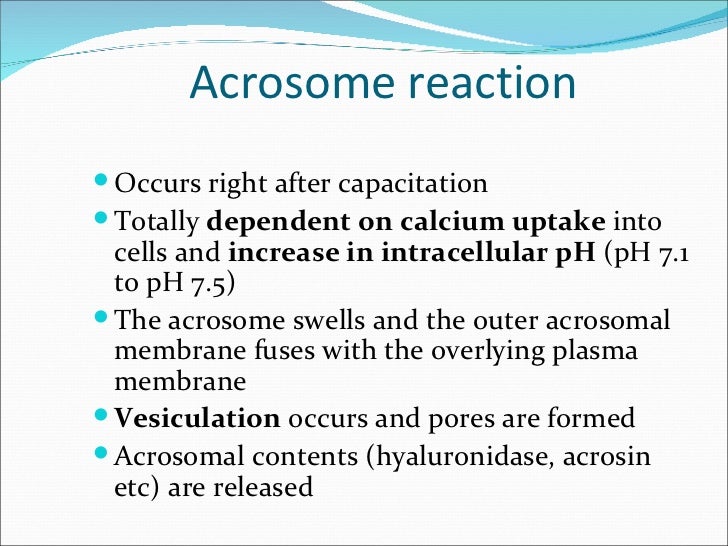
After the acrosome reaction, the exposed acrosome becomes the head of the spermatozoon. This is covered in the acrosome reaction by proteolytic enzymes. These digest a path through the zona pellucida
Zona pellucida
The zona pellucida is a glycoprotein layer surrounding the plasma membrane of mammalian oocytes. It is a vital constitutive part of the oocyte. The zona pellucida first appears in unilaminar primary oocytes. It is secreted by both the oocyte and the ovarian follicles. The zona pellucida is surrounded by the cumulus oophorus. The cumulus is composed of cells that care for the egg when it is emitted from th…
What are the steps in the acrosome reaction?
The acrosome reaction must occur before the sperm cell reaches the zona pellucida. Acrosin digests the zona pellucida and membrane of the oocyte. Part of the sperm's cell membrane then fuses with the egg cell's membrane, and the contents of the head sink into the egg.
What happens when sperm cells undergo the Acrosomal reaction?
This initiates a process called the acrosomal reaction in which the enzyme-filled “cap” of the sperm, called the acrosome, releases its stored digestive enzymes. These enzymes clear a path through the zona pellucida that allows sperm to reach the oocyte.
What is the role of acrosome reaction?
The acrosome reaction is a crucial step during gamete interaction in all species, including man. It allows spermatozoa to penetrate the zona pellucida and fuse with the oocyte membrane. Spermatozoa unable to undergo the acrosome reaction will not fertilize intact oocytes.
What are the 7 steps of fertilization?
In overview, fertilization can be described as the following steps:Sperm Capacitation. ... Sperm-Zona Pellucida Binding. ... The Acrosome Reaction. ... Penetration of the Zona Pellucida. ... Sperm-Oocyte Binding. ... Egg Activation and the Cortical Reaction. ... The Zona Reaction. ... Post-fertilization Events.
What are the 4 steps to fertilization?
The stages of fertilization can be divided into four processes: 1) sperm preparation, 2) sperm-egg recognition and binding, 3) sperm-egg fusion and 4) fusion of sperm and egg pronuclei and activation of the zygote.
Which enzyme is released by acrosome?
In higher mammals including humans, the acrosome releases two digestive enzymes, namely, hyaluronidase and acrosin. These two enzymes break down the outer membrane of the ovum, known as the zona pellucida. This facilitates the fusion of the sperm cell with the ovum.
Does acrosomal reaction prevent polyspermy?
Abstract: At fertilization, the acrosome reaction and cortical reaction are crucial process to block polyspermy and the prevention of triploidy.
What is the role of acrosome in human sperm?
The acrosome is a unique membranous organelle located over the anterior part of the sperm nucleus that is highly conserved throughout evolution. This acidic vacuole contains a number of hydrolytic enzymes that, when secreted, help the sperm penetrate the egg's coats.
What triggers the acrosome reaction in sperm?
AR-inducing activity of the purified ZP3 has been reported in many other mammalian species including humans [75]. ZP2, another zona glycoprotein of the mouse, is responsible for the binding of acrosome-reacted spermatozoa to ZP.
What are the 5 steps of plant reproduction?
There are the 5 stages of plant life cycle. The seed, germination, growth, reproduction, pollination, and seed spreading stages.
Can human sperm fertilize animals?
Their genomes are simply too different to come together and make something that will live. Their genomes cannot mix in any productive way. Imagine you take the instructions for making an airplane and instructions for making a curling iron and mix them together.
What is formed immediately after fertilization?
The result of fertilization is a cell (zygote) capable of undergoing cell division to form a new individual.
How does acrosome help a sperm cell?
The function of the acrosome reaction is to help the sperm get through the egg's protective coat and to allow the plasma membranes of the sperm and egg to fuse. This places both haploid nuclei (one from the sperm and one from the egg) into the same cell, where they form the diploid genome of the new organism.
What is the acrosomal reaction quizlet?
what is the acrosomal reaction? This reaction begins with the discharge of hydrolytic enzymes from the acrosome, a specialized vesicle at the tip of the sperm. These enzymes partially digest the jelly coat, enabling a sperm structure called the acrosomal process to elongate and penetrate the coat.
How does the acrosome help the sperm cell to carry out its function?
The acrosome in the head contains enzymes so that a sperm can penetrate an egg. The middle piece is packed with mitochondria to release energy needed to swim and fertilise the egg. The tail enables the sperm to swim.
What happens Spermiogenesis?
Spermiogenesis is the process by which haploid round spermatids complete an extraordinary series of events to become streamlined spermatozoa capable of motility. Spermiogenesis begins after spermatocytes complete 2 quick successive meiotic reductive divisions to produce haploid round spermatids.
What is the acrosome reaction?
As the sperm approaches the zona pellucida of the egg, which is necessary for initiating the acrosome reaction, the membrane surrounding the acrosome fuses with the plasma membrane of the sperm's head, exposing the contents of the acrosome. The contents include surface antigens necessary for binding to the egg's cell membrane, and numerous enzymes which are responsible for breaking through the egg's tough coating and allowing fertilization to occur.
Where is the trigger for the acrosome reaction?
In several species, the trigger for the acrosome reaction has been identified in a layer that surrounds the egg.
What is the process of sperm cells going through?
Therefore, sperm cells go through a process known as the acrosome reaction, which is the reaction that occurs in the acrosome of the sperm as it approaches the egg. The acrosome is a cap-like structure over the anterior half of the sperm's head. As the sperm approaches the zona pellucida of the egg, which is necessary for initiating ...
What happens to sperm during fertilization?
Acrosome reaction. During fertilization, a sperm must first fuse with the plasma membrane and then penetrate the female egg cell to fertilize it. Fusing to the egg cell usually causes little problem, whereas penetrating through the egg's hard shell or extracellular matrix can be more difficult. Therefore, sperm cells go through a process known as ...
What happens when sperm and oocytes meet?
Once the two meet, a calcium influx occurs, causing a signaling cascade. The cortical granules inside the oocyte then fuse to the outer membrane, and a quick fast block reaction occurs. It also alters a patch of pre-existing sperm plasma membrane so that it can fuse with the egg plasma membrane. A sperm penetration assay includes an acrosome ...
Why is it disputed that the acrosome reaction is initiated in physiological fertilization?
In humans, on the other hand, it remains disputed where exactly the acrosome reaction is initiated in physiological fertilization, due to experimental constraints (for example, animal studies may make use of transgenic mice with fluorescent sperm, while human studies cannot).
Where does the acrosomal reaction take place?
The process. The acrosomal reaction usually takes place in the ampulla of the fallopian tube (site of fertilization) when the sperm penetrates the secondary oocyte. A few events precede the actual acrosome reaction.
What Does Acrosome Reaction Mean?
The acrosomal reaction is the process of the egg and sperm cells fusing together during fertilization. Acrosomal reactions are an essential step of conception, and any abnormality can prevent fertilization and cause infertility.
Can acrosomal reaction cause infertility?
In some cases, the acrosomal reaction cannot occur, preventing fertilization from occurring. When the prevention is caused by health factors of the egg or sperm, it can lead to infertility. Complications of the acrosomal reaction include: Abnormal or missing acrosome.
What is the acrosome reaction?
The acrosome reaction that occurs after sperm capacitation, is an exocytotic event induced by a Ca++ influx. It plays an essential role during fertilization, by making spermatozoa able of penetrating the zona and capable of fusing with the egg plasma membrane.
What is the natural inducer of the acrosome reaction?
Zona pellucida is the natural inducer of the acrosome reaction. Binding of the sperm receptor to ZP3, a zona glycoprotein acting as ligand, triggers the molecular events leading to acrosomal exocytosis. G-proteins may be involved in the signal-transduction pathway during the acrosome reaction.
Does progesterone affect sperm?
Progesterone acts through a receptor on the sperm plasma membrane, while the ionophore promotes non-physiological sperm Ca++ uptake. Several cytochemical procedures have been proposed for evaluating the acrosome reaction: the acrosomal status can be observed after staining or after labeling with lectins or antibodies.
What is the acrosome reaction?
Acrosome reaction is a complex process which appear to be controlled by cross-talks between different pathways including the NO dependent pathway (Herrero and Gagnon, 2001).
Where does the acrosome reaction take place?
It is generally believed that the acrosome reaction of the fertilizing sperm must take place at or near the zona pellucida and that the natural stimulus for this event may involve molecules associated with the oocyte or its investments. Because acrosome reactions at other times or locations may render sperm infertile, prolonged acrosomal stability of sperm in vivo may ensure that sperm reaching the oocyte are competent to fertilize, regardless of their period of residence in the female tract.
How to stain acrosomes?
In general, fluorescent staining of acrosomes can be achieved by two methods: (1) using spermatozoa with alcohol-permeabilized plasma and acrosomal membranes,116,159 which allow fluorescent-labeled lectins to enter and stain intact acrosomes, or (2) using viable non-permeabilized spermatozoa . The ideal standard acrosomal stain is using fluorescently labeled agglutinins from peas (PSA) or peanut (PNA) plants. The most commonly used method to analyze acrosomal integrity is with a plant lectin labeled by a fluorescent probe (lectins conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate [FITC]). PNA ( Arachis hypogea agglutinin) is a lectin from the peanut plant that binds to β-galactose moieties, which are exclusively associated with the outer acrosomal membrane; thus, FITC-PNA (excitation/emission 488/515 nm wavelength) has been used successfully to determine the acrosomal status of acrosome-intact stallion sperm.115,116 PSA ( Pisum sativum agglutinin) is a lectin from the pea plant that binds to α-mannose and α-galactose moieties of the acrosomal matrix. Since PSA cannot penetrate an intact acrosomal membrane, only acrosome-reacted or damaged spermatozoa will stain, which is commonly assessed in combination with fluorescence microscopy. 113,117 Permeabilization of spermatozoal membranes has the disadvantage that acrosomal integrity and viability cannot be assessed simultaneously. However, PNA is believed to display less non-specific binding to other areas of the sperm, thus some laboratories favor this over PSA. FITC-PSA or FITC-PNA labeling of stallion spermatozoa is used in order to determine whether there is an association between the acrosome reaction and the incidence of subfertility in stallions. Acrosome-intact sperm will fluoresce evenly across the entire acrosomal cap. Under a fluorescent microscope, sperm in the process of acrosome reaction show patchy fluorescence over the acrosome, whereas those that have acrosome reacted most typically do not fluoresce or fluoresce only over the equatorial segment (see Fig. 6-6 ). Acrosome-intact and reacted sperm can be counted manually using a fluorescent microscope, or alternatively, flow cytometry can be used to count larger numbers of sperm.
What is the acrosomal reaction in amphibians?
The acrosome reaction in amphibians more closely resembles that of mammals, as fusion of the acrosomal vesicle and the sperm plasma membrane leads to exposure of the inner acrosomal membrane without formation of an acrosomal process (Ueda et al., 2007; Ueda, Yoshizaki, & Iwao, 2002 ). Most characterization of the AR-inducing substance in amphibians has been done in Xenopus laevis, belonging to Order Anura. Ueda et al. (2002) first identified this substance, ARISX, in extract from the pars recta (PRE) of the oviduct as well as the VE. Based on biochemical data, the AR-inducing activity of ARISX depends on a terminal α- d -GalNAc residue within its sugar chains and is not due to a protein constituent ( Ueda et al., 2007; Ueda, Kubo, & Iwao, 2003 ). In investigating its species-specificity, Ueda et al. (2007) discovered that ARISX from X. laevis PRE could induce the AR in anuran sperm from species in three other genera, as well as two urodelean species, but to lower, varying degrees (2–43% vs 63% in conspecific sperm). However, despite AR induction occurring in these cases, only Cynops pyrrhogaster sperm was able to enter the egg cytoplasm. Thus, while there is a degree of specificity in AR induction among amphibians, the inability of most AR-reacted sperm to fertilize heterospecific eggs implies the existence of other, currently unknown mechanisms that prevent cross-fertilization in amphibians.
How to determine acrosomal integrity?
Most methods available to assess acrosomal integrity are based on the use of dyes or fluorescent markers. These methods are inadequate for evaluating the existence of primary acrosomal defects (e.g., knobbed acrosomes). Intact acrosomes will be labeled with the acrosome-specific dye or fluorophore, whereas sperm with reacted acrosomes will not; this relationship could be determined either by microscopical counting or, in the case of fluorophores, by using a flow cytometer. 112,133
Why is the acrosome reacting ability important?
Thus, determining the acrosome reacting ability is important in the diagnostic and therapeutic approach to couples undergoing conventional assisted reproductive technology treatment. In cases of a poor acrosome reaction, ICSI therapy may be advised. Unfortunately, since most centers indicate ICSI as primary ART procedure, the AR assay is rarely used.
How long to incubate A23187?
Add 10 μM of A23187 calcium ionophore (alternative: zona pellucida) and incubate for 15 min to induce acrosome reaction.
Overview
During fertilization, a sperm must first fuse with the plasma membrane and then penetrate the female egg cell to fertilize it. Fusing to the egg cell usually causes little problem, whereas penetrating through the egg's hard shell or extracellular matrix can be more difficult. Therefore, sperm cells go through a process known as the acrosome reaction, which is the reaction that occurs in the acrosome of …
Variations among species
There are considerable species variations in the morphology and consequences of the acrosome reaction. In several species, the trigger for the acrosome reaction has been identified in a layer that surrounds the egg.
In some lower animal species, a protuberance (the acrosomal process) forms at the apex of the sperm head, supported by a core of actin microfilaments. The membrane at the tip of the acroso…
The process
The acrosomal reaction usually takes place in the ampulla of the fallopian tube (site of fertilization) when the sperm penetrates the secondary oocyte. A few events precede the actual acrosome reaction. The sperm cell acquires a "hyperactive motility pattern" by which its flagellum produces vigorous whip-like movements that propel the sperm through the cervical canal and uterine cavity until it reaches the isthmus of the fallopian tube. The sperm approaches the ovum in the ampull…
Spontaneous acrosome reaction
Spermatozoa can initiate the acrosomal reaction well in advance of reaching the zona pellucida, as well as in vitro in an appropriate culture medium. This is referred to as spontaneous acrosome reaction (SAR).
It is now known that in a certain sense, this phenomenon is physiologically normal across mammalian species. The acrosome reaction is induced by passage through the cumulus oophor…
In in vitro fertilization
When using intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) for IVF, the implantation rate is higher in oocytes injected with spermatozoa that have undergone acrosome reaction (~40%) vs. those injected with nonreacted spermatozoa (~10%). The implantation rate is ~25% in when injected with both reacted and nonreacted spermatozoa. The delivery rate per cycle follows the same trend.
The acrosome reaction can be stimulated in vitro by substances a sperm cell may encounter nat…
See also
• Cortical reaction
• Hamster zona-free ovum test
• ZP3
External links
• Acrosome+reaction at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
• Nosek, Thomas M. "Section 5/5ch8/s5ch8_21". Essentials of Human Physiology. Archived from the original on 2016-03-24.
• Animation at stanford.edu