
What is the difference between penicillin and cephalosporin?
The key difference between penicillin and cephalosporin is that penicillin is more susceptible to β-lactamases, whereas cephalosporin is less susceptible to β-lactamases. Both penicillin and cephalosporin are antibacterial drugs.
What is the difference between cefazolin and cephalexin?
• Cefazolin is more active against Staphylococcus aureus 3 , Streptococcus spp. 4 and H. influenzae 5 than cephalexin. • Bactericidal. • Cephalosporins inhibit the synthesis of bacterial cell walls at the later stages through inactivation of penicillin-binding proteins.
What drug class is cefazolin?
Used for:
- Respiratory tract infections
- Urinary tract infections
- Skin infections
- Liver and gallbladder infections
- Bone and joint infections
- Genital infections
- Bloodstream infections
- Heart infections
- Prevention of infection from surgery
What conditions does cefuroxime treat?
- Back, leg, or stomach pains
- bladder pain
- bleeding gums
- bloody or cloudy urine
- body aches or pain
- burning while urinating
- dark urine
- difficulty with breathing
- ear congestion
- fast, pounding, or irregular heartbeat or pulse
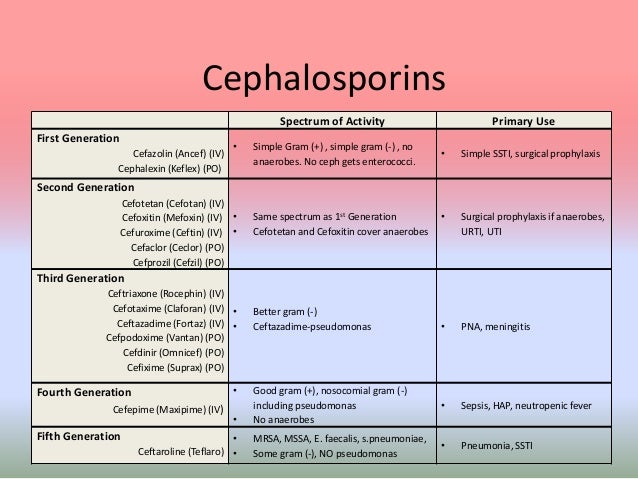
Is Keflex 3rd generation?
Examples of first-generation cephalosporins include the following: Cephalexin (Keflex)
What are 3rd generation cephalosporins?
Third-generation cephalosporins are broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents useful in a variety of clinical situations. No one cephalosporin is appropriate for all infectious disease problems. Cefotaxime and ceftizoxime have the best gram-positive coverage of the third-generation agents.
What are 2nd generation cephalosporins?
The new second-generation cephalosporins, cefonicid, ceforanide, and cefuroxime, have recently become available. These agents are generally less active against gram-positive cocci than first-generation cephalosporins and, at best, equal to cefoxitin and cefamandole against many gram-negative bacteria.
What are the 4 generations of cephalosporins?
Four Generation of CephalosporinsFirst Generation: cefazolin, cefalexin, cefadroxil.Second Generation: cefamandole, cefoxitin, cefaclor, cefuroxime, loracarbef, cefotetan.Third generation: cefotaxime, cefpodoxime, ceftizoxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, cefoperazone.More items...
Is cephalexin first-generation?
Cephalexin is an FDA-approved antibiotic. Cephalexin is a first-generation cephalosporin utilized in the treatment of urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and other bacterial infections.
What are 4th generation antibiotics?
The fourth generation penicillins are semisynthetic modifications of natural penicillin that have the advantage of an extended spectrum of activity particularly against gram negative bacteria including Pseudomonas, Enterobacter, Proteus and Klebsiella species.
Is cefazolin and Keflex the same?
Keflex (cephalexin) Ancef (cefazolin) is only available as an injectable, so it is usually only used in the hospital. It's good for treating many bacterial infections. Treats bacterial infections. Keflex (cephalexin) is good for treating many bacterial infections, and is available as a generic.
Is cephalexin a third generation cephalosporin?
Examples of first-generation cephalosporins include: cephalexin (Keflex)
What are 2nd and 3rd generation cephalosporins?
Second-generation cephalosporins have coverage against Haemophilus influenza (H. influenza), Moraxella catarrhalis, and Bacteroides spp. Third-generation cephalosporins have less coverage against most gram-positive organisms but have increase coverage against Enterobacteriaceae, Neisseria spp., and H. influenza.
What kind of antibiotic is Keflex?
This medication is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. This medication is known as a cephalosporin antibiotic. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria. This medication will not work for viral infections (such as common cold, flu).
Are Keflex and Ceftin the same?
Keflex (cephalexin) Ceftin (cefuroxime axetil) is good for treating many bacterial infections, but be sure to take the full course without stopping so that the medication can work. Treats bacterial infections. Keflex (cephalexin) is good for treating many bacterial infections, and is available as a generic.
Is Keflex a penicillin?
Keflex (cephalexin) and penicillin are antibiotics used to treat bacterial infections. Keflex and penicillin are in different drug classes. Keflex is a cephalosporin antibiotic, and penicillin is a penicillin-type antibiotic. Brand names for penicillin include Bicillin, Bicillin CR, and Bicillin LA.
What are 3rd and 4th generation cephalosporins?
Fourth generation cephalosporins refer to the fourth group of cephalosporins discovered. They are structurally related to third-generation cephalosporins but possess an extra ammonium group, which allows them to rapidly penetrate through the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, enhancing their activity.
What are 3rd generation antibiotics?
Third-generation beta-lactam antibiotics are effective against a wider range of microorganisms than are older antibiotics. Cefotaxime, moxalactam, cefoperazone, ceftizoxime, ceftazidime, cefsulodin, and ceftriaxone were used to treat 102 patients hospitalized with orthopedic infections.
What does 3rd generation drug mean?
Third-generation cephalosporins are medications used in the management and treatment of gram-negative and gram-positive organisms. They are encompassed among the beta-lactam class of drugs.
What are second and third-generation cephalosporins?
Second-generation cephalosporins have coverage against Haemophilus influenza (H. influenza), Moraxella catarrhalis, and Bacteroides spp. Third-generation cephalosporins have less coverage against most gram-positive organisms but have increase coverage against Enterobacteriaceae, Neisseria spp., and H. influenza.
What is the first generation of cephalosporins?
First generation cephalospor ins refer to the first group of cephalosporins discovered. Their optimum activity is against gram-positive bacteria such as staphylococci and streptococci. They have little activity against gram-negative bacteria.
When was the first cephalosporin discovered?
Since the first cephalosporin was discovered in 1945 , scientists have been improving the structure of cephalosporins to make them more effective against a wider range of bacteria. Each time the structure changes, a new "generation" of cephalosporins are made. So far there are five generations of cephalosporins.
What is the name of the antibiotic that kills bacteria?
Cephalosporins are a large group of antibiotics derived from the mold Acremonium (previously called Cephalosporium ). Cephalosporins are bactericidal (kill bacteria) and work in a similar way to penicillins.
What are the side effects of cephalosporins?
The most common side effects reported include diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, dyspepsia, gastritis and abdominal pain. Transient liver problems have also been reported.
Can cephalosporin cause rash?
Allergic reactions have been reported with cephalosporins ( including first generation cephalosporins) and symptoms may include a rash, hives ( urticaria ), swelling, or rarely, anaphylaxis. Up to 10% of people with a history of penicillin allergy will also be allergic to cephalosporins.
Can you take cephalosporin long term?
People with ki dney or liver disease, nutritionally deprived, taking cephalosporins long-term, or concurrently receiving anticoagulant therapy are more at risk. For a complete list of severe side effects, please refer to the individual drug monographs.
Can cephalexin be given by injection?
Cephalexin and cefadroxil can be given by mouth, whereas cefazolin can only be given by injection (IV/IM). There are also differences with regards to how frequently the different first-generation cephalosporins need to be dosed. Generic name.
What Is Keflex?
For certain bacterial infections, your healthcare provider may prescribe an oral antibiotic called Keflex (cephalexin). Keflex belongs to a class of antibiotics called cephalosporins. 1 It kills bacteria by blocking the bacterial cell wall formation around each cell.
What Is Keflex Used For?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Keflex to treat the following infections caused by susceptible gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria: 1
What Are the Side Effects of Keflex?
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. A medical professional can advise you on side effects. If you experience other effects, contact your pharmacist or a medical professional. You may report side effects to the FDA at www.fda.gov/medwatch or 1-800-FDA-1088 .
Dosage: How Much Keflex Should I Take?
The dose of this medicine will be different for different patients. Follow your doctor's orders or the directions on the label. The following information includes only the average doses of this medicine. If your dose is different, do not change it unless your doctor tells you to do so.
Overdose: What Happens If I Take Too Much Keflex?
According to the National Poison Control Center, antibiotic overdoses are rarely dangerous but may cause side effects like upset stomach or diarrhea. The same is true even in children. 18
Precautions
If your symptoms do not improve within a few days, or if they become worse, check with your doctor.
What Medications Are Similar?
There are five generations of cephalosporin antibiotics, each of which has similar mechanisms of action but different types of antibacterial activity. Some of the drugs are taken by mouth, delivered by injection, or both. Keflex is a first-generation cephalosporin.
What is a cephalosporin?
Cephalosporins are a type of antibiotic. Antibiotics are medications that treat bacterial infections. There are many types, often called classes, of antibiotics available. Cephalosporins are a type of beta-lactam antibiotic. They can be taken orally or injected into a vein (intravenous injection), depending on the infection.
What is the 4th generation cephalosporin used for?
Fourth-generation cephalosporins work against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. They’re generally used for more severe infections or for those with weakened immune systems.
What are some examples of infections that cephalosporins can treat?
Some examples of infections that cephalosporins can treat include: skin or soft tissue infections . urinary tract infections (UTIs)
How many generations of cephalosporins are there?
These groups are referred to as generations. There are five generations of cephalosporins. To understand the differences between the generations, it’s important to understand the difference between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. One of the main distinctions between the two is their cell wall structure:
Can you take cephalosporins with penicillin?
But if you’ve had a serious anaphylactic reaction to penicillin antibiotics in the past, you shouldn’t take cephalosporins. It’s uncommon to have an allergy to both penicillin antibiotics and cephalosporins, so cephalosporins can be used cautiously in people with a penicillin allergy.
Can cephalosporins cause anaphylaxis?
As with any kind of medication, you can be allergic to cephalosporins. The most common sign of an allergic reaction to cephalosproins is a skin rash. In rare cases, cephalosprins may cause a serious allergic reaction known as anaphy l axis. Symptoms of anaphylaxis include:
Can cephalosporins be used for infections?
There are different generations of cephalosporins, and some are better suited to treat certain infections than others. If you have to take antibiotics, make sure to tell your doctor about all other medications you take, as well as any previous allergic reactions to antibiotics. Remember.
When was cephalosporin first used?
Due to its low adverse reactions and toxic side effects, it has developed rapidly since its first clinical application in the early 1960s, and many varieties have been produced. Cephalosporins have been developed for five generations.
How many generations of cephalosporins are there?
So people divide "cephalosporins" into five generations based on their antibacterial spectrum and antibacterial activity. In this way, when choosing drugs, doctors can make a wise choice based on the structural characteristics of the bacteria and the action characteristics of the drugs. Quick Navigation.
How are cephalosporins divided?
Cephalosporins are mainly divided into different generations according to their development sequence, antibacterial spectrum, stability to beta lactamase, and toxicity to kidneys. 1.
What antibiotics are used for injection?
Commonly used varieties of antibiotics of this generation include cefazolin, cephalexin, cefradine, cefadroxil and so on. Among them, cefazolin can only be used for injection, the others can be used for oral administration. Cefalotin, cefotaxime, cefacetonitrile, cefpirin, etc. have been used less or not. 2.
What are the different types of cephalosporins?
Like penicillin, they are all beta lactam antibiotics. People usually divide microorganisms into 8 categories: bacteria, viruses, fungi, actinomycetes, rickettsiae, mycoplasma, chlamydia, and spirochetes. These microorganisms can cause us to get sick under certain conditions, ...
Which is better, cephalothin or cefazolin?
For example, cephalothin has better antibacterial effect on gram-positive bacteria, while cefazolin has a certain effect on some gram-negative bacteria. However, the first generation cephalo sporins are less resistant to the beta lactamase of gram-negative bacteria. Therefore, gram-negative bacteria are more resistant to antibiotics ...
Which generation of cephalosporins has the strongest effect on Gram positive bacteria?
The fifth generation cephalosporins have stronger effects on Gram-positive bacteria than the previous four generations, especially on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis, penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumonia and some anaerobic bacteria.
What is cephalexin used for?
Cephalexin is a first-generation cephalosporin utilized in the treatment of urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and other bacterial infections. Both streptococci and staphylococci species can cause these infections.
How long does cephalexin last?
These capsules can be given 1 to 4 times daily, usually administered for seven days. Patients often report cephalexin capsules to have an unpleasant taste. The capsule is also notably large, which may be difficult to swallow. Cephalexin should be given on an empty stomach, as it is absorbed better in this environment.
What are the adverse effects of cephalexin?
Adverse effects associated with toxicity include soreness of the oral cavity, gastrointestinal symptoms, and pruritus of pregnancy.[1] Additionally, the are only a few very rare documented cases of cephalexin inducing a fatal episode of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
What is the mechanism of action of cephalexin?
Mechanism of Action. Cephalexin is a first-generation cephalosporin. Cephalexin is a beta-lactam antibiotic, meaning its structure contains a beta-lactam ring. In a bacterial cell, peptidoglycan gives the cell wall mechanical stability. Cephalexin (and other beta-lactam antibiotics) use a beta-lactam ring to inhibit the synthesis of peptidoglycan, ...
Where does cephalexin get excreted?
Cephalexin gets excreted in the kidneys, which is a characteristic that makes it particularly useful in treating urinary tract infections. Additionally, patients with kidney disease may have prolonged excretion rates of cephalexin due to renal malfunction. [1][9][1] Toxicity.
Is cephalexin contraindicated for penicillin allergy?
Contraindications. Cephalexin and other cephalosporins are contraindicated in patients with a penicillin allergy, as this poses an increased risk of an allergic reaction to cephalexin and other cephalosporins.[7] .
Is cephalexin FDA approved?
Last Update: May 17, 2021. Continuing Education Activity. Cephalexin is an FDA-approved antibiotic. Cephalexin is a first-generation cephalosporin utilized in the treatment of urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and other bacterial infections. Both streptococci and staphylococci species can cause these infections.
What is the difference between first and second generation cephalosporins?
Cephalosporins are sometimes grouped into "generations" by their antimicrobial properties. The first cephalosporins were designated first-generation cephalosporins, where as, later , more extended- spectrum cephalosporins were classified as second-generation cephalosporins. Each newer generation has significantly greater Gram-negative antimicrobial properties than the preceding generation, in most cases with decreased activity against Gram-positive organisms. Fourth-generation cephalosporins, however, have true broad-spectrum activity.
How many generations of cephalosporins are there?
Some state that cephalosporins can be divided into five or even six generations, although the usefulness of this organization system is of limited clinical relevance.
What is the name of the fungus that causes cephalosporins?
The cephalosporins (sg. / ˌsɛfələˈspɔːrɪn, ˌkɛ -, - loʊ -/) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus Acremonium, which was previously known as " Cephalosporium ". Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems.
What is cephalosporin used for?
Medical uses. Cephalosporins are indicated for the prophylaxis and treatment of infections caused by bacteria susceptible to this particular form of antibiotic. First-generation cephalosporins are active predominantly against Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus.
What is the resistance to cephalosporin?
Resistance to cephalosporin antibiotics can involve either reduced affinity of existing PBP components or the acquisition of a supplementary β-lactam-insensitive PBP. Currently, some Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter cloacae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Escherichia coli strains are resistant to cephalosporins.
What is the name of the antibiotic that is made from fungus?
Cephalosporin. The cephalosporins (sg. / ˌsɛfələˈspɔːrɪn, ˌkɛ -, - loʊ -/) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus Acremonium, which was previously known as " Cephalosporium ". Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems.
Where was cephalosporin C found?
Discovery. The aerobic mold which yielded cephalosporin C was found in the sea near a sewage outfall in Su Siccu, by Cagliari harbour in Sardinia, by the Italian pharmacologist Giuseppe Brotzu in July 1945.
How many generations of cephalosporins are there?
So far there are five generations of cephalosporins. Third generation cephalosporins were the third generation of cephalosporins to be developed.
What is the name of the antibiotic that kills bacteria?
Cephalosporins are a large group of antibiotics derived from the mold Acremonium (previously called Cephalosporium ). Cephalosporins are bactericidal (kill bacteria) and work in a similar way to penicillins. They bind to and block the activity of enzymes responsible for making peptidoglycan, an important component of the bacterial cell wall.
Why are antibiotics called broad spectrum antibiotics?
They are called broad-spectrum antibiotics because they are effective against a wide range of bacteria. Since the first cephalosporin was discovered in 1945, scientists have been improving the structure of cephalosporins to make them more effective against a wider range of bacteria.
Is it safe to take cephalosporins?
Third generation cephalosporins are generally safe, with low toxicity and good efficacy against susceptible bacteria. Allergic reactions have been reported with all cephalosporins including third generation cephalosporins and symptoms may include a rash, hives ( urticaria ), swelling, or rarely, anaphylaxis. Up to 10% of people with ...
Can cephalosporin cause seizures?
Rarely, seizures have been reported with cephalosporins; the risk may be greatest in those with kidney disease. Cephalosporin should be given exactly as directed. Potentially life-threatening arrhythmias have been reported following rapid bolus administration of cefotaxime, a third generation cephalosporin.
Can cephalosporins be used as a first choice antibiotic?
Skin and skin structure infections. Urinary tract infections. Cephalosporins are not usually used as a first-choice antibiotic. They tend to be reserved for use when other antibiotics (often penicillins) cannot be used.
i. Cephalexin (Keflex, Keforal)
Properties and uses: Cephalexin monohydrate is a white crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water, and practically insoluble in alcohol. The α-amino group of cephalexin renders it acid stable. The 3-methyl group is responsible for the metabolic stability. It is particularly recommended for urinary tract infection.
ii. Cefadroxil (Cefadrox, Droxyl, Codroxil)
Properties and uses: Cefadroxil monohydrate is a white or almost white powder, slightly soluble in water, and sparingly soluble in ethanol. The antibacterial spectrum of action and therapeutic indications of cefadroxil are very similar to those of cephalexin and cephradine. The D-p-hydroxyphenylglycyl isomer is much more active than the L-isomer.
iii. Cephalothin (Keflin)
Properties: Cephalothin is a white, odourless, crystalline powder, insoluble in most organic solvents, soluble in organic solvents and it is acid stable. It is hygroscopic and decomposes on heating, and it has been described as broad-spectrum antibacterial compound, it is not in the same class as the tetracyclines.
iv. Cefsulodin
Properties and uses: It is indicated for use in staphylococcal and pseudomonal infections.

What Are Cephalosporins?
First-Generation Cephalosporins
- First-generation cephalosporins come in oral and intravenous forms. They are active against Viridans streptococci, group A hemolytic streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, E. coli, Klebsiella and Proteus bacteria. Like all other cephalosporins, first-generation cephalosporins don't work on enterococci. Examples of first-generation cephalosporins include the following: 1. Cephalexin (K…
Second-Generation Cephalosporins
- In general, second-generation cephalosporins are more active against gram-negative organisms, making them more useful in many clinical situations. For example, second-generation cephalosporins are active against strains of Proteus and Klebsiella. Second-generation cephalosporins also combat H. influenza—a cause of pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis. Nevert…
Third-Generation Cephalosporins
- A major advantage of third- and fourth-generation antibiotics is significantly expanded coverage against gram-negative bacteria. Furthermore, the third-generation cephalosporin ceftazidime is active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a bacteria that can cause skin infections in people with normal immune systems (such as after exposure to an under-chlorinated hot tub or pool) as wel…
Fifth-Generation Cephalosporin
- In 2010, the FDA approved Ceftaroline (Teflaro), the only fifth- or advanced-generation cephalosporin. Like cefepime, ceftaroline is a potent antibiotic that should be reserved for serious infection. Specifically, it's active against multidrug-resistant infections like MRSA (methicillin-resistant S. aureus) and VRSA (vancomycin-resistant S. aureus). This drug is also injectable and …
A Word from Verywell
- As you can now appreciate, cephalosporins are a remarkably diverse class of antibiotics with broad coverage. However, as with most antibiotics, antibiotic resistanceis a concern for many clinicians, epidemiologists, public health officials, and patients. Bacterial resistance is partially due to physicians' overprescription; nevertheless, we can also help combat the development of r…