What is the base of the posterior triangle?
Posterior Triangle. The base of the posterior triangle is formed by the middle third of the clavicle. The investing layer of deep cervical fascia and integument forms the roof of the space, while the floor is covered with the prevertebral fascia along with levator scapulae, splenius capitis and the scalene muscles .
What muscle forms the floor of the posterior triangle?
The floor of the posterior triangle is formed primarily by four muscles: the splenius capitis, levator scapulae, middle scalene and posterior scalene. Ok, so, the splenius capitis originates on the inferior half of the nuchal ligament and the spinous processes of C7 to T4.
What is the posterior triangle of the neck made of?
The posterior triangle of the neck is covered by the investing layer of fascia, and the floor is formed by the prevertebral fascia (see fascial layers of the neck ). The posterior triangle of the neck contains many muscles, which make up the borders and the floor of the area.
What is the fascial carpet of the posterior triangle?
The muscular floor of posterior triangle is covered by prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia, which creates the fascial carpeting of the floor of the posterior triangle. It creates axillary sheath around subclavian artery and brachial plexus going from the root of the neck to the upper limb.

What forms the posterior triangle roof?
Superiorly, the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and stylohyoid close the triangle. It is floored by the inferior and middle pharyngeal constrictors, hyoglossus and parts of thyrohyoid. Its roof is formed by deep and superficial fascia, platysma and skin.
What is found in the posterior triangle?
Contents. The posterior triangle contains level 5 lymph node chains. These include spinal accessory and transverse cervical nodes. Depending on the location of the nodes above or below the accessory nerve, they are sub grouped as level 5a (above) or level 5b (below).
What divides the posterior triangle?
Divisions. The posterior triangle is crossed, about 2.5 cm above the clavicle, by the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle, which divides the space into two triangles: an upper or occipital triangle. a lower or subclavian triangle (or supraclavicular triangle)
What is the floor of the occipital triangle?
Occipital triangle Its floor consists of the levator scapulae, splenius capitis, and middle and posterior scalene muscles. The semispinalis capitis muscle is sometimes observed at the apex as well as occipital lymph nodes. The triangle is bounded by the superficial and deep layers of the deep cervical fascia.
Which is considered a content of the posterior triangle of the neck?
Contents. The posterior triangle contains level 5 lymph node chains. These include spinal accessory and transverse cervical nodes. Depending on the location of the nodes above or below the accessory nerve, they are sub grouped as level 5a (above) or level 5b (below).
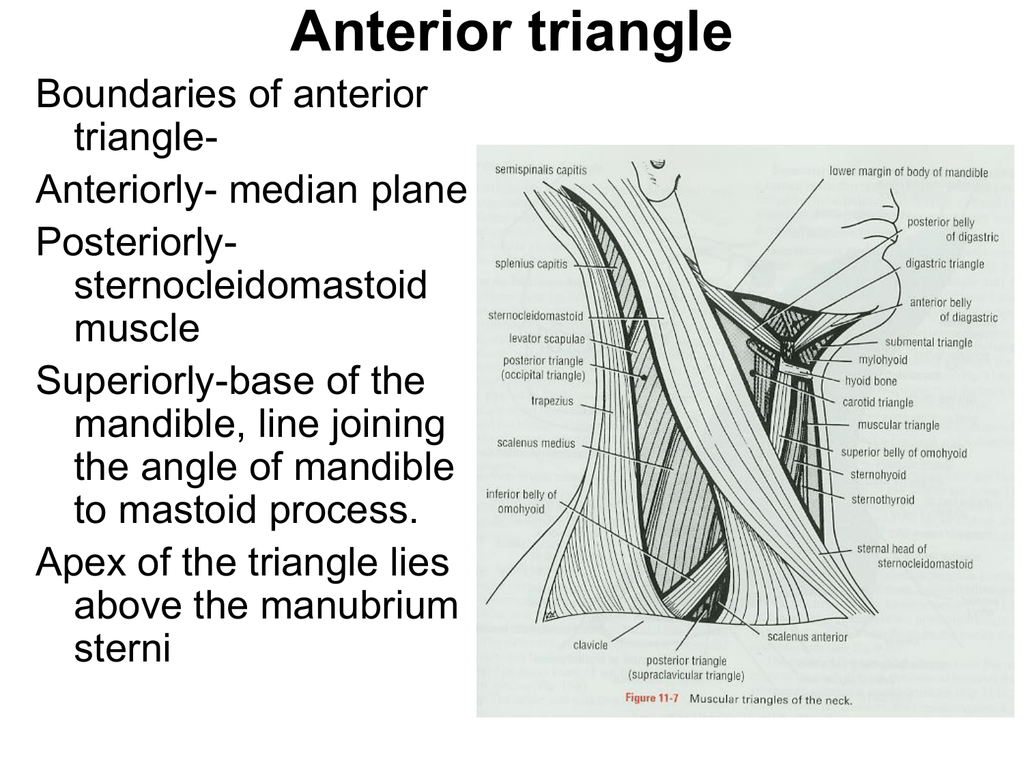
What makes up the anterior triangle?
The anterior triangles refer to bilateral anatomic subdivisions of the neck comprising the anterior surface of the neck, deep to the superficial cervical fascia and platysma muscle. Laterally, the anterior triangle is bounded by the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
What structure forms the anterior border of the posterior triangle?
The posterior triangle is bound by the posterior edge of SCM anteriorly, the anterior border of the trapezius posteriorly and the middle 1/3 of the clavicle inferiorly. The omohyoid is the important structure that subdivides the triangle into the occipital triangle above and the subclavian triangle below.
What are the anterior and posterior triangles of the neck?
The triangular space in front of this muscle is called the anterior triangle of the neck; and that behind it, the posterior triangle of the neck. The anterior triangle is further divided into muscular, carotid, submandibular and submental and the posterior into occipital and subclavian triangles.
How is ANSA Cervicalis formed?
The ansa cervicalis is a neural loop in the neck formed by connecting the superior root from the cervical spinal nerves (C1–2) and the inferior root descending from C2–C3. It has various anatomical variations and can be an important acknowledgment in specific operations of the neck region.
Is suboccipital triangle part of posterior triangle?
The suboccipital triangle is contained within a space bordered by muscles and ligaments deep to the nuchal region (posterior neck). The suboccipital triangle has three boundaries contained between a floor and roof. Floor - posterior arch of atlas and posterior atlantooccipital membrane (ligament).
What muscles make up the occipital triangle?
The suboccipital muscles are a group of four muscles located inferior to the occipital bone. These four muscles include the rectus capitis posterior major, rectus capitis posterior minor, obliquus capitis superior, and obliquus capitis inferior.
What is found in the carotid triangle?
As previously stated, the contents of the carotid triangle are made up of arteries, veins, and nerves.
What structures are found in the Omoclavicular triangle?
It contains:the subclavian artery.the inferior part of the external jugular vein,the investing layer of deep cervical fascia which separates the vessels mentioned above,the trunks of the brachial plexus, which may be felt above and behind the triangle.
Which triangle is the submandibular gland found?
The submandibular gland is located in the submandibular triangle, below the mylohyoid muscle, with its posterior portion wrapped around the posterior border of the mylohyoid and extending anteriorly for a short distance.
Is the phrenic nerve in the posterior triangle?
The phrenic nerve arises in the posterior triangle near the nerve point, then descends to the anterior surface of the anterior scalene muscle in the supraclavian triangle. It is necessary to be aware of the supraclavian triangle below Erb's point during neck dissection procedures.
What are the anterior and posterior triangles of the neck?
The triangular space in front of this muscle is called the anterior triangle of the neck; and that behind it, the posterior triangle of the neck. The anterior triangle is further divided into muscular, carotid, submandibular and submental and the posterior into occipital and subclavian triangles.
Which fascia forms the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck?
The prevertebral fascia forms the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck (Figure 26-1C and D).
What triangle is used to invest fascia?
Investing fascia forming the roof over — the posterior triangle
What is the prevertebral fascia?
Prevertebral fascia covering the floor of the posterior triangle. Prevertebral fascia covering the floor of the posterior triangle. Investing fascia (cut edges) Inferior belly of omohyoid m. Investing fascia (cut edges) Inferior belly of omohyoid m. KEY.
What is the transverse cervical artery?
Transverse cervical artery. A branch from the thyrocervical trunk that courses along the floor of the posterior triangle en route to the deep surface of the trapezius muscle. The artery bifurcates into a superficial branch, which courses superficial to the rhomboid muscles, and a deep branch, which courses deep to the rhomboid muscles.
Which artery is located between the scalene muscles?
Brachial plexus and subclavian arter y. The brachial plexus and the subclavian artery course between the anterior and middle scalene muscles, and as the nerve plexus and artery emerge from those muscles, they carry an extension of the prevertebral fascia along to form the axillary sheath.
Which structures are deep to the prevertebral fascia?
The following structures are deep to the prevertebral fascia: Cervical muscles, from superior to inferior: • Anterior scalene (notice that the phrenic nerve descends vertically along the anterior surface of the anterior scalene muscle en route to the thoracic cavity). ▼. Brachial plexus and subclavian artery.
Which artery crosses the supraspinous fossa?
Suprascapular artery. The most inferior branch from the thyrocervical trunk, the suprascapular artery courses across the anterior scalene muscle and the phrenic nerve, where it crosses over the superior transverse scapular ligament to enter the supraspinous fossa. Spinal accessory nerve [cranial nerve ( CN) XI ].
Where is the posterior triangle located?
All the significant contents of the posterior triangle are located deep to the fascial carpeting of the floor with the exception of spinal accessory nerve, which is located just underneath the roofing. In procedures on the posterior triangle all the structures with the exception of spinal accessory nerve are safe, supplied fascial carpeting of posterior triangle is left undamaged.
Which part of the posterior triangle is subdivided into 2 parts?
The posterior triangle is subdivided into 2 parts by the inferior belly of the omohyoid, which crosses the lower part of the triangle obliquely upwards and forwards (a) a bigger upper part named occipital triangle and (b) a small lower part termed subclavian (supraclavicular) triangle.
What is the fascial carpeting of the posterior triangle?
Fascial Carpeting of the Posterior Triangle. The muscular floor of posterior triangle is covered by prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia, which creates the fascial carpeting of the floor of the posterior triangle . It creates axillary sheath around subclavian artery and brachial plexus going from the root of the neck to the upper limb.
What is the terminal part of the external jugular vein?
Terminal part of external jugular vein: It pierces the fascial roof of the posterior triangle about 2.5 cm above the clavicle to terminate in the subclavian vein. Lymph nodes: These are deep cervical lymph nodes seen at these sites in the posterior triangle:
What nerves pierce the roof of the posterior triangle?
Lesser occipital nerve (C2). Great auricular nerve (C2, C3). Transverse cervical nerve (C2, C3). Supraclavicular nerves (C3, C4). They pierce the roof near the middle of the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Where does the nerve go when it crosses the posterior triangle?
The nerve then crosses the posterior triangle by running downwards and laterally around and parallel to the fibres of levator scapulae muscle to evaporate below to the anterior border of tra pezius (about 5-6 cm above the clavicle) and supplies trapezius muscle.
What is the triangular space on the side of the neck called?
Behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the triangular space on the side of neck is called the Posterior triangle. Its base downwards in the direction of the clavicle and apex is pointed upwards and backwards in the direction of the mastoid process.
What is posterior neck triangle?
Introduction. The posterior neck triangle is a clinically relevant anatomic region that contains many important vascular and neural structures. The clinical aspect of the anatomy contained in the posterior neck triangle is useful for a wide variety of medical specialties, including anesthesiology, otolaryngology, ...
Which muscle is the posterior neck triangle bounded by?
Bounding a large anatomic region, the posterior neck triangle further divides into two smaller triangles by the inferior omohyoid muscle. These subdivisions include the occipital and subclavian triangles. The occipital triangle is bounded by the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle, the trapezius muscle, and the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
What is the subclavian triangle?
The subclavian triangle, sometimes referred to as the supraclavicular triangle, is bounded by the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle, the clavicle, and the sternocleidomastoid muscle. [2][3] Embryology.
What is the supply of lymphatics in the posterior neck triangle?
Lymphatic supply within the posterior neck triangle includes the occipital, transverse cervical, and supraclavicular chains of lymph nodes. The clinical relevance of the supraclavicular lymph node, also known as Virchow’s node, will be elaborated upon in the Clinical Significance section. [5][1]
Which muscle is at the apex of the neck triangle?
The union of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles at their insertion on the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone form the apex of the triangle. The posterior neck triangle is covered superficially to deep by the skin, superficial and deep cervical fascia, and the platysma muscle.
Which veins are located in the posterior neck triangle?
Prominent veins coursing through the posterior neck triangle include the terminal portion of the external jugular vein located on the inferior portion, as well as the subclavian vein. The suprascapular vein and transverse cervical vein join the external carotid vein in the inferior portion of the triangle.
Which artery gives rise to the superficial scapular and dorsal arteries?
The following variants are common in frequency and arise from either the subclavian artery of the thyrocervical trunk: Cervico-scapular trunk: Gives rise to the superficial scapular and dorsal scapular arteries. Cervico-dorsal trunk: Gives rise to the cervical and dorsal scapular arteries.
What is posterior triangle?
The posterior triangle (or lateral cervical region) is a region of the neck .
Where is the apex of the sternocleidomastoid located?
Apex: Union of the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius muscles at the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone
What is the anterior triangle?
The anterior triangle is the triangular area of the neck found anteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It is formed by the anterior border of sternocleidomastoid laterally, the median line of the neck medially and by the inferior border of the mandible superiorly. The apex of the anterior triangle extends towards the manubrium sterni. The anterior triangle is further subdivided into the: 1 Muscular (omotracheal/infrahyoid) triangle 2 Carotid triangle 3 Submandibular triangle 4 Submental triangle
Where is the anterior triangle located?
The anterior triangle is the triangular area of the neck found anteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It is formed by the anterior border of sternocleidomastoid laterally, the median line of the neck medially and by the inferior border of the mandible superiorly. The apex of the anterior triangle extends towards the manubrium sterni.
What is the apex of the digastric triangle?
The apex of the triangle rests at the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle. Its floor is formed by the mylohyoid and hyoglossus, while it is roofed by skin, fascia and platysma.
What is the apex of the muscular triangle?
The apex of the muscular triangle is at the intersection of sternocleidomastoid and omohyoid muscles. The muscular triangle contains: the infrahyoid muscles ( thyrohyoid, sternothyroid, sternohyoid ), vessels ( superior and inferior thyroid arteries, anterior jugular veins) and viscera ( thyroid and parathyroid glands, larynx, trachea, esophagus ).
What is the base of a triangle?
The base of the triangle is formed by the body of the hyoid bone and its apex extends towards the symphysis menti. This triangle, like the submandibular triangle, is floored by the mylohyoid muscles and roofed by the platysma, fascia and skin. Borders and contents of the submental triangle. Borders.
Which muscle is floored by the inferior and middle pharyngeal constrictors, hyog?
Superiorly, the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and stylohyoid close the triangle. It is floored by the inferior and middle pharyngeal constrictors, hyoglossus and parts of thyrohyoid. Its roof is formed by deep and superficial fascia, platysma and skin. This triangle contains major arteries, veins and nerves of the neck and head .
What are the three borders of the clavicle?
It has three borders; anterior, posterior and inferior borders. The anterior border is the posterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The posterior border is the anterior margin of the trapezius muscle, while the inferior border is the middle one-third of the clavicle .
What muscles make up the posterior triangle?
The floor of the posterior triangle is formed primarily by four muscles: the splenius capitis, levator scapulae, middle scalene and posterior scalene.
How many sides does a posterior triangle have?
Now, the posterior triangle, like any respectable triangle, has three sides, called boundaries.
What are the structures of the neck?
In the neck, there are superficial structures, located in the anterior and posterior triangles, and deep structures, including the cervical viscera and prevertebral muscles. Now, the neck is divided into the anterior and posterior triangles mainly by the borders of the sternocleidomastoid, or SCM, and trapezius muscles.
Where does the trapezius originate?
It originates from the medial third of superior nuchal line, external occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament and the spinous processes of the C7 toT12 vertebrae. It inserts onto the lateral third of the clavicle, acromion and spine of the scapula. The anterior border of the trapezius forms the posterior boundary of the posterior triangle.
Where are the superficial structures of the neck located?
In the neck, there are superficial structures, located in the anterior and posterior triangles, and deep structures, including the cervical viscera and prevertebral muscles.
Which fibers work together to produce upward rotation of the scapula?
The superior and inferior fibers can also work together to produce upward rotation of the scapula, causing the glenoid cavity to tilt superiorly.
Which muscle covers the posterolateral aspect of the neck and thorax?
And then there’s the trapezius, which is a large triangular muscle that covers the posterolateral aspect of the neck and thorax.
