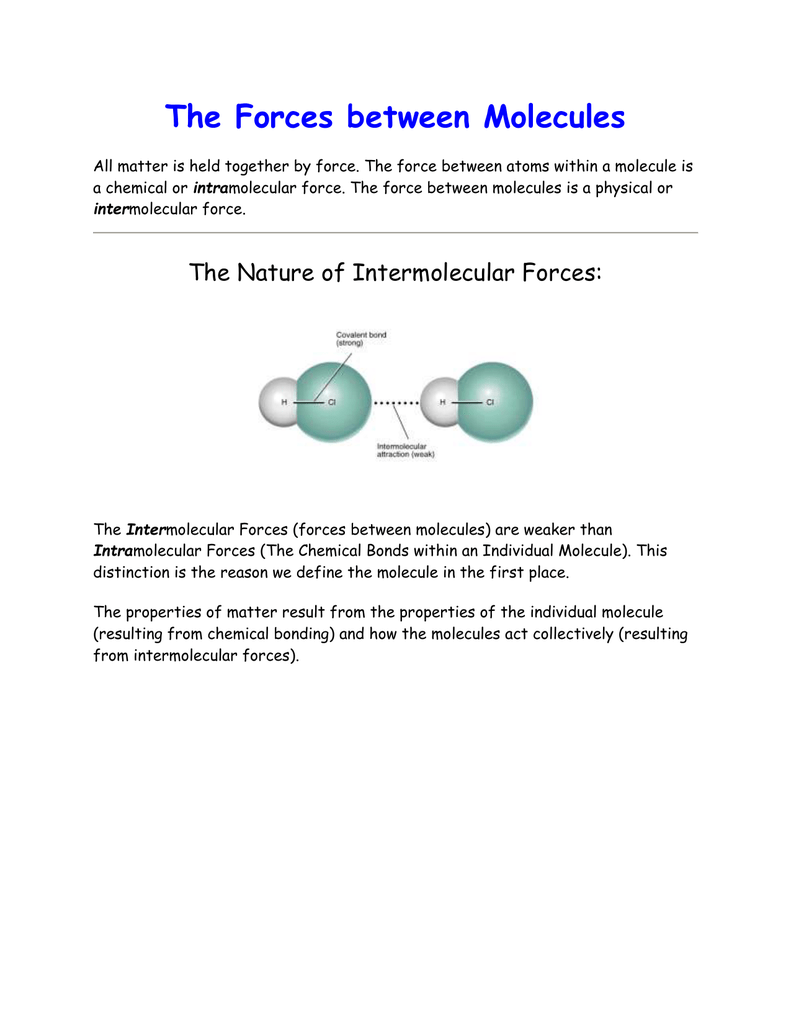
What is the force that holds atoms together?
A chemical bond is the force that holds the atoms of a molecules together, as in a compound. A chemical bond is an electrical force linking atoms. Do intermolecular forces hold the atoms in molecules together?
How are atoms bonded together to form molecules?
The bonds that hold atoms together to form molecules are called covalent bonds. They are pretty tough and not easily made or broken apart. It takes energy to make the bonds and energy is released when the bonds are broken. How are atoms bonded in molecules? Chemical bonds are forces that hold atoms together to make compounds or molecules.
What holds the nucleus of an atom together?
The nucleus of an atom is held together by the strong nuclear force that binds together protons and neutrons. Although the strong nuclear force is the strongest of the four fundamental forces, it acts only over very short – typically nuclear – distances. It binds together the protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
How does the iodine molecule stick together?
Holding molecules together - van der Waals forces. It's a transient dipole, and a transient force, but when you have millions of molecules making millions of connections enough force is generated to hold the iodine molecules in a (mostly) solid state.

What happens when a dipole forms on one side of a molecule?
When a dipole forms on one molecule it will start effecting molecules around it. A build-up of electrons on one side of a molecule forms a slight negative force, which will repel electrons on nearby molecules, making them slightly positive on one side and thus propagating the dipole.
Is hydrogen bonding weak?
Hydrogen bonds (covered here) are often thought of as fairly weak, but they are solid iron-and-concrete compared to van der Waals forces. Like hydrogen bonds van der Waals rely on dipoles, a difference in charge between two molecules. But unlike hydrogen bonds the van der Waals dipole is not permanent, but transient.
Does iodine have a dipole?
That's fine for molecules like water which have a dipole, but for molecules like, say, iodine which is composed of two iodine atoms sharing electrons, it's a problem. In iodine all the electrons are shared equally between the two atomic centres and there is no dipole.
What holds the atoms in a molecule together?
The bonds that hold atoms together to form molecules are called covalent bonds. They are pretty tough and not easily made or broken apart. It takes energy to make the bonds and energy is released when the bonds are broken.
How are atoms bonded in molecules?
Chemical bonds are forces that hold atoms together to make compounds or molecules. Chemical bonds include covalent, polar covalent, and ionic bonds. Atoms with relatively similar electronegativities share electrons between them and are connected by covalent bonds. The ions then are attracted to each other.
Which electrostatic forces hold atoms together in a molecule?
The atoms in chemical compounds are held together by attractive electrostatic interactions known as chemical bonds. Most covalent compounds consist of molecules, groups of atoms in which one or more pairs of electrons are shared by at least two atoms to form a covalent bond.
How are atoms held together in a molecule?
The inner ones are more tightly bound to their own nucleus, and don’t pay much attention to the passing of other atoms. Covalent bonding can produce much larger molecules as well. DNA molecules consist of huge numbers of atoms held together mainly by covalent bonds. But there are other ways to hold atoms together.
What Forces Hold Molecular Solids Together?
A molecular solid is composed of molecules held together by van der Waals forces. Its properties are dictated by the weak nature of these intermolecular forces. Molecular solids are soft often volatile have low melting temperatures and are electrical insulators.
How are molecular solids held together?
Molecular solids are held together by relatively weak forces such as dipole–dipole interactions hydrogen bonds and London dispersion forces. … Covalent solids consist of two- or three-dimensional networks of atoms held together by covalent bonds they tend to be very hard and have high melting points.
What kinds of forces hold molecular solids together quizlet?
Covalent bonds. What are non bonding solids held together by? Relatively weak dispersion forces.
What types of forces hold molecules together in crystals and liquids?
Van der Waals forces form electrostatic bonds between molecules. Intermolecular bonds including Van der Waals bonds hold the molecules together in liquids and solids and are responsible for phenomena such as the surface tension in liquids and crystals in solids.
Which forces are associated with solids?
Solids are generally held together by ionic or strong covalent bonding and the attractive forces between the atoms ions or molecules in solids are very strong. In fact these forces are so strong that particles in a solid are held in fixed positions and have very little freedom of movement.
What forces hold ionic solids together apex?
Ionic solids are formed by ionic bonds and the electrostatic attraction from the cation and anion component of the compound holds it together.
Does MgI2 have dipole dipole forces?
What kind of force is MgI2? Dipole-dipole forces: CH3OH NH3ION-Dipole Forces: CuCl2 MgI24.
Which forces are dependent on the protein composition of the cellular membrane?
These elastic forces are dependent on both the protein composition of the cellular membrane, and its lipid composition.
What forces are involved in packing phospholipids?
This is like packing of phospholipid molecules assisted by hydrophobic forces internally and hydrophilic forces like hydrogen bonds on either side of membrane.
What is a membrane made of?
Membrane is actually a bilayer structure and is made up of phospholipids molecules in which the proteins are embedded at random locations.
How do phospholipids interact with each other?
The phospholipid molecules within each monolayers interact with each other at tail by hydrophobic forces and at head region by hydrophilic interaction with external or internal aqueous environment of the membrane.
What are the intermediate structures of membrane fusion?
Typically, the process of membrane fusion involves formation of some specific intermediate structures. These structures are either pores or hemifusion stalks and diaphragms:
Why do marbles stick together at the bottom?
You can compare your question to asking “if I put a group of marbles on a u-shaped track, why do they stick together at the bottom?” There is no attractive force between the marbles! The u-shaped track here is helping gravity to push all of them to the bottom, and that is why they end up together. In a molecule, the Schrödinger equation is playing a similar role to keep the atoms together even though there is no fundamental force between them.
What is the role of proteins?
What is the role of proteins? Fusion proteins (and peptides like antimicrobial peptides) can control the spontaneous curvature of bilayers and hence their bending energy.
What holds nucleons together in a nucleus?
Nuclear forces (also known as nuclear interactions or strong forces) are the forces that act between two or more nucleons. They bind protons and neutrons (“nucleons”) into atomic nuclei. The nuclear force is about 10 millions times stronger than the chemical binding that holds atoms together in molecules.
What holds the atom together?
The bonds that hold atoms together to form molecules are called covalent bonds. They are pretty tough and not easily made or broken apart. It takes energy to make the bonds and energy is released when the bonds are broken.
What holds proton and neutron together?
Called the strong interaction, its origins lie in the particles lurking inside both protons and neutrons, called quarks. These possess a weird form of charge, whimsically termed ‘colour’, which glues them together inside their host particles – and also seeps out to bind the protons and neutrons together, too.
What type of forces hold nucleus and their particles together?
The strong force binds quarks together within protons, neutrons, and other subatomic particles. Rather as the electromagnetic force is ultimately responsible for holding bulk matter together, so the strong force also keeps protons and neutrons together within atomic nuclei.
Do neutrons hold the nucleus together?
Answer. Protons and neutrons are held together in a nucleus of an atom by the strong force. The strong force gets it name by being the strongest attractive force. It is 137 times more powerful than electromagnetic, which by the way cannot hold neutrons to protons because neutrons are not charged.
Why does the nucleus stay together?
They interact via the strong force! In fact, the strong force interaction “leaks out” of each proton and neutron, producing the nuclear strong force that binds the nucleus together . So, at its root, an atomic nucleus is held together by a force that reaches out from the very quarks within the neutrons and protons.
What force hold protons in nucleus?
The strong nuclear force. At extremely short range, it is stronger than electrostatic repulsion, and allows protons to stick together in a nucleus even though their charges repel each other.