
The Crimean War was a military conflict fought from October 1853 to February 1856 in which Russia lost to an alliance made up of France, the Ottoman Empire, the United Kingdom and Sardinia. The immediate cause of the war involved the rights of Christian minorities in the Holy Land, then a part of the Ottoman Empire.
Why did Russia fight in the Crimean War?
Turco-Mongol raids The Crimean War was a military conflict fought from October 1853 to February 1856 in which Russia lost to an alliance made up of France, the Ottoman Empire, the United Kingdom and Sardinia. The immediate cause of the war involved the rights of Christian minorities in the Holy Land, then a part of the Ottoman Empire.
When did the Crimean War start and end?
Last Updated: Sep 27, 2018 See Article History. Crimean War, (October 1853–February 1856), war fought mainly on the Crimean Peninsula between the Russians and the British, French, and Ottoman Turkish, with support from January 1855 by the army of Sardinia-Piedmont.
What happened in the Crimean War in 1854?
Crimean War. The Siege of Sevastopol (at the time called in English the Siege of Sebastopol) lasted from October 1854 until September 1855, during the Crimean War. The allies (French, Ottoman, and British) landed at Eupatoria on 14 September 1854, intending to make a triumphal march to Sevastopol, the capital of the Crimea, with 50,000 men.
What happened in the Crimea?
A force of five British and four French divisions dutifully sailed for the Crimea, landing at Eupatoria in September. None of the contending armies had fought a serious war since 1815, and it showed.

Who fought the Crimean War?
The Crimean War was fought between Russia and the forces of Britain, France, and the Ottoman Empire, later joined by the army of Sardinia-Piedmont.
What led to the Crimean War?
The Crimean War was the result of Russian demands to exercise protection over the Orthodox subjects of the Ottoman sultan. Another cause was a disp...
What was the outcome of the Crimean War?
After Austria threatened to join the allies during the Crimean War, Russia accepted preliminary peace terms in 1856. The Congress of Paris worked o...
How many people died in the Crimean War?
The Crimean War produced about 500,000 total casualties, with about half suffered by each side. A disproportionate number of deaths were caused by...
How did the Crimean War affect the future treatment of wounded soldiers?
After details of the deplorable conditions faced by wounded soldiers during the Crimean War reached the British public, nurses such as Mary Seacole...
What was the Crimean War?
Crimean War, (October 1853–February 1856), war fought mainly on the Crimean Peninsula between the Russians and the British, French, and Ottoman Turkish, with support from January 1855 by the army of Sardinia-Piedmont . The war arose from the conflict of great powers in the Middle East and was more directly caused by Russian demands ...
When did Britain and France declare war on Russia?
On March 28 Britain and France declared war on Russia. To satisfy Austria and avoid having that country also enter the war, Russia evacuated the Danubian principalities. Austria occupied them in August 1854. British soldiers leaving for the Crimean War, February 1854.
What was the name of the river that was opened to the shipping of all nations?
The Black Sea was neutralized, and the Danube River was opened to the shipping of all nations. Crimean War. Four Zouaves with their bayonetted rifles during the Crimean War, 1855. Harry Ransom Center, The University of Texas at Austin. Roger Fenton Photography Collection (Photography Collection PH-00023).
What battle did the Allies fight in 1854?
Charge of the Light Brigade. October 25, 1854. Battle of Balaklava. October 25, 1854. keyboard_arrow_right. In September 1854 the allies landed troops in Russian Crimea, on the north shore of the Black Sea, and began a yearlong siege of the Russian fortress of Sevastopol.
Why did the British and French enter the Black Sea?
After the Russian Black Sea fleet destroyed a Turkish squadron at Sinope, on the Turkish side of the Black Sea, the British and French fleets entered the Black Sea on January 3, 1854, to protect Turkish transports. On March 28 Britain and France declared war on Russia.
What countries did Austria become dependent on?
Austria became dependent on Britain and France, which failed to support that country, leading to the Austrian defeats in 1859 and 1866 that, in turn, led to the unification of Italy and of Germany. The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Michael Ray, Editor.
When did the British invade Constantinople?
The British fleet was ordered to Constantinople (Istanbul) on September 23. On October 4 the Turks declared war on Russia and in the same month opened an offensive against the Russians in the Danubian principalities.
What was the cause of the Crimean War?
The immediate cause of the war involved the rights of Christian minorities in the Holy Land, then a part of the Ottoman Empire.
Why did the British fight the Crimean War?
The British fought Russia out of resentment and supposed that her defeat would strengthen the European Balance of Power. Russian siege of Kars, Russo-Turkish War of 1828–29.
What was the Greek War of Independence?
The Greek War of Independence, which began in early 1821, provided further evidence of the internal and military weakness of the Ottoman Empire, and the commission of atrocities by Ottoman military forces (see Chios massacre) further undermined the Ottomans.
Why did Austria support Russia?
On 27 February 1854, the United Kingdom and France demanded the withdrawal of Russian forces from the principalities. Austria supported them, and, though it did not declare war on Russia, it refused to guarantee its neutrality. Russia's rejection of the ultimatum proved to be the justification used by Britain and France to enter the war.
What were the first technologies used in the Crimean War?
The Crimean War was one of the first conflicts in which the military used modern technologies such as explosive naval shells, railways, and telegraphs. The war was one of the first to be documented extensively in written reports and in photographs.
When did Russia sue for peace?
Isolated and facing a bleak prospect of invasion from the west if the war continued, Russia sued for peace in March 1856. France and Britain welcomed this development, as the conflict was growing unpopular at home. The Treaty of Paris, signed on 30 March 1856, ended the war.
Where did the Allies attack Russia?
Frustrated by the wasted effort, and with demands for action from their citizens, the allied commanders decided to attack Russia's main naval base in the Black Sea: Sevastopol on the Crimean peninsula.
What was the outcome of the Crimean War?
The Outcome of the Crimean War. by Jessica Brain. On 30th March 1856, the Crimean War was formally brought to an end with the signing of the Treaty of Paris. This formal recognition signed at the Congress of Paris came after Russia accepted a humiliating defeat against the alliance of Britain, France, the Ottoman Empire and Sardinia.
How did the Crimean War affect Russia?
This was particularly pertinent for Russia which suffered terribly, losing around 500,000 of its troops. The Crimean War thus instigated an era of self-evaluation in Russia which threw off the shackles of archaic traditions and embraced modernisation.
What was the purpose of the Treaty of Paris?
The treaty itself would address Russian expansionism, quashing dreams of a Russian empire equal to none, whilst at the same time confirming the importance of the Ottoman Empire in maintaining a very tentative balance of power in Europe .
How long did the Crimean War last?
The Crimean War which had begun in October 1853 lasted eighteen months and in that time had escalated into a series of fragmented battles and sieges, causing huge loss of life and highlighting wider issues and failures pertaining to leadership, military intervention, mortality rates, medicine and mismanagement.
What were the names of the towns and cities that were named after the Crimean War?
History of Britain. Many British towns and cities have streets named after battles fought during the Crimean War, such as Alma, Sebastapol, Balaclava and Inkerman.
What was the main agreement between the Tsar and the Sultan?
This agreement was between the Tsar and the Sultan who maintained that no arsenal could be established on the coastline. For Russia this clause in particular proved to be a major blow, weakening its power base as it no longer could threaten the Ottoman Empire via its navy. This was thus an important step in scaling down the potential for escalating violence.
Why was Crimea important to Britain?
Meanwhile, Crimea was significant for Britain as it marked one of its first military interventions in Europe for forty years. The repercussions for Westminster would be massive as the portrayal of the war in British media allowed the public for the first time to receive information day-by-day about the carnage abroad.
What was the Crimean War?
by Jessica Brain. The Crimean War was a conflict fought between the Russian Empire against an alliance of French, British, Ottoman and Sardinian troops. The war broke out in the autumn of 1853 and came to a conclusion in March 1856 with the Treaty of Paris.
What happened in 1854?
3rd January 1854- The Ottomans receive back-up in the Black Sea as French and British fleets enter the waters. 28th March 1854- Britain and France declare war on Russia. August 1854- Austria, which remains neutral in the war, occupies the Danubian principalities which Russia had evacuated some months previously.
What happened in October 1853?
October 1853- The conflict ensues with the Turks leading an offensive against the Russians in the disputed Danubian territories.
What country did the Tsar send his army to?
June 1853- Following the breakdown in diplomatic discussions between the Ottomans and the Russians, the Tsar decides to send an army to the Danubian Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia.
What was the fateful choice that led to the Charge of the Light Brigade?
As the Russians are held off, the Allied forces make the crucial decision to recover some of their guns, a fateful choice that led to the infamous Charge of the Light Brigade.
Why did the Ottomans need reserves in Kars?
October 1855- The Ottomans are in desperate need of reserves in Kars as they are running out of supplies. Due to treacherous weather conditions, reinforcements are unable to reach the garrison.
Where did the Allies march?
The Allies march towards Sevastapol which they deem to be strategically significant whilst the Russians go to the Alma Heights, a position offering some defensive protection, led by their commander Prince Alexander Sergeyevich Menshikov.
Why did France and Britain declare war on Russia?
Fearing that the Czar was looking to dismantle the Ottoman Empire—a weak regime he called the “sick man of Europe”—France and Britain cast their lot with the Turks and declared war on Russia in March 1854. The Crimean War soon transformed into an imperial struggle for influence over the ailing Ottoman Empire, but it never lost its religious overtones. British and French Christians roundly denounced the Russian Orthodox Church in the press, and many Russians and Turks came to view the conflict as a holy war between Eastern Christianity and Islam.
Why was the Creole with the Tea Mug nicknamed Dasha?
Newspapers later nicknamed her “The Creole with the Tea Mug” for her work in providing battle-weary troops with the comforts of home. On the Russian side, a woman named Daria Mikhailova became known as “Dasha from Sevastopol” for dressing soldiers’ wounds using supplies purchased on her own dime, and doctor Nikolai Pirogov helped introduce field surgery and the use of anesthetics. Despite the best efforts of people like Nightingale and Pirogov, infectious disease still killed far more Crimean War soldiers than combat. The British alone suffered an estimated 16,000 deaths from illnesses compared to just 5,000 from battle.
What caused the Crimean War?
1. Religious tensions helped trigger the war. While it’s remembered as a clash of empires, the Crimean War was sparked by a seemingly minor religious dispute. For years, Orthodox Christians and Roman Catholics had squabbled over access to holy sites within the borders of the majority-Muslim Ottoman Empire. Both France and Russia purported ...
What was the first major conflict where civilian journalists sent dispatches from the battlefield?
political party. Thanks to new technologies such as the steamship and the electric telegraph, the Crimean War was the first major conflict where civilian journalists sent dispatches from the battlefield.
What was the first war to feature news correspondents and battlefield photographers?
Thanks to new technologies such as the steamship and the electric telegraph, the Crimean War was the first major conflict where civilian journalists sent dispatches from the battlefield.
What was the price of Alaska in 1867?
In 1867, after a delay caused by the Civil War, Secretary of State William Seward inked a deal to purchase Alaska for the cut-rate price of $7.2 million —the equivalent of just two cents an acre.
How long did it take for the Russians to evacuate Sevastopol?
It would eventually take 11 months before a French assault forced the Russians to evacuate Sevastopol.
What was the Crimean War?
The Crimean War. The Crimean War of 1854-56 was a classic example of the peninsula's lure. In December 1852, a diplomatic clash arose between Russia and France over the status of a handful of Christian shrines and churches in the Holy Land, then under Ottoman Turkish rule.
Where did the Soviets land in Crimea?
As Manstein pondered his failure, the Soviets landed a blow on the eastern side of the Crimea, a series of amphibious landings on the Kerch peninsula. Three complete armies came ashore (51st, 44th, 47th), and Soviet commander General D. T. Kozlov now hurled them at the German defenses in the Parpach bottleneck.
What is the peninsula of Crimea?
Take the Crimea. A diamond-shaped peninsula dominating the Black Sea, it has enticed hundreds of would-be overlords over the millennia. While it is a natural naval base, the tenuous link with the mainland via the Perekop Isthmus is also just wide enough to lure land armies. And lure them it has, one after the other: Tauri and Scythians, Greeks and Romans, Byzantines and Kievan Rus, Mongols and Ottoman Turks and Russians, Soviet commissars and German Field Marshals. All felt the pull of its beauty and its temperate climate, to be sure, but what really drew them was the location. The ruler of the peninsula has 360-degree power projection at his fingertips: north into Ukraine, east into the Caucasus, south into Asia Minor, or west into the Balkans.
What was the purpose of the Turkish invasion of Wallachia?
Their purpose was to prop up the teetering Ottoman Empire, but it hardly seemed necessary. After declaring war, Turkish forces had carried the fight to the Russians, invading Wallachia and fortifying a number of positions along the Danube river. The Russian drive south faltered, and in April 1854 they began a desultory siege of the fortress of Silistra. The Ottomans were holding their own, in other words, but unfortunately, an Allied expeditionary force was already at sea. It landed at Varna on the Black Sea in May, where poor sanitation promptly brought on a cholera epidemic that killed thousands. At the same time, recognizing that they would never take Silistra, the Russians abandoned the siege in June, and after an ultimatum from neutral Austria, they evacuated Wallachia and Moldavia altogether.
What was the Russians' defense of the Redoubts?
The Russians defended their redoubts south of the river bravely at first, but superior Allied firepower, courtesy of the new Minié rifle, soon forced them to retreat. It started out orderly enough, but as their shaky command and control broke down, degenerated into a confused rout.
Where did the Russians launch their relief efforts?
On the ground, the Russians launched three inept relief attempts of Sevastopol, at Balaklava in October (site of the charge of the British Light Brigade), Inkerman Ridge in No-vember, and the Tchernaya river in August 1855. The Allies beat back each one with heavy losses, and the issue was no longer in doubt.
Did the Russians renounce the Crimean War?
That was about it, however, and even those meager clauses would have a very short half-life. With Europe distracted by the Franco-Prussian War in 1870-71, the Russians would renounce the entire treaty. Largely forgotten today, the Crimean War was a signal moment in history for many reasons.
What were the rivals of the 1840s?
"In the 1840s, 1850s, Britain and America are not the chief rivals; it's Britain and Russia. Britain and Russia are rivals for world power, and Turkey, the Ottoman Empire, which is much larger than modern Turkey — it includes modern Romania, Bulgaria, parts of Serbia, and also Egypt and Arabia — is a declining empire. But it's the bulwark between Russia, which is advancing south and west, and Britain, which is advancing east and is looking to open its connections up through the Mediterranean into its empire in India and the Pacific. And it's really about who is running Turkey. Is it going to be a Russian satellite, a bit like the Eastern Bloc was in the Cold War, or is it going to be a British satellite, really run by British capital, a market for British goods? And the Crimean War is going to be the fulcrum for this cold war to actually go hot for a couple of years, and Sevastopol is going to be the fulcrum for that fighting."
Who invaded Russia?
"People have always attacked and invaded Russia. The Golden Horde of Genghis Khan completely destroyed medieval Russia. Napoleon invaded, Hitler invaded, the Swedes invaded, the Poles invaded, the British invaded. The history of Russia is about being invaded by dangerous, aggressive, foreign countries, and their strategy is to build a buffer zone of protective zones through which people have to advance, and the Ukraine has been one of those for 300 years, and hope that they can avoid being conquered by what seems to be an endless litany of aggressive foreign conquerors."
Who wrote the poem "The Charge of the Light Brigade"?
Today, popular knowledge about the war is limited to the poem Alfred Lord Tennyson wrote about one of its battles, "The Charge of the Light Brigade," and from the story of the British nurse Florence Nightingale.
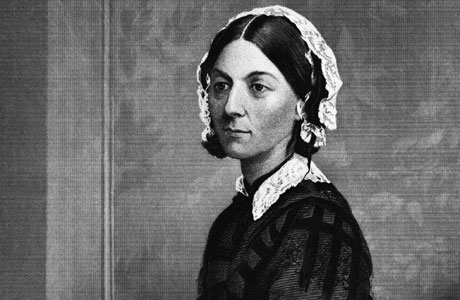
Overview
Eastern Question
As the Ottoman Empire steadily weakened during the 19th century, the Russian Empire stood poised to take advantage by expanding southward. In the 1850s, the British and the French Empires were allied with the Ottoman Empire and were determined to prevent that from happening. The historian A. J. P. Taylor argued that the war had resulted not from aggression, but from the interacting …
Battles
The Danube campaign opened when the Russians occupied the Danubian Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia in July 1853, which brought their forces to the north bank of the River Danube. In response, the Ottoman Empire also moved its forces up to the river, establishing strongholds at Vidin in the west and Silistra in the east, near the mouth of the Danube. The Ottoman move up the Ri…
End of the war
Dissatisfaction with the conduct of the war was growing with the public in Britain and other countries and was worsened by reports of fiascos, especially the devastating losses of the Charge of the Light Brigade at the Battle of Balaclava. On Sunday, 21 January 1855, a "snowball riot" occurred in Trafalgar Square near St Martin-in-the-Fields in which 1,500 people gathered to protest ag…
Long-term effects
Orlando Figes points to the long-term damage Russia suffered:
The demilitarization of the Black Sea was a major blow to Russia, which was no longer able to protect its vulnerable southern coastal frontier against the British or any other fleet… The destruction of the Russian Black Sea Fleet, Sevastopol and other naval docks was a humiliation. No compulsory disarmament had ev…
Orlando Figes points to the long-term damage Russia suffered:
The demilitarization of the Black Sea was a major blow to Russia, which was no longer able to protect its vulnerable southern coastal frontier against the British or any other fleet… The destruction of the Russian Black Sea Fleet, Sevastopol and other naval docks was a humiliation. No compulsory disarmament had ev…
Documentation
Documentation of the war was provided by William Howard Russell, who wrote for The Times newspaper, and by Roger Fenton's photographs. News from war correspondents reached all of the nations involved in the war and kept the public citizenry of those nations better informed of the day-to-day events of the war than had been the case in any earlier war. The British public was very well informed on the day-to-day realities of the war. After the French extended the telegraph to t…
Criticisms and reform
Historian R. B. McCallum points out the war was enthusiastically supported by the British populace as it was happening, but the mood changed very dramatically afterwards. Pacifists and critics were unpopular but:
in the end they won. Cobden and Bright were true to their principles of foreign policy, which laid down the absolute minimum of intervention in European affa…
Chronology of major battles of the war
• Battle of Sinop, 30 November 1853
• Siege of Silistra, 5 April – 25 June 1854
• First Battle of Bomarsund, 21 June 1854
• Second Battle of Bomarsund, 15 August 1854