What is the conflict between Arab and Israel?
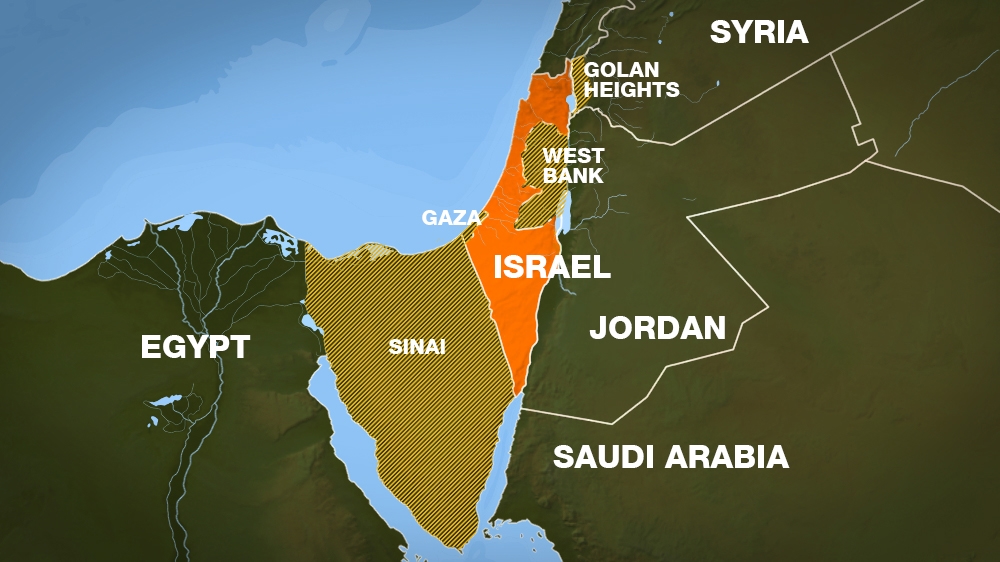
The Arab–Israeli conflict is an ongoing intercommunal phenomenon involving political tension, military conflicts, and other disputes between Arab countries and Israel, which escalated during the 20th century, but had mostly faded out by the early 21st century.
What were some key events in the Arab-Israeli conflict?
Here are 15 key moments in this long-running conflict:First Arab-Israeli War (1948-49) ... Six Day War (1967) ... Munich Olympics (1972) ... Camp David Accord (1977) ... Invasion of Lebanon (1982) ... First Palestinian Intifada (1987-1993) ... Oslo Declaration (1993) ... Pullout from Lebanon (2000)More items...
What is the cause of the Israel conflict?
The history of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict began with the establishment of the state of Israel in 1948. This conflict came from the intercommunal violence in Mandatory Palestine between Arabs and Jews from 1920, and erupted into full-scale hostilities in the 1947–48 civil war.
What is the major reason for conflict between Israel and Palestine?
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is over who gets what land and how it's controlled. Though both Jews and Arab Muslims date their claims to the land back a couple thousand years, the current political conflict began in the early 20th century.
What major events happened in Israel?
HISTORY of Israel: Timeline17th-6th C. BCEBIBLICAL TIMES1939-45World War II; Holocaust in Europe.1941Lehi underground movement formed; Palmach, strike force of Haganah, set up.1944Jewish Brigade formed as part of British forces.1947UN proposes the establishment of Arab and Jewish states in the Land.104 more rows
What did Israel do to Palestine?
Unlawful attacks During the armed conflict in May, Israel committed apparent war crimes and possible crimes against humanity in the Gaza Strip. According to the OHCHR and the WHO, 242 Palestinians were killed, including 63 children, and some 9,000 were injured. More than 74,000 Palestinians were displaced.
Overview
The Arab–Israeli conflict is an ongoing intercommunal phenomenon involving political tension, military conflicts, and other disputes between Arab countries and Israel, which escalated during the 20th century, but had mostly faded out by the early 21st century. The roots of the Arab–Israeli conflict have been attributed to the support by Arab League member countries for the Palestinians, …
Background
The Arab–Israeli conflict has a religious aspect. The beliefs of the various sides and their ideas and views of the chosen people in their policies with regard to the "Promised Land" and the "Chosen City" of Jerusalem.
The Land of Canaan or Eretz Yisrael (Land of Israel) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, promised by God to the Children of Israel. This is also mentioned …
History
On 14 May 1948, the day on which the British Mandate over Palestine expired, the Jewish People's Council gathered at the Tel Aviv Museum and approved a proclamation that declared the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz Israel, to be known as the State of Israel. The declaration was made by David Ben-Gurion, the Executive Head of the World Zionist Organization.
There were no mention of the borders of the new state other than that it was in Eretz Israel. An o…
Cost of conflict
A report by the Strategic Foresight Group estimated the opportunity cost of conflict for the Middle East from 1991 to 2010 at $12 trillion. The report's opportunity cost calculates the peace GDP of countries in the Middle East by comparing the current GDP to the potential GDP in times of peace. Israel's share is almost $1 trillion, with Iraq and Saudi Arabia having approximately $2.2 and $4.5 trillion, respectively. For example, had there been peace and cooperation between Israel and Ara…
See also
• One-state solution
• Two-state solution
• International law and the Arab–Israeli conflict
• Media coverage of the Arab–Israeli conflict
Further reading
• Associated Press, comp. (1996). Lightning Out of Israel: [The Six-Day War in the Middle East]: The Arab-Israeli Conflict. Commemorative Ed. Western Printing and Lithographing Company for the Associated Press. ASIN B000BGT89M.
• Bard, Mitchell (1999). Middle East Conflict. Indianapolis: Alpha Books. ISBN 0-02-863261-3.
Why Did The Three Countries Go to War?
How Did The War Unfold?
- To catch Israel off guard, the Egyptians and Syrians decided to launch an attack on the Yom Kippur religious holiday, the only day in the year in which there are no radio or television broadcasts, shops close and transportation shuts down as part of religious observations. The holiday fell on Saturday, October 6, 1973, and just after 2pm, the Egyptian and Syrian armies, wit…
Diplomatic Track
- By the last week of October, the two sides were ready and willing to accept a ceasefire deal. Estimates put the number of Israeli soldiers killed at 2,600 and 8,800 wounded, significantly larger in proportion compared with the Israeli population at the time, while Egypt was reported to have lost 7,700 men and Syria some 3,500. On October 22, the UN Security Council passed Resolutio…
Aftermath of The War
- Both the Arabs and Israel declared victory in the war. The Arab countries managed to salvage their defeats after repeated losses in the 1948, 1956 and 1967 wars with Israel. Within four years, in 1977, Sadat was in Jerusalemgiving a speech of peace to the Israeli parliament, the Knesset. Then US President Jimmy Carter invited both Sadat and former ...