spinach has the highest amounts of insulin?
In particular, Senecio biafrae (a spinach leaf type green) was found to contain the highest quantities within the samples studied. 7. Peanut Butter based meals and insulin levels. Peanut butter is a high fibrous food that helps with preventing inflammation in the body.
What fish can lower insulin levels?
Eating fatty fish like salmon, sardine, mackerel, herring, and anchovies regularly can lower your insulin levels. These fish have a high content of omega-3 fats which help in weight loss and decreasing insulin resistance. Fatty fish have other benefits also, as they are a great source of protein.
What does high insulin levels mean?
Therefore, high insulin levels indicate that someone may be at an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and may experience weight gain due to this.
What are some ways to lower blood sugar?
Eating legumes such as yellow peas, lentils, navy beans, and chickpeas help lower insulin levels. They have a low glycemic index, which means they will not increase blood sugar rapidly.
Why is it important to lower insulin levels?
Normally a person’s body will maintain a balance between insulin levels and blood sugar levels. This balance allows your body to utilize glucose for energy properly while also keeping your blood glucose at a normal level.
How to reduce insulin sensitivity?
So, implementing fruits and vegetables into your daily diet can help you prevent inflammation and increase insulin sensitivity. Aside from this, eating foods that contain plant compounds are linked to higher insulin sensitivity and thereby reduce insulin levels in the body.
Can diabetes cause insulin resistance?
However, a person’s cells may become resistant to insulin if they have prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. This can cause an uptick in blood sugar levels. This causes the pancreas to produce an excessive amount of insulin.
What macronutrients do not cause insulin?
Contrary to what many believe, carbohydrates -- that is, sugar and starch -- are not the only macronutrient that stimulates the release of insulin, the hormone responsible for clearing excess glucose from the bloodstream and packing it, in the form of fatty triglycerides, into fat cells. Protein also stimulates insulin release. Dietary fat is the only one of the three macronutrients that does not cause insulin release. Therefore, food that is made up entirely of, or predominantly of, fat is the only type that does not cause insulin release. Note that this categorization does not apply to type I diabetics, who are not able to produce insulin at all. Video of the Day Olive Oil and Other Plant-Derived Oils Oil is pure plant-source fat, whether it is olive, canola, sunflower, sesame, peanut, coconut, soy or corn. One ounce of oil is about 28 grams of fat because 1 ounce converts to about 28 grams in the metric system. It makes no difference to this equation whether the fat is saturated or unsaturated. It is probably more helpful, and certainly more accurate, to think of oil as being fat, rather than containing fat. Dietary fat by itself, including these foods, does not cause insulin release. Two tbsp. butter, about 1 ounce, contain 22 grams of fat and no carbohydrates or protein. The other 6 grams in the 28 grams ounces of butter is made up mostly of water, along with a small amount of milk solids. Butter eaten by itself does not stimulate the release of insulin. Nearly all of cream cheese's macronutrient value is in fat, as 1 ounce of cream cheese contains 9 grams of fat, but only 1 gram of carbs and 2 grams protein. That would mean that it stimulates little insulin release. One ounce of macadamia nuts contains 21grams fat, with only 4 grams carbohydrate and 2 grams protei Continue reading >>
What is the insulin index of food?
The Insulin Index of a food represents how much it elevates the concentration of insulin in the blood during the two-hour period after the food is ingested . The index is similar to the Glycemic Index (GI) and Glycemic Load (GL), but rather than relying on blood glucose levels, the Insulin Index is based upon blood insulin levels. The Insulin Index represents a comparison of food portions with equal overall caloric content (250 kcal or 1000 kJ), while GI represents a comparison of portions with equal digestible carbohydrate content (typically 50 g) and the GL represents portions of a typical serving size for various foods. The Insulin Index can be more useful than either the Glycemic Index or the Glycemic Load because certain foods (e.g., lean meats and proteins) cause an insulin response despite there being no carbohydrates present, and some foods cause a disproportionate insulin response relative to their carbohydrate load. Holt et al. [1] have noted that the glucose and insulin scores of most foods are highly correlated, [2] but high-protein foods and bakery products that are rich in fat and refined carbohydrates "elicit insulin responses that were disproportionately higher than their glycemic responses." They also conclude that insulin indices may be useful for dietary management and avoidance of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia. Explanation of Index The Insulin Index is not the same as a glycemic index (GI), which is based exclusively on the digestible carbohydrate content of a food, and represents a comparison of foods in amounts with equal digestible carbohydrate content (typically 50 g). The insulin index compares foods in amounts with equal overall caloric content (250 kcal or 1000 kJ). Insulin indexes are scaled relative to white b Continue reading >>
How does the body process carbohydrates?
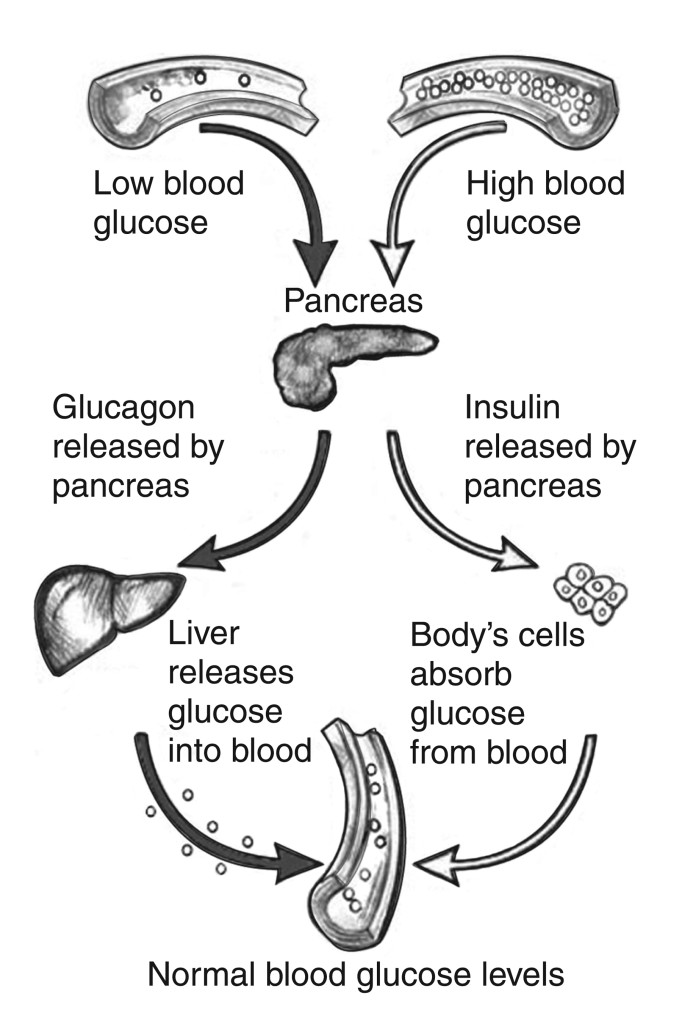
When people eat a food containing carbohydrates, the digestive system breaks down the digestible ones into sugar, which enters the blood. As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that prompts cells to absorb blood sugar for energy or storage. As cells absorb blood sugar, levels in the bloodstream begin to fall. When this happens, the pancreas start making glucagon, a hormone that signals the liver to start releasing stored sugar. This interplay of insulin and glucagon ensure that cells throughout the body, and especially in the brain, have a steady supply of blood sugar. Carbohydrate metabolism is important in the development of type 2 diabetes, which occurs when the body can’t make enough insulin or can’t properly use the insulin it makes. Type 2 diabetes usually develops gradually over a number of years, beginning when muscle and other cells stop responding to insulin. This condition, known as insulin resistance, causes blood sugar and insulin levels to stay high long after eating. Over time, the heavy demands made on the insulin-making cells wears them out, and insulin production eventually stops. Glycemic index In the past, carbohydrates were commonly classified as being either “simple” or “complex,” and described as follows: Simple carbohydrates: These carbohydrates are composed of sugars (such as fructose and glucose) which have simple chemical structures composed of only one sugar (monosaccharides) or two sugars (disaccharides). Simple carbohydrates are easily and quickly utilized for energy by the body because of their simple chemical structure, often leading to a faster rise in blood sugar and insulin secretion from the pancreas – which can have negative health effects. Complex carbohydrates: These carbohydrates have mo Continue reading >>
How does insulin affect your body?
Insulin is an extremely important hormone that's produced by your pancreas. It has many functions, such as allowing your cells to take in sugar from your blood for energy. However, too much insulin can lead to serious health problems. Having high levels, also known as hyperinsulinemia, has been linked to obesity, heart disease and cancer (1, 2, 3). High blood insulin levels also cause your cells to become resistant to the hormone's effects. When you become insulin resistant, your pancreas produces even more insulin, creating a vicious cycle (4). Here are 14 things you can do to lower your insulin levels. Of the three macronutrients — carbs, protein and fat — carbs raise blood sugar and insulin levels the most. For this and other reasons, low-carb diets can be very effective for losing weight and controlling diabetes. Many studies have confirmed their ability to lower insulin levels and increase insulin sensitivity, compared to other diets (5, 6, 7, 8, 9). People with health conditions characterized by insulin resistance, such as metabolic syndrome and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), may experience a dramatic lowering of insulin with carb restriction. In one study, individuals with metabolic syndrome were randomized to receive either a low-fat or low-carb diet containing 1,500 calories. Insulin levels dropped by an average of 50% in the low-carb group, compared to 19% in the low-fat group (10). In another study, when women with PCOS ate a lower-carb diet containing enough calories to maintain their weight, they experienced greater reductions in insulin levels than when they ate a higher-carb diet (11). Low-carb diets have been shown to increase insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin levels in people with obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and PCOS. Apple cider v Continue reading >>
Why are people overweight on a low carb diet?
Due to rising obesity and insulin resistance rates, low-carb and Paleo diets have become a popular approach to the growing population of overweight Americans. As stated by Dr. John McDougall, "Advocates of high-protein diets explain the reason people are fat is not because of the fat they eat, but because of hyperinsulinism and insulin resistance. Insulin encourages fat cells to store fat and prevents the release of fat from these cells. Therefore, high levels of insulin, known as hyperinsulinism, would be expected to promote obesity." One high-protein, low-carb website, emphasizes that carbohydrates are the "root of all evil" when it comes to weight loss and health. Consequently, the majority of calories from a low-carb diet come from meat, which contains protein and fat, but no carbs. Although carbs do make our insulin levels go up, Dr. Micheal Greger points out in the video above that scientists have known for over a half century that protein makes it go up as well. An "Insulin Index of Foods" was published in 1997 which listed 38 foods that produced higher insulin levels. This study and subsequent studies showed that any type of meat (beef, chicken, and pork) produced substantial insulin secretion. "In fact meat protein causes as much insulin release as pure sugar." Meat raised insulin levels higher than a large apple, a cup of oatmeal, a cup and a half of white flour pasta. Below we've highlighted a few points from the Insulin Index: "Some of the protein-rich foods (beef, cheese, eggs) had larger insulin responses per gram than did many of the foods consisting predominately of carbohydrate." "Carbohydrate is not the only stimulus for insulin secretion." Protein-rich foods can also stimulate insulin secretion without increasing blood glucose concentrations. "A low-f Continue reading >>
How does the body get energy from food?
Your body draws energy from food by transforming what you eat into glucose, a kind of sugar. A hormone called insulin then works in your bloodstream to release that glucose to your muscles and organs. Most of the time, this system runs like a fine-tuned machine, but in some people, insulin malfunction may result in an unhealthy build-up of glucose. Knowing which foods to avoid helps you balance your insulin and manage blood glucose to stay healthy. Produced in the pancreas, insulin’s main functions are to facilitate the absorption of glucose into your cells and the storage of excess glucose for future use. If you have prediabetes and diabetes, however, your body either can’t produce enough insulin, or it doesn’t use the hormone properly, resulting in too much circulating glucose in your blood. Monitoring your food choices helps you avoid a rush of glucose your body can’t handle. Foods That Spike Blood Sugar Foods containing carbohydrates affect blood sugar the most. Maintaining healthy blood sugar doesn’t mean cutting out this food group altogether though. Instead, avoid those carb-containing foods that digest quickly, taking your blood glucose levels on a hair-raising ride through peaks and valleys. Among the biggest offenders are: Table sugar Regular sodas and other sweetened beverages Baked goods like cookies, cakes and other sugary desserts Candy Processed foods with high sugar content, like cereal, granola and granola bars Refined grains, like white bread, rice, bagels and pasta Jellies and jams Fruit-flavored yogurt and sweetened milk If you do occasionally use processed foods, check the Nutrition Facts label on the packaging for the grams of sugar in a serving. The higher the sugar content, the faster the food will raise your blood sugar. Better Carbs f Continue reading >>
Does fiber cause obesity?
Abstract Epidemiologic evidence favors the hypothesis that obesity may result from the fiber-depleted diet of industrialized societies. Since hyperinsulinemia is a universal characteristic and perhaps causal of obesity, the possibility is considered that dietary factors causing excess insulin secretion might lead to obesity. Dietary glucose causes a slightly greater insulin rise than cooked starch containing an equal amount of carbohydrate, and high fiber starchy foods cause a much lesser insulin response than does glucose in solution. Doubling the dose of carbohydrate in a meal causes only a small increase in glucose response but a large increase in insulin response. Dietary fiber could act by displacing some of the carbohydrate that would normally be absorbable in the small intestine, or could translocate the carbohydrate to a point lower in the intestinal tract where less effect on insulin secretion would be observed. Evidence is presented that a higher fiber diet is associated with a higher concentration of fasting circulating free fatty acids, a lesser post-cibal decrease in circulating free fatty acids and triglycerides and less chronic increase in fasting triglycerides than a low fiber diet. These differences are associated with a lesser insulin response to high fiber meals. The extreme fluctuations between the fed and fasted states seen with low fiber diets are thus dampened by high fiber diets. The less complete inhibition of lipolysis during the fed state, and more intense lipolysis during fasting, suggested by the above data, might tend to prevent obesity. The mechanisms of the lesser insulin response to high rather than low fiber meals are not known, but the possibility that dietary fiber decreases the GIP response is considered. Continue reading >>