
Lactic Acid Fermentation. In lactic acid fermentation, the pyruvic acid from glycolysis is reduced to lactic acid by NADH, which is oxidized to NAD+. This commonly occurs in muscle cells. Lactic acid fermentation allows glycolysis to continue by ensuring that NADH is returned to its oxidized state (NAD+).
Where in the body does latic acid fermentation occur?
Lactic acid builds up in your muscle cells as fermentation occurs after severe exercise. During these moments, your respiratory and cardiovascular systems are unable to provide enough oxygen to your muscle cells, particularly those in your legs, to maintain aerobic respiration.
What kinds of organism perform lactic acid fermentation?
- Lactic acid fermentation. Yeast strains and bacteria convert starches or sugars into lactic acid, requiring no heat in preparation.
- Ethanol fermentation/alcohol fermentation.
- Acetic acid fermentation.
What is an example of lactic fermentation?
What is an example of lactic acid fermentation? Once the stored ATP is used, your muscles will start producing ATP through lactic acid fermentation. Fermentation makes it possible for cells to continue generating ATP through glycolysis. For example, bacteria used in the production of cheese, yogurt, buttermilk, sour cream, and pickles are ...
Does lactic fermentation require oxgyen?
Lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid (lactate) and NAD+. What happens if oxygen is present during fermentation? Pyruvic acid supplies energy to living cells through the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) when oxygen is present (aerobic respiration), and alternatively ferments to produce lactic acid when oxygen is lacking (fermentation).
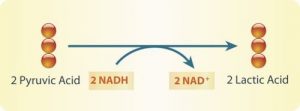
What comes out of lactic acid fermentation?
4: Lactic acid fermentation makes ATP in the absence of oxygen by converting glucose to lactic acid (through a pyruvate intermediate). Making lactic acid from pyruvate oxidizes NADH, regenerating NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue to make more ATP rapidly.
What goes in and out during fermentation?
Fermentation is the process by which yeast converts the glucose in the wort to ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide gas -- giving the beer both its alcohol content and its carbonation.
What products does lactic acid fermentation produce?
Kimchi, sauerkraut, pickles, sourdough bread and yogurt are all fermented foods created using the method called lactic acid fermentation.
What happens during lactate fermentation?
Some organisms, such as some bacteria, will undergo lactate fermentation. Two pyruvates are converted to two lactic acid molecules, which ionize to form lactate. In this process two NADH + H+ are converted to two NAD+. Our muscle cells can undergo this process when they are in oxygen debt.
What are the inputs of fermentation?
Fermentation happens in anaerobic conditions (i.e.,without oxygen). Fermentation begins with glycolysis which breaks down glucose into two pyruvate molecules and produces two ATP (net) and two NADH. Fermentation allows glucose to be continuously broken down to make ATP due to the recycling of NADH to NAD+.
What are the reactants of lactic acid fermentation?
An example (if a bit lengthy) energy story for lactic acid fermentation: The reactants are pyruvate, NADH and a proton. The products are lactate and NAD+. The process of fermentation results in the reduction of pyruvate to form lactic acid and the oxidation of NADH to form NAD + .
What are the products of lactic acid fermentation quizlet?
Lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid and NAD+, while alcohol fermentation produces alcohol, carbon dioxide, and NAD+. They both have the same reactance, pyruvic acid and NADH.
Is co2 released in lactic acid fermentation?
Lactate fermentation is an anaerobic fermentation reaction taking place in some types of bacteria and animal cells, like muscle cells. In this carbon dioxide is not released.
What are the steps of lactic acid fermentation?
Lactic acid fermentation has two steps: glycolysis and NADH regeneration. During glycolysis, one glucose molecule is converted to two pyruvate molecules, producing two net ATP and two NADH.
What is lactic acid fermentation for dummies?
Lactic acid fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration (or fermentation) that breaks down sugars to produce energy in the form of ATP. It is called anaerobic because it occurs in the absence of oxygen. Lactic acid is generated as a byproduct of this reaction, which is what gives this type of fermentation its name.
What are the products of fermentation?
Lactic acids, flavour-generating components (e.g., acetaldehyde), ethanol and carbon dioxide are all by-products of fermentation and contribute to the organoleptic properties of kefir [35].
What is produced from fermentation?
Upon a strictly biochemical point of view, fermentation is a process of central metabolism in which an organism converts a carbohydrate, such as starch or sugar, into an alcohol or an acid. For example, yeast performs fermentation to obtain energy by converting sugar into alcohol.
What happens during fermentation?
Fermentation is a metabolic process in which an organism converts a carbohydrate, such as starch or a sugar, into an alcohol or an acid. For example, yeast performs fermentation to obtain energy by converting sugar into alcohol. Bacteria perform fermentation, converting carbohydrates into lactic acid.
How does the process of fermentation work?
What is fermentation? Fermentation is the process of sugars being broken down by enzymes of microorganisms in the absence of oxygen. Microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi have unique sets of metabolic genes, allowing them to produce enzymes to break down distinct types of sugar metabolites.
What are the steps of fermentation?
The fermentation process consists of four stages. The four stages are: (1) Inoculum Preservation (2) Inoculum Build-up (3) Pre-Fermenter Culture and (4) Production Fermentation. A classification, based on the product formation in relation to energy metabolism is briefly discussed below (Fig. 19.15).
What are the two fermentation processes?
There are two types of fermentation: lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. Both types of fermentation are described below.
Where Does Lactic Acid Fermentation Occur?
The lactic acid fermentation occurs in certain animal cells and bacterial organisms . In animal cells, aerobic respiration is generally preferred - this process doesn't involve lactic acid fermentation. However, in conditions where the oxygen supply is insufficient - primarily in muscle tissues, during periods of strenuous exercise - cells must undergo anaerobic respiration in order to adequately meet the demand for energy. This process of anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid as a byproduct, which accumulates in the muscle tissues. The increased acidity is responsible for the burning sensation and weakness you feel in your muscles during exercise, and this is believed to help prevent you from overworking your muscles. Contrary to popular opinion, however, lactic acid is not the cause of delayed-onset muscle soreness (i.e. the soreness you might feel the day after an intense workout.)
What sugars are used in lactic acid fermentation?
Apart from glucose, other sugars such as lactose and maltose can also be used in lactic acid fermentation.
How is lactic acid made?
Lactic acid is produced on an industrial scale through chemical manufacturing, as well as, biological manufacturing (using microbes that carry out lactic acid fermentation.) This lactic acid has several uses in the cosmetic, food, and pharmaceutical industries. This includes uses as a food preservative, a skin treatment, and as a reactant to create drugs. Lactic acid is also being studied for its ability to polymerize and form Poly Lactic Acid, a renewable and biodegradable plastic.
What is the process of converting glucose into pyruvic acid?
The first process is called glycolysis (which is also a part of the aerobic respiration pathway.) Glycolysis involves the conversion of glucose into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid, creating 2 ATP and 2NADH (from ADP and NAD+) in the process. Because glycolysis does not require oxygen, it is considered an anaerobic process.
Why is lactic acid anaerobic?
It is called anaerobic because it occurs in the absence of oxygen. Lactic acid is generated as a byproduct of this reaction, which is what gives this type of fermentation its name. One well-known example of lactic acid fermentation occurs during the production of yogurt by Lactobacillus bacteria.
How many NAD+ are generated in pyruvic acid?
In the next step, each molecule of pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid. As a byproduct, 4 NAD+ is generated, 2 of which go back to continue the glycolysis pathway.
Where does lactic acid go after muscle contraction?
After the muscle activity is over, lactic acid is removed from the muscle tissue through the bloodstream. It is then sent to the liver, where it undergoes chemical reactions to form pyruvic acid, which is used to produce additional energy as ATP.

Anaerobic Respiration
- Anaerobic respiration is a kind of cellular respiration that happens in the absence of oxygen. The two types of anaerobic respiration are – Lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation.
Fermentation
- Fermentation usually happens in yeast cells and bacteria. Also, the animal muscle cells show lactic acid fermentation in case of inadequate oxygen supply. In yeast, there is incomplete oxidation of glucose that happens in an anaerobic environment. Here, pyruvic acid is converted into carbon dioxide and ethanol. Some bacteria produce lactic acid from pyruvic acid by means …
Steps Involved in Lactic Acid Fermentation
- The glucose or 6-carbon molecule is broken down into Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and then to 3-Phosphoglyceric acid.
- During this, NAD+ is converted into NADH+H+.
- The 3-Phosphoglyceric acid forms Phosphoenol pyruvic acid, which later forms the Pyruvic acid.
- The glucose or 6-carbon molecule is broken down into Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and then to 3-Phosphoglyceric acid.
- During this, NAD+ is converted into NADH+H+.
- The 3-Phosphoglyceric acid forms Phosphoenol pyruvic acid, which later forms the Pyruvic acid.
- Net 2 ATP molecules are formed in this process (glycolysis).
Applications
- Lactic acid fermentation is the best method used for food preservation. Lactobacillus is the most commercially used bacteria for this process. They are used in the production of pickles, sour beer, fermented fish, yoghurt, etc. Also Read: 1. Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 2. Fermentation – Anaerobic Respiration 3. Glycolysis Visit BYJU’S Biologyfor more exciting topics.