The purpose of DNA replication is the creation of accurate copies of DNA in a cell. After replication is complete, the cell divides, forming to two identical daughter cells. This process is important for the replacement of damaged or dead cells as well as for the proper formation of gametes needed for fertility.
What are the five steps of DNA replication?
What are the five steps of DNA replication? The viral replication involves five steps. They are : 1. Attachment 2. Penetration 3. Uncoating 4.Replication, transcription and translation, 5. Assembly and Release from host cell. What is the correct order for DNA replication? DNA replication steps.
When is it necessary for DNA to replicate itself?
What are two reasons your body would replicate its DNA? DNA replication needs to occur because existing cells divide to produce new cells. Each cell needs a full instruction manual to operate properly. So the DNA needs to be copied before cell division so that each new cell receives a full set of instructions!
What is the first step in the process of DNA replication?
What are the 4 steps of replication?
- Replication Fork Formation Before DNA can be replicated, the double stranded molecule must be “unzipped” into two single strands. ...
- Primer Binding The leading strand is the simplest to replicate. ...
- Elongation Enzymes known as DNA polymerases are responsible creating the new strand by a process called elongation. ...
- Termination
What are the steps to DNA replication?
DNA replication occurs in a series of five steps: initiation at the origin of replication, unwinding to expose the strands, synthesis on both strands with many enzymes adding nucleotides 3′ to 5′, lengthening by RNA primers, and separation into two complete molecules.

Why Replicate DNA?
DNA, found within the nucleus, must be replicated in order to ensure that each new cell receives the correct number of chromosomes. The process of DNA duplication is called DNA replication. Replication follows several steps that involve multiple proteins called replication enzymes and RNA. In eukaryotic cells, such as animal cells and plant cells, DNA replication occurs in the S phase of interphase during the cell cycle. The process of DNA replication is vital for cell growth, repair, and reproduction in organisms.
What are the steps of DNA replication?
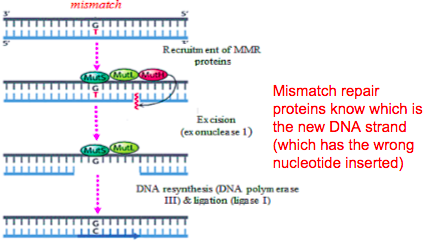
DNA replication would not occur without enzymes that catalyze various steps in the process. Enzymes that participate in the eukaryotic DNA replication process include: 1 DNA helicase - unwinds and separates double stranded DNA as it moves along the DNA. It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in DNA. 2 DNA primase - a type of RNA polymerase that generates RNA primers. Primers are short RNA molecules that act as templates for the starting point of DNA replication. 3 DNA polymerases - synthesize new DNA molecules by adding nucleotides to leading and lagging DNA strands. 4 Topoisomerase or DNA Gyrase - unwinds and rewinds DNA strands to prevent the DNA from becoming tangled or supercoiled. 5 Exonucleases - group of enzymes that remove nucleotide bases from the end of a DNA chain. 6 DNA ligase - joins DNA fragments together by forming phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides.
How does lagging DNA work?
The lagging strand begins replication by binding with multiple primers. Each primer is only several bases apart. DNA polymerase then adds pieces of DNA, called Okazaki fragments, to the strand between primers. This process of replication is discontinuous as the newly created fragments are disjointed.
How many bases are needed for DNA replication?
Before DNA can be replicated, the double stranded molecule must be “unzipped” into two single strands. DNA has four bases called adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G) that form pairs between the two strands. Adenine only pairs with thymine and cytosine only binds with guanine. In order to unwind DNA, these interactions between base pairs must be broken. This is performed by an enzyme known as DNA helicase. DNA helicase disrupts the hydrogen bonding between base pairs to separate the strands into a Y shape known as the replication fork. This area will be the template for replication to begin.
What phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur?
In eukaryotic cells, such as animal cells and plant cells, DNA replication occurs in the S phase of interphase during the cell cycle. The process of DNA replication is vital for cell growth, repair, and reproduction in organisms.
What is DNA made of?
It consists of a 5-carbon deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. Double-stranded DNA consists of two spiral nucleic acid chains that are twisted into a double helix shape. This twisting allows DNA to be more compact.
Why is DNA packed into chromatin?
In order to fit within the nucleus, DNA is packed into tightly coiled structures called chromatin. Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes during cell division. Prior to DNA replication, the chromatin loosens giving cell replication machinery access to the DNA strands.
How does DNA replication work?
And we start out from a single cell and we end up with trillions of cells. And during that process of cell division, all of the information in a cell has to be copied, and it has to be copied perfectly. And so DNA is a molecule that can be replicated to make almost perfect copies of itself. Which is all the more amazing considering that there are almost three billion base pairs of DNA to be copied. And replication uses DNA polymerases which are molecules specifically dedicated to just copying DNA. Replicating all of the DNA in a single human cell takes several hours of just pure copying time. At the end of this process, once the DNA is all replicated, the cell actually has twice the amount of DNA that it needs, and the cell can then divide and parcel this DNA into the daughter cell, so that the daughter cell and the parental cell in many case are absolutely genetically identical.
What happens to DNA at the end of the process?
At the end of this process, once the DNA is all replicated, the cell actually has twice the amount of DNA that it needs, and the cell can then divide and parcel this DNA into the daughter cell, so that the daughter cell and the parental cell in many case are absolutely genetically identical. Lawrence C. Brody, Ph.D.
What is the process by which a molecule of DNA is duplicated?
DNA Replication . DNA replication is the process by which a molecule of DNA is duplicated.
Can DNA be replicated?
And so DNA is a molecule that can be replicated to make almost perfect copies of itself. Which is all the more amazing considering that there are almost three billion base pairs of DNA to be copied. And replication uses DNA polymerases which are molecules specifically dedicated to just copying DNA.