Urinary Bladder. The urinary bladder develops from the upper end of the urogenital sinus, which is continuous with the allantois. It is lined with endoderm. The lower ends of the metanephric ducts are incorporated into the wall of the urogenital sinus and form the trigone of the bladder.
Full Answer
Is the urinary bladder and the bladder the same thing?
Bladder. Urinary bladder is a part of the urinary system that stores urine produced by kidneys until urination takes place. It is found anterior and inferior to the pelvic cavity and posterior to the symphysis pubis. Bladder receives urine through ureters, the small tubes connecting two kidneys and the urinary bladder.
What tissue forms the inner lining of the urinary bladder?
- Mucous membrane (mucosa) Transitional epithelium; lines the bladder, ureters, and urethra.
- Muscular coat (muscularis propria) Three layers: inner longitudinal, middle circular, and outer longitudinal.
- Serous coat (serosa)
- Adventitia.
- Perivesical fat.
- Equivalent Terms for Layers of Bladder Wall.
Is the urinary bladder and the gallbladder the same structure?
• Bladder is in the pelvis and a part of the urinary system, whereas gallbladder is in the abdomen and a part of the digestive system. • External and internal urethral sphincter muscles in the bladder help to control the urination, whereas smooth muscle fibers in the fibromuscular layer control the bile ejection.
What is the purpose of the urinary bladder?
The urinary bladder is an organ that serves to collect urine to be voided through urination after the urine is filtered through the kidneys (where the necessary ions are reabsorbed if physiologically needed through feedback mechanisms found throughout the body and in the nephrons of the kidneys, such as the macula densa).
What does the urinary bladder develop from?
The urinary bladder develops from the upper end of the urogenital sinus, which is continuous with the allantois. It is lined with endoderm. The lower ends of the metanephric ducts are incorporated into the wall of the urogenital sinus and form the trigone of the bladder.
What type of tissue makes up the urinary bladder?
Urinary bladder and urethra are consisting of epithelium on the lumen surrounded by a collagen rich connective tissue and muscle layer. The epithelial layer serves as a barrier that prevents the urine from sweeping into the body cavity.
What are the 4 layers of the urinary bladder?
Urinary Bladder. The wall of the urinary bladder has four layers. From the inside towards the outside they are: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa or adventitia.
What are the three layers of the urinary bladder?
mucosa. submucosa. muscularis.
Does urinary bladder have mucosa?
The internal face of the detrusor smooth muscle wall of the urinary bladder is covered by a mucosa, separating muscle from the hostile environment of urine.
Why is the urinary bladder made up of transitional cells?
The ability of the cells in the superficial layer of this epithelium to change shape (transition from a rounded cuboidal shape to a flattened squamous structure) allows these organs to stretch without exposing underlying tissue to the toxic substances in the urine.
What type of epithelial tissue is found in the urethra?
stratified squamous cellsThe urethral epithelium is composed of stratified squamous cells, which variably becomes transitional as the bladder is approached. The epithelium is arranged in longitudinal folds. At the base of the folds are scattered gland openings along the entire urethral length.
What is epithelial tissue and its type?
Epithelium, endothelium and mesothelium are three types of epithelial cell layers that line your internal organs, body cavities and form the outer layer of your skin. Epithelium generally lines pathways that are open to the external environment, such as your respiratory tract and digestive system.
Where is the urinary bladder located?
It is located in the pelvic cavity anterior to the rectum and superior to the reproductive organs of the pelvis. In females the urinary bladder is somewhat reduced in size and must share the limited space of the pelvic cavity with the uterus that rests superior and posterior to it.
What are the layers of the bladder?
The urinary bladder is made of several distinct tissue layers: 1 The innermost layer of the bladder is the mucosa layer that lines the hollow lumen. Unlike the mucosa of other hollow organs, the urinary bladder is lined with transitional epithelial tissue that is able to stretch significantly to accommodate large volumes of urine. The transitional epithelium also provides protection to the underlying tissues from acidic or alkaline urine. 2 Surrounding the mucosal layer is the submucosa, a layer of connective tissue with blood vessels and nervous tissue that supports and controls the surrounding tissue layers. 3 The visceral muscles of the muscularis layer surround the submucosa and provide the urinary bladder with its ability to expand and contract. The muscularis is commonly referred to as the detrusor muscle and contracts during urination to expel urine from the body. The muscularis also forms the internal urethral sphincter, a ring of muscle that surrounds the urethral opening and holds urine in the urinary bladde. During urination, the sphincter relaxes to allow urine to flow into the urethra.
What organ is responsible for storing urine?
The adventitia loosely connects the urinary bladder to the surrounding tissues of the pelvis. The urinary bladder functions as a storage vessel for urine to delay the frequency of urination. It is one of the most elastic organs of the body and is able to increase its volume greatly to accommodate between 600 to 800 ml of urine at maximum capacity.
What is the tube that carries urine out of the body?
A small funnel forms at the inferior end of the urinary bladder leading into the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body during urination. The urinary bladder is made of several distinct tissue layers: The innermost layer of the bladder is the mucosa layer that lines the hollow lumen.
Which muscle is responsible for urinating?
The muscularis is commonly referred to as the detrusor muscle and contracts during urination to expel urine from the body. The muscularis also forms the internal urethral sphincter, a ring of muscle that surrounds the urethral opening and holds urine in the urinary bladde. During urination, the sphincter relaxes to allow urine to flow into ...
What is the innermost layer of the bladder?
The innermost layer of the bladder is the mucosa layer that lines the hollow lumen. Unlike the mucosa of other hollow organs, the urinary bladder is lined with transitional epithelial tissue that is able to stretch significantly to accommodate large volumes of urine.
What are the wrinkles on the bladder?
During pregnancy the uterus takes up significantly more space and severely limits the expansion of the urinary bladder. Many tiny wrinkles, known as rugae, line the inner surface of the urinary bladder and allow it to stretch as it fills with urine.
What is the structure of the bladder?
The structural composition of the bladder includes a broad fundus, body, apex, and neck. The human bladder contains three openings, each covered by a mucosal flab that prevents urine from flowing backward into the ureters. The anatomical position of the bladder differs between men and women.
What is the function of the urinary bladder?
Prior to urination, it stores urine produced and delivered by the kidneys through two ureters. The human urinary bladder is hollow, muscular, and can hold up to four cups of urine.
What are bladder stones?
Bladder stones are hard deposits composed of minerals found in the bladder caused by dehydration and highly concentrated urine residing in the bladder. Stones can vary in size and are typically asymptomatic. Common symptoms are typically pain, blood in the urine, and irritation.
What is the most common cause of urinary tract infections?
These infections are caused by bacterial infections in the bladder, usually caused by bacteria traveling up the urethra and into the bladder. When left untreated, UTIs can be very dangerous, as the infection can progress from the bladder into the kidneys. Common symptoms include a burning sensation during urination, cloudy and/or foul-smelling urine, and the frequent urge to urinate, despite little urine being released.
What is the term for the protrusion of the bladder through the wall of the abdomen?
Bladder Exstrophy. Bladder exstrophy is a congenital abnormality which involves the protrusion of the bladder through the wall of the abdomen. This condition is extremely rare and is often accompanied by the abnormal development of the pelvic floor and other muscles, as well as the genitals, especially in women.
Why does my bladder stop urinating?
This disorder is caused by a sympathetic nervous system response which tightens the sphincters in the bladder in response to adrenaline, thereby preventing urination . Typically, treating this condition requires psychological therapy.
What is the condition where you need to urinate?
Trigonitis is a condition involving inflammation of the trigone region of the bladder. In particular, the trigone is a smooth triangular-shaped region and signals the need for urination in response to stretching. An inflammation of this region can result in an urgent need to urinate, pain in the pelvic region, and pain or difficulty urinating. Although there are several causes of trigonitis, bladder infections are the most common etiology.
What are the symptoms of a bladder problem?
See a health care professional if you have symptoms of a bladder problem, such as trouble urinating, a loss of bladder control, waking to use the bathroom, pelvic pain, or leaking urine.
What causes bladder control problems?
Health changes and problems, including those with your nervous system, and lifestyle factors can cause or contribute to UI in women and men.
What muscles can allow your bladder to leak?
Weak pelvic floor muscles can allow your bladder to leak.
How do you know if you have urinary incontinence?
Signs and symptoms of urinary incontinence can include. leaking urine during everyday activities, such as lifting, bending, coughing, or exercising. feeling a sudden, strong urge to urinate right away. leaking urine without any warning or urge. being unable to reach a toilet in time. wetting your bed during sleep.
Why is it so hard to pee?
When the prostate gets too big it can squeeze the urethra, making it hard to start urinating. You also may have a slow urine stream or be unable to completely empty your bladder.
What is temporary incontinence?
Temporary incontinence is usually a side effect of a medicine or short-term health condition. Temporary incontinence can also be a result of eating and drinking habits, including using alcohol or caffeine.
Can't pass urine?
can’t pass urine or empty your bladder. urinate too often—8 or more bathroom visits a day—also called frequency. see blood in the urine, also called hematuria. have bladder infection symptoms, including painful urination.
Which muscle layer in the bladder contracts to propel urine?
carry urine from kidneys to bladder; smooth muscle layers in walls contract to propel urine by peristalsis
What is the function of the bladder opening?
3-4cm/1.5 in long; opening lies anterior to vaginal opening; only function is to conduct urine from bladder to body exterior
When reflex contractions become stronger and stored urine is forced past the internal urethral sphincter into?
when reflex contractions become stronger and stored urine is forced past the internal urethral sphincter into the upper part of the urethra
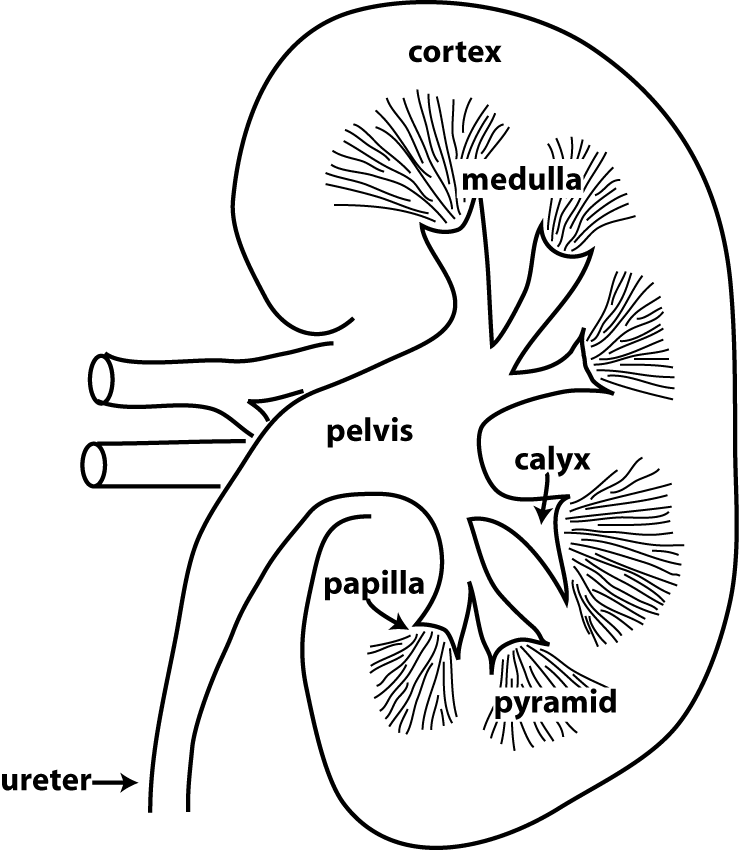
What form crystals in the renal pelvis?
solutes such as uric acid salts form crystals that precipitate in the renal pelvis when urine becomes extremely concentrated
Which orifice drains the bladder?
2 ureteral orifices and single opening of the urethra which drains the bladder
Can a bladder empty its contained urine?
bladder is unable to empty its contained urine

Urinary Bladder Definition
Urinary Bladder Overview
- The structural composition of the bladder includes a broad fundus, body, apex, and neck. The human bladder contains three openings, each covered by a mucosal flab that prevents urine from flowing backward into the ureters. The anatomical positionof the bladder differs between men and women. In men, the urinary bladder is located in front of the rectum, whereas, in women, it i…
Urinary Bladder Function
- The function of the urinary bladder is to collect and store urine from the kidneys until it can be excreted via urination. The typical human bladder can store an average of 300 mL to 500 mL of urine. As described above, the urinary bladder is highly elastic and is able to accommodate an increased volume of liquid due to the flattening of the rugae folds. Urination is not controlled by …
Diseases of The Urinary Bladder
- There are several diseases of the urinary bladder. The typical symptoms of bladder diseases include frequent urination, pain, incomplete emptying, and irritation. Occasionally, diseases of other tissues or organs can affect the urinary bladder.For example, an enlarged prostate can cause frequent urination. The following are some of the most common pathologies of the urinar…