Divergent Plate Boundaries
- Mid-Ocean Ridges. At oceanic divergent boundaries, new lithosphere is born hot and cools over millions of years. ...
- Iceland. At over 10,000 miles, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge is the longest mountain chain in the world, stretching from the Arctic to just above Antarctica.
- Continental Spreading. ...
- String Cheese and Moving Rifts. ...
What forms as a result when a divergent boundary happens?
When a divergent boundary occurs on land, it leads to the formation of a valley known as a rift. One example of a divergent boundary that is occurring on land is the Great Rift Valley. This divergent boundary is pulling the continent of Africa in two different directions.
What occurs at divergent boundaries and creates new seafloor?
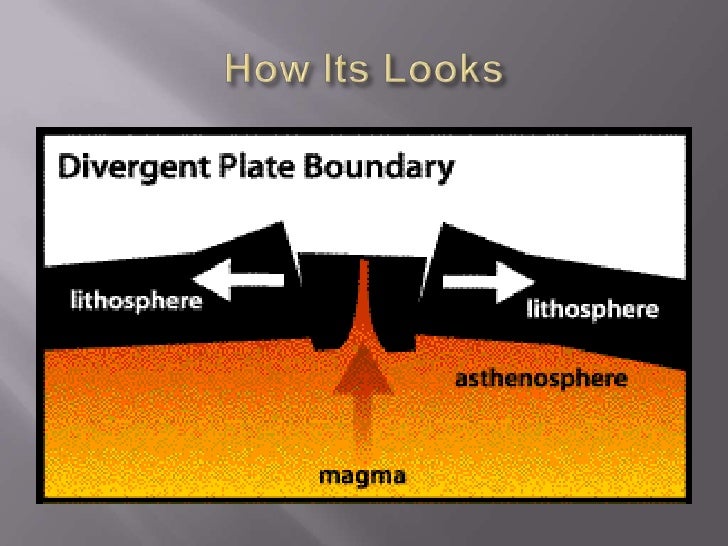
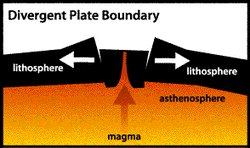
Seafloor Spreading is the usual process at work at divergent plate boundaries, leading to the creation of new ocean floor. As two tectonic plates slowly separate, molten material rises up from within the mantle to fill the opening. In this way the rugged volcanic landscape of a mid-ocean ridge is created along the plate boundary.
What is created along a divergent boundary?
New crust is formed at divergent boundaries on the ocean floor where the lithosphere is thin. Magma from the upper mantle presses against the plate, pushing it upward, then flows off in opposite directions at the plate. The plate, constructed of brittle lithosphere rock, is stretched by the movement of the convection and soon cracks.
What are formed at divergent and converging boundaries?
- There are three main types of plate boundaries:
- Convergent boundaries: where two plates are colliding.
- Divergent boundaries – where two plates are moving apart.
- Transform boundaries – where plates slide passed each other.
What are 3 things that are formed at a divergent boundary?
Most divergent plate boundaries are underwater and form submarine mountain ranges called oceanic spreading ridges. While the process of forming these mountain ranges is volcanic, volcanoes and earthquakes along oceanic spreading ridges are not as violent as they are at convergent plate boundaries.
What is formed at a divergent plate boundary?
A divergent plate boundary often forms a mountain chain known as a ridge. This feature forms as magma escapes into the space between the spreading tectonic plates.
What features are created from divergent?
Opposite of a convergent boundary, a divergent boundary is formed by the spreading of a tectonic plate. This process feeds magma to the surface, creating new crust. Divergent zones in oceanic plates form a geological feature called a ridge, forced upward by the pressure of the rising magma.
Do earthquakes occur at divergent boundaries?
Shallow, low-magnitude earthquakes commonly occur at divergent plate boundaries. Earthquakes at divergent plate boundaries are distributed with predictable locations and depths. Earthquakes at divergent plate boundaries occur as new crust is created and other crust is pushed apart.
Where are divergent boundaries found?
The vast majority of divergent boundaries are found in the ocean, where they were not mapped or understood until the mid-to-late 20th century.
Where does divergence occur?
Divergence happens in the continental setting too—that's how new oceans form. The exact reasons as to why it happens where it does, and how it happens, are still being studied. The best example on Earth today is the narrow Red Sea, where the Arabian plate has pulled away from the Nubian plate.
Why do divergent zones take the form of long, wide swells running along the ocean floor?
As it cools it shrinks, thus the fresh seafloor stands higher than the older lithosphere on either side. This is why divergent zones take the form of long, wide swells running along the ocean floor: mid-ocean ridges. The ridges are only a few kilometers high but hundreds wide.
Why do ridges have steeper sides?
Slow-spreading ridges like the Mid-Atlantic Ridge have steeper-sloping sides because it takes less distance for their new lithosphere to cool. They have relatively little magma production so that the ridge crest can develop a deep dropped-down block, a rift valley, at its center.
What is the slope of a ridge?
The ridges are only a few kilometers high but hundreds wide. The slope on the flanks of a ridge means that diverging plates get an assist from gravity, a force called "ridge push" that, together with slab pull, accounts for most of the energy driving the plates. On the crest of each ridge is a line of volcanic activity.
What is the main force driving plate motion?
In divergent zones, the plates are pulled, and not pushed, apart. The main force driving this plate motion (although there are other lesser forces) is the "slab pull" that arises when plates sink into the mantle under their own weight at subduction zones.
What happens when you move your hands apart?
If you move your hands apart, both at the same speed, the "rift" in the cheese stays put. If you move your hands at different speeds—which is what the plates generally do—the rift moves too. This is how a spreading ridge can migrate right into a continent and vanish, as is happening in western North America today.
What happens when a divergent boundary occurs?
When a divergent boundary occurs beneath oceanic lithosphere, the rising convection current below lifts the lithosphere, producing a mid-ocean ridge. Extensional forces stretch the lithosphere and produce a deep fissure. When the fissure opens, pressure is reduced on the super-heated mantle material below.
How does a divergent boundary occur?
When a divergent boundary occurs beneath a thick continental plate, the pull-apart is not vigorous enough to create a clean , single break through the thick plate material. Here the thick continental plate is arched upwards from the convection current's lift, pulled thin by extensional forces, and fractured into a rift-shaped structure. As the two plates pull apart, normal faults develop on both sides of the rift, and the central blocks slide downwards. Earthquakes occur as a result of this fracturing and movement. Early in the rift-forming process, streams and rivers will flow into the sinking rift valley to form a long linear lake. As the rift grows deeper it might drop below sea level, allowing ocean waters to flow in. This will produce a narrow, shallow sea within the rift. This rift can then grow deeper and wider. If rifting continues, a new ocean basin could be produced.
How do earthquakes occur?
Earthquakes occur as a result of this fracturing and movement. Early in the rift-forming process, streams and rivers will flow into the sinking rift valley to form a long linear lake. As the rift grows deeper it might drop below sea level, allowing ocean waters to flow in.
What are the effects of a rift valley?
Effects that are found at this type of plate boundary include: a rift valley sometimes occupied by long linear lakes or a shallow arm of the ocean; numerous normal faults bounding a central rift valley; shallow earthquake activity along the normal faults. Volcanic activity sometimes occurs within the rift.
What type of boundary is the Mid Atlantic Ridge?
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a classic example of this type of plate boundary. The Ridge is a high area compared to the surrounding seafloor because of the lift from the convection current below. A frequent misconception is that the Ridge is a build-up of volcanic materials; however, the magma that fills the fissure does not flood extensively over ...
What is divergent plate boundary?
Divergent plate boundaries are locations where plates are moving away from one another. This occurs above rising convection currents. The rising current pushes up on the bottom of the lithosphere, lifting it and flowing laterally beneath it. This lateral flow causes the plate material above to be dragged along in the direction of flow.
Where is the Mid Atlantic Ridge?
Two locations are marked: 1) the Mid-Atlantic Ridge exposed above sea level on the island of Iceland, and 2) the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Africa. Effects that are found at a divergent boundary between oceanic plates include: a submarine mountain range such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge; volcanic activity in the form ...
