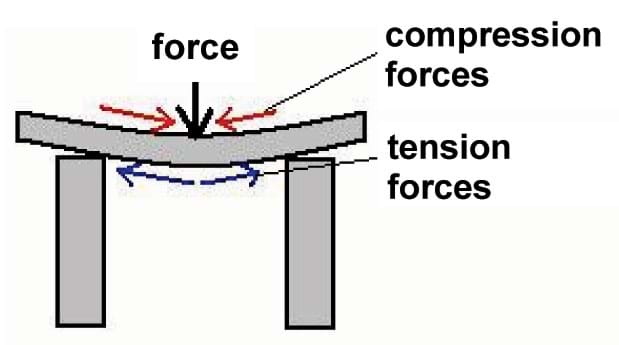
Forces act mostly on the top and bottom surfaces of a beam bridge. The force of gravity, acts downwards on objects on the bridge. The reactions in the bridge supports make the beam bend in the middle. This squashes (compresses), the top surface of the beam. At the same time the bottom surface is stretched (in tension).
What are the four basic forces that act on bridges?
- What happens to the parallel lines drawn on the top and bottom? (Answer: The lines on the top move closer together. The lines on the bottom move farther apart.)
- Where are the compressive forces located? (Answer: The compressive forces are located on the top.)
- Where are the tensile forces located? (Answer: The tensile forces are located on the bottom.)
How do bridges withstand the forces acting on them?
Forces that Act on Bridges
- Compression: Compression is a pushing (compressing) force. The shorter a piece of wood is, the more compression it can hold.
- Tension: Tension is a pulling force. Wood has the ability to resist a lot of tension. ...
- Torsion: Torsion is a twisting force. When you wring out a cloth, you are applying torsion to the cloth. ...
What forces affect bridges?
Types of bridges
- Beam
- Arch
- Truss
- Cantilever
- Suspension
- Through arch and tied-arch (bowstring)
- Lifting and swinging bridges
What is the reaction force of a bridge?
Torsion involves two forces. When forces at opposite ends of a bridge rotate the bridge in different directions, torsion is acting on the bridge. An example is a dish towel being wrung out. In a bridge, however, a much more rigid structure is needed, so torsional effects are far more severe than those from a wrung dish towel.
What are the forces of a beam bridge?
How many feet does a beam bridge span?
How does torsion work on a bridge?
What is compressive force?

What are 3 forces that act on bridges?
Three kinds of forces operate on any bridge: the dead load, the live load, and the dynamic load. The first of these terms refers to the weight of the bridge itself.
What type of force is most important in a beam bridge?
Compression The force of compression manifests itself on the top side of the beam bridge's deck (or roadway). This causes the upper portion of the deck to shorten. Tension The result of the compression on the upper portion of the deck causes tension in the lower portion of the deck.
What are the 5 forces that can act on a bridge?
Forces that Act on BridgesCompression. Tension: Tension is a pulling force. Wood has the ability to resist a lot of tension. ... Tension. Torsion: Torsion is a twisting force. When you wring out a cloth, you are applying torsion to the cloth. ... Torsion. Shear: Shear is an interesting force.
What 4 kinds of forces act on a bridge?
1:294:46How Bridge Balance Forces? | Different Type of Forces on BridgeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBut most stand happily still for years decades or even centuries. They do it by carefully balancingMoreBut most stand happily still for years decades or even centuries. They do it by carefully balancing two main kinds of forces. Called compression a pushing or squeezing force acting inward. And tension
What is the term for the balance of the downward forces of a beam?
Equilibrium. When a beam is simply supported at each end, all the downward forces are balanced by equal and opposite upward forces and the beam is said to be held in Equilibrium (i.e. the total load exerted by the beam's own weight plus any additional applied load are completely balanced by the sum of the two reactions at the two supports) .
Why does the shear force act downwards?
Half way across the beam, the Shear Force then acts downwards because of the load W and is constant along the right half of the beam to R2. Since the beam is in Equilibrium, the Shearing Forces must each start and finish on the same line.
What is the SF of a beam?
The Shearing Force (SF) at any section of a beam represents the tendency for the portion of the beam on one side of the section to slide or shear laterally relative to the other portion.
What is the force of wind on a flagpole?
In the examples of a flag on a flagpole, or a sail on a yacht mast, the force of the wind can be assumed to act through the Centre of Area or Centroid . For a rectangular flag, this is where the diagonals cross and, for a triangle, it is where each Median intersects.
What is the force multiplied by its distance from the pivot (or fulcrum)?
The force (created by the load or the effort) multiplied by its distance from the pivot (or fulcrum) is known as the Moment of Force .
Is it easier to bend a rule when it is held flat or on edge?
We also know from experience that if we walk along a builder's plank, for example, it will wobble up and down, or deflect, and we know that it is easier to bend a rule when it is held flat rather than on edge.
What are the forces of a beam bridge?
Forces in Beam Bridges. Forces act mostly on the top and bottom surfaces of a beam bridge. The force of gravity, acts downwards on objects on the bridge. The reactions in the bridge supports make the beam bend in the middle. This squashes (compresses), the top surface of the beam. Click to see full answer.
How many feet does a beam bridge span?
The weight of the beam pushes straight down on the piers. This is why beam bridges rarely span more than 250 feet . What is a beam on a bridge?
How does torsion work on a bridge?
Furthermore, how does torsion act on a bridge? When forces at opposite ends of a bridge rotate the bridge in different directions, torsion is acting on the bridge. An example is a dish towel being wrung out. In a bridge, however, a much more rigid structure is needed, so torsional effects are far more severe than those from a wrung dish towel. ...
What is compressive force?
Compression, or compressive force, is a force that acts to compress or shorten the thing it is acting on. Tension, or tensile force, is a force that acts to expand or lengthen the thing it is acting on. Furthermore, how does torsion act on a bridge?
