
The Battle of Issus (also Issos) occurred in southern Anatolia, on November 5, 333 BC between the Hellenic League led by Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Empire, led by Darius III, in the second great battle of Alexander's conquest of Asia.The invading Macedonian troops defeated Persia. After the Hellenic League soundly defeated the Persian satraps of Asia Minor (led by Greek mercenary ...
What happened at the Battle of Issus in ancient Greece?
Battle of Issus. Battle of Issus, (333 bce ), conflict early in Alexander the Great’s invasion of Asia in which he defeated a Persian army under King Darius III. This was one of the decisive victories by which Alexander conquered the Achaemenian Empire. Issus is a plain on the coast of the Gulf of İskenderun, in present-day southern Turkey.
When did the Battle of Issus take place?
/ 36.7525; 36.1923 The Battle of Issus (also Issos) occurred in southern Anatolia, on November 5, 333 BC between the Hellenic League led by Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Empire, led by Darius III. It was the second great battle of Alexander's conquest of Asia, and the first encounter between Darius III and Alexander the Great.
How many casualties were there in the Battle of Issus?
452 casualties. 5,000 wounded. ~20,000-40,000 casualties. The Battle of Issus (also Issos) occurred in southern Anatolia, on November 5, 333 BC between the Hellenic League led by Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Empire, led by Darius III, in the second great battle of Alexander's conquest of Asia.
Why did Alexander the great fight at Issus?
Alexander the Great fought the Battle at Issus soon after the Battle at the Granicus. Like his father Philip, the glory-seeking Alexander aimed to conquer the Persian Empire. Although greatly outnumbered, Alexander was a better tactician.

When was Battle of Issus fought?
November 5, 333 BCBattle of Issus / Erupt date
How many died in the Battle of Issus?
However, when the Persian forces saw their leader flee, they fled, too; many were trampled to death in the mass exit. In all, the Persians lost 100,000 foot soldiers and 10,000 cavalry while Alexander only lost 1,200.
When did the Battle of Issus end?
November 5, 333 BCBattle of Issus / End date
What was the aftermath of the Battle of Issus?
Once Darius' army had been routed, Persian soldiers fled for their lives. Macedonian soldiers chased them until nightfall whereupon they gave up their pursuit 'and turned to plunder'. Their target was, of course, the Persian camp.
Did Alexander ever lose a battle?
In 15 years of conquest Alexander never lost a battle. The centerpiece of Alexander's fighting force was the 15,000-strong Macedonian phalanx, whose units held off the sword-wielding Persians with 20-foot-long pikes called sarissa.
Why did Alexander the Great Win the Battle of Issus?
Alexander led the charge across the river, shattering the Persian left wing before turning against the Greek mercenaries who formed the Persian centre.
How do you pronounce the Battle of Issus?
Phonetic spelling of battle of Issusbattle of Is-sus. Etha Jenkins.bat-tle of Is-sus.battle of issus. Hilma Dibbert.
Who crushed the Persian Empire?
Alexander the GreatThe Battle of Issus, in which Alexander the Great secured a decisive victory over Darius III of Persia.
How did the Persian Empire fall?
The Persian Empire began to decline under the reign of Darius's son, Xerxes. Xerxes depleted the royal treasury with an unsuccessful campaign to invade Greece and continued with irresponsible spending upon returning home. Persia was eventually conquered by Alexander the Great in 334 B.C.E.
What weapons were used in the Battle of Issus?
The Greek phalanx, armed with three meter spears that were, when the two arrays collided, used in the same way as the six meter Macedonian lance, now had the advantage of its superior numbers.
Who defeated Alexander the Great?
Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath on Sunday (November 14) said that Chandragupta Maurya, who founded the Mauryan empire in the 4th century BC, had defeated Alexander of Macedon in battle — and yet, it is the latter whom historians have chosen to call “great”.
Who defeated the Persian army?
Battle of Gaugamela, also called Battle of Arbela, (Oct. 1, 331 bc) battle in which Alexander the Great completed his conquest of Darius III's Persian Empire. It was an extraordinary victory achieved against a numerically superior army on ground chosen by the Persians.
Who was killed by Alexander in a drunken brawl?
Cleitus the BlackCleitus the Black (Greek: Κλεῖτος ὁ μέλας; c. 375 BC – 328 BC), was an officer of the Macedonian army led by Alexander the Great. He saved Alexander's life at the Battle of the Granicus in 334 BC and was killed by him in a drunken quarrel six years later.
Who defeated Xerxes?
In August 465 BC, Artabanus, the commander of the royal bodyguard and the most powerful official in the Persian court, assassinated Xerxes with the help of a eunuch, Aspamitres.
Who defeated king Darius?
Alexander the GreatThe Battle of Issus, in which Alexander the Great secured a decisive victory over Darius III of Persia.
Who defeated Alexander the Great?
Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath on Sunday (November 14) said that Chandragupta Maurya, who founded the Mauryan empire in the 4th century BC, had defeated Alexander of Macedon in battle — and yet, it is the latter whom historians have chosen to call “great”.
What was the Battle of Issus?
Full Article. Battle of Issus, (333 bce ), conflict early in Alexander the Great’s invasion of Asia in which he defeated a Persian army under King Darius III. This was one of the decisive victories by which Alexander conquered the Achaemenian Empire. Issus is a plain on the coast of the Gulf of İskenderun, in present-day southern Turkey.
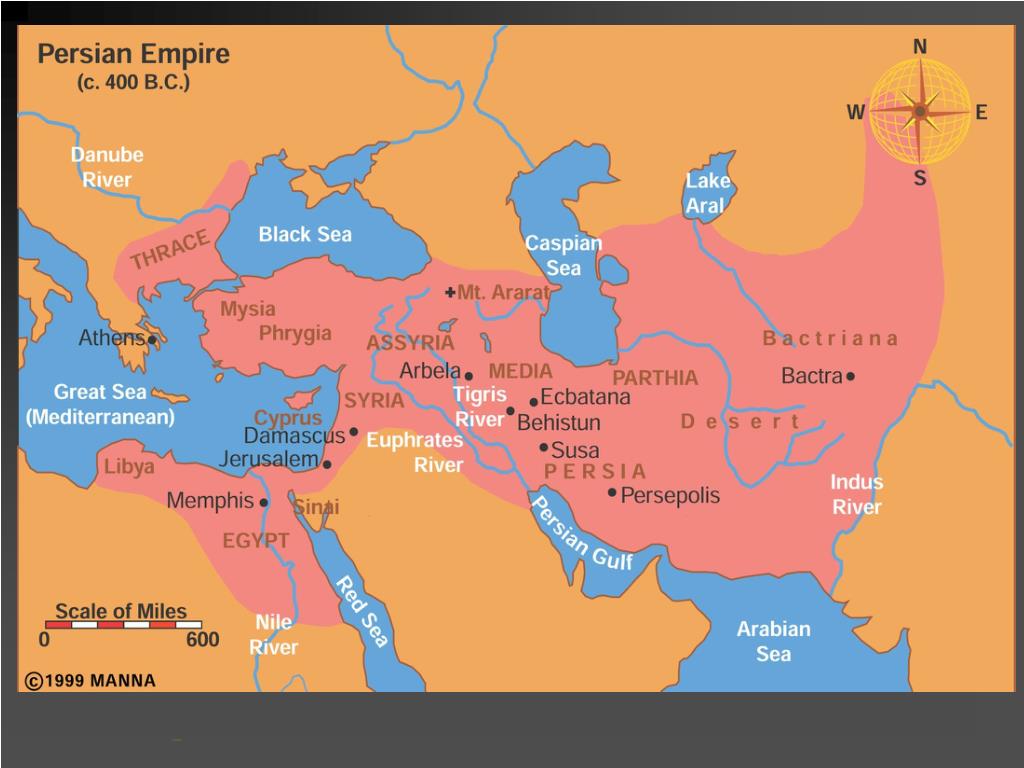
Which river was the army of Darius drawn up on?
The Macedonian forces, with an infantry phalanx in the centre and cavalry on the sides, approached the army of Darius, which was drawn up on the opposite bank of the Pinarus River (possibly present-day Yakacık Çayı or Deli Çayı).
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
What was Alexander the Great's first order of business?
After the death of his father and his ascension to the Macedonian throne, Alexander's first order of business was to pursue his father's dream, the conquest of the Persian Empire. Using the excuse that he was seeking revenge for the invasion of Greece by Darius I and Xerxes, Alexander crossed the Hellespont into Asia Minor. As he moved southward he defeated the Persian forces at Granicus and Halicarnassus. His next major confrontation would be at Issus in November 333 BCE. This battle would be the first of two meetings between Alexander the Great and King Darius of Persia; both would end in a defeat of the Persian forces.
How many battalions did Alexander have?
Alexander, on the other hand, was able to use his trusted phalanx formation. His right flank extended to the mountains and his left to the sea. He had three battalions on the right and four to the left with heavy infantry in the middle. After viewing Alexander's formation, Darius moved his cavalry to attack Alexander's right with hopes of breaking through his right flank. Although hampered by the river bank and stockades erected by Darius, Alexander and his Companion cavalry moved quickly through the Darius's left flank. Attempts to drive Alexander back across the Pinarus failed. Historian Arrian in his The Campaigns of Alexander said:
What flank did Darius attack?
After viewing Alexander's formation, Darius moved his cavalry to attack Alexander's right with hopes of breaking through his right flank. Although hampered by the river bank and stockades erected by Darius, Alexander and his Companion cavalry moved quickly through the Darius's left flank.
How many mercenaries did Darius have?
Basing her estimates on ancient sources, historian Ruth Sheppard has Darius with an estimated army of between 300,000 and 600,000 as well as 30,000 Greek mercenaries while more modern numbers are from 25,000 to 100,000 with only 10,000 Greek mercenaries.
Where did Darius move to?
Focusing on his rendezvous with Alexander, Darius moved north from Babylon to an area east of the Issus River.
What happened to Alexander's left flank?
Meanwhile, Alexander's left flank, under the leadership of Parmenion, was having problems with Darius's right. However, when the Persian forces saw their leader flee, they fled, too; many were trampled to death in the mass exit.
Where did Darius torture and execute the Macedonian soldiers?
Later, as Darius marched his troops to meet Alexander at the River Penarus, the Persian king stopped at the Greek base camp where he tortured and executed the recuperating Macedonian soldiers, cutting off the right hand of those who were allowed to live.
What did Alexander's men do to Darius' women?
At Issus, Alexander's men rewarded themselves richly with Persian loot. Darius' women at Issus were frightened. At best they could expect to become the concubine of a high-status Greek. Alexander reassured them. He told them not only was Darius still alive, but they would be kept safe and honored. Alexander kept his word and has been honored for this treatment of the women in Darius' family.
Why did Alexander go to a mountaintop?
At the reunion, Alexander rallied his troops and prepared for battle the following morning. Alexander went to a mountaintop to offer sacrifices to the presiding gods , according to Curtius Rufus. Darius' enormous army was on the other side of the Pinarus River, stretching from the Mediterranean Sea to foothills in an area too narrow to give an advantage to his numbers:
What was Alexander the Great's goal in the Battle of Issus?
Like his father Philip, the glory-seeking Alexander aimed to conquer the Persian Empire. Although greatly outnumbered, Alexander was a better tactician. The battle was bloody, Alexander suffered a thigh wound, and the Pinarus River was said to have run red ...
What was the name of the gate that Alexander was cut off from?
Worse, Alexander was cut off from most of his troops. "Darius crossed the mountain range by what are called the Amanic Gates, and advancing towards Issus, came without being noticed to the rear of Alexander.
What was Alexander's companion's role in the Persian invasion?
Alexander's Companion Cavalry headed across the river where they faced the Greek mercenary forces, veterans and some of the best of the Persian army. The mercenaries saw an opening in Alexander's line and rushed in. Alexander moved to gain the Persian's flank.
Was Memnon a bribe?
In "Upset at Issus" (Military History Magazine), Harry J. Maihafer says Memnon was not only astute militarily, but doled out bribes. A Greek, Memnon almost persuaded Sparta to back him. As Greeks, the Spartans should have been expected to support Alexander, but not all Greeks preferred rule by Alexander to rule by the king of Persia.
Where did Darius gather his troops?
Meanwhile, Darius' troops gathered in the plains east of the Amanus Mountains. Alexander led some of his troops to the Syrian Gates, where he expected Darius to pass, but his intelligence was flawed: Darius marched across another pass, to Issus.
Location
The battle took place south of the ancient town Issus, which is close to present-day Turkish town of Iskenderun (the Turkish equivalent of "Alexandria", founded by Alexander to commemorate his victory), on either side of a small river called Pinarus.
Battle
The Macedonians advanced through the Pillar of Jonah. Alexander led his Companion cavalry on the right flank and he set his Thessalian allied cavalry on the left of the phalanx with Parmenion in command.
Aftermath
The Battle of Issus was a decisive Macedonian victory and it marked the beginning of the end of Persian power. It was the first time the Persian army had been defeated with the King ( Darius III at the time) present.
Why did Alexander allow Darius to get away?
Darius was allowed to get away by Alexander as the left and central lines of his army were struggling to restrain the cavalry charges of the Persians. To help Alexander and his army pushed from the right into the Greek Hoplite mercenaries fighting for the Persians central line.
How did the Battle of Issus change the power of the Persian Empire?
The battle of Issus changed the power of the time as the Persian Empire entered a period of decline and Alexander the Great went on to enjoy many more victories in battle increasing the lands of his Empire.
What did Darius not know until he reached the River Pinarus?
What Darius did not know until he reached the River Pinarus was that Alexander had started marching north, here 7 miles from Issues on a narrow coastal plain the battle would occur.
Which armies formed a line with Alexander on the right of his and Parmenion on his left in support?
Both armies formed a line with Alexander on the right of his and Parmenion on his left in support. Darius was in the centre of his army.
What was the significance of the Battle of Issus?
As the battle ensued on November 5th 333 BC the tides of change that still reverberate around the world could be felt.
Who was the leader of the Persian army?
The Persian army saw that their esteemed leader of Darius III had fled the field of battle and knew they had lost so tried to flee the battlefield. The cavalry of Alexander followed the fleeing Persians and slaughtered thousands as they went.
Who was the leader of the Battle of Issus?
The Battle of Issus occurred in southern Anatolia, part of present day Turkey. The battle was fought between Alexander the Great and Darius III of Persia. What is interesting in this battle is that Alexander the Great (Alexander of Macedonia) took overall command of his army although did allow a war council to offer guidance. Darius III on the other hand had five commanders supporting him.
Alexander's Opponents
The Persian King
Alexander's Illness
- Alexander became seriously ill at Tarsus, a city in Cilicia that would later become the capital of that Roman province. While recovering, Alexander sent Parmenio to capture the harbor town of Issus and watch for Darius' approach into Cilicia with his perhaps 100,000 men. [Ancient sources say the Persian army had much more.]
Faulty Intelligence
- When Alexander recovered sufficiently, he rode to Issus, deposited the sick and wounded, and traveled on. Meanwhile, Darius' troops gathered in the plains east of the Amanus Mountains. Alexander led some of his troops to the Syrian Gates, where he expected Darius to pass, but his intelligence was flawed: Darius marched across another pass, to Issus. There the Persians mutil…
Battle Prep
- Alexander quickly led the men who had traveled with him back to the main body of the Macedonians and sent out scouting horsemen to learn exactly what Darius was up to. At the reunion, Alexander rallied his troops and prepared for battle the following morning. Alexander went to a mountaintop to offer sacrifices to the presiding gods, according to Curtius Rufus. Dari…
The Fighting
- Parmenio was in charge of the those of Alexander's troops deployed to the seaside of the battle line. He was enjoined not to let the Persians get around them, but to bend back, if necessary, and stick to the sea. Alexander stretched his troops parallel to the Persian forces: Alexander's Companion Cavalry headed across the river where they faced the Greek mercenary forces, veter…
The Aftermath
- At Issus, Alexander's men rewarded themselves richly with Persian loot. Darius' women at Issus were frightened. At best they could expect to become the concubine of a high-status Greek. Alexander reassured them. He told them not only was Darius still alive, but they would be kept safe and honored. Alexander kept his word and has been honored for th...