Mutations summary table
| Mutation | Description |
| Missense | Mistake in the DNA code, one of the DNA ... |
| Nonsense | Single change in DNA code produces stop ... |
| Insertion | Addition of one (or more) nucleotide bas ... |
| Deletion | A piece of DNA is removed from the seque ... |
What does missense mutation mean and how is it caused?
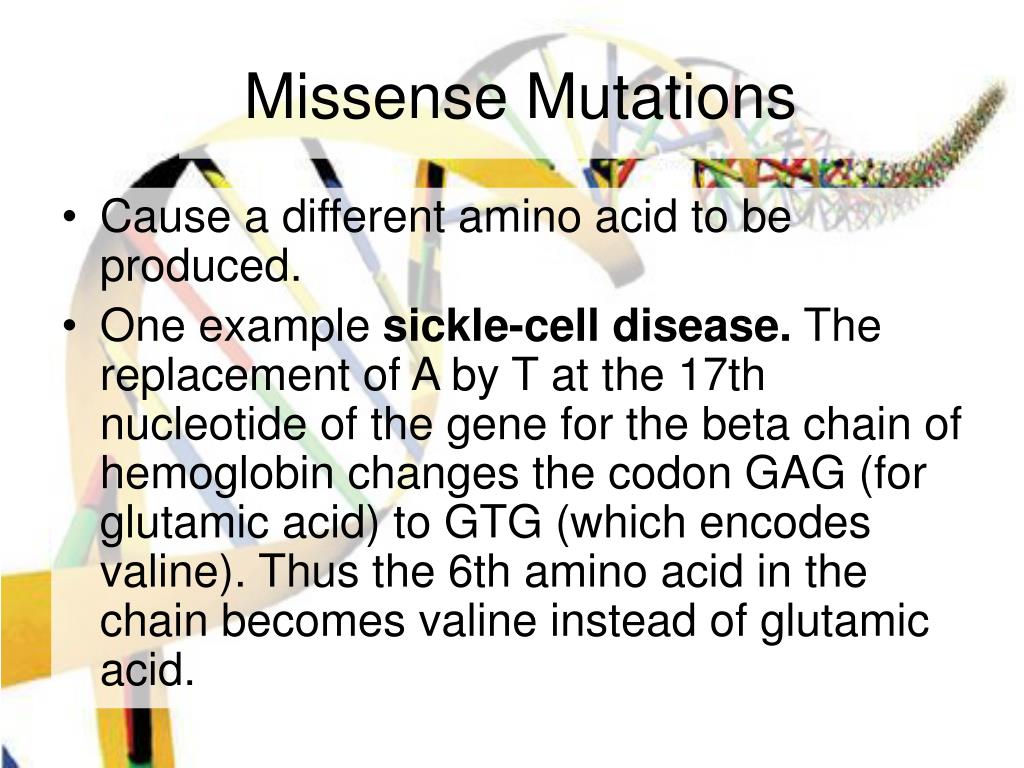
The missense mutation which causes all of this is the difference of one nucleotide. It is first translated into mRNA, then into a protein. The missense mutation causes a valine to be placed where a glutamic acid normally goes. This non-conservative missense mutation causes the shape of the protein, hemoglobin, to change.
What does a missense mutation look like?
Nonsense Mutation A nonsense mutation is the substitution of a single base pair that leads to the appearance of a stop codon where previously there was a codon specifying an amino acid. The presence of this premature stop codon results in the production of a shortened, and likely nonfunctional, protein.
How does missense and nonsense mutation differ?
What is a Mutation?
- Missense Mutations. What is a missense mutation? Missense mutations are mutations that change the amino acid sequence of a protein.
- Nonsense Mutations. Nonsense mutations are mutations that introduce a stop codon into the amino acid sequence prematurely.
- Silent Mutations. Which type of mutation has no effect on phenotype? ...
Is mutation always harmful for human body?
They have no effect on the phenotype. That most mutations are harmful is a creationist myth. Second, “beneficial” or “harmful” are in relation to the environment. Only about 2.6 per thousand mutations are absolutely harmful; they cause the death or significant harm to the organism.
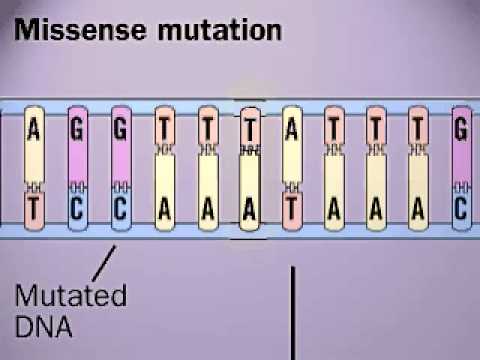
What happens in missense mutations?
A genetic alteration in which a single base pair substitution alters the genetic code in a way that produces an amino acid that is different from the usual amino acid at that position. Some missense variants (or mutations) will alter the function of the protein.
During which process do missense mutations occur?
A missense mutation occurs when a change in the DNA sequence results in the substitution of a different amino acid in the protein. A nonsense mutation occurs when a change in the DNA sequence leads to a stop codon, resulting in the termination of translation and truncation of the protein.
What occurs in a missense mutation quizlet?
A missense mutation is a gene mutation in which a base-pair change in the DNA causes a change in an mRNA codon so that a different amino acid is inserted into the polypeptide.
What is an example of missense mutation?
A common and well-known example of a missense mutation is sickle-cell anemia, a blood disease. People with sickle-cell anemia have a missense mutation at a single point in the DNA. This missense mutation calls for a different amino acid, and affects the overall shape of the protein produced.
Which two statements describe missense mutations?
Which two statements correctly describe missense mutations? Effects range from no change to complete loss of normal gene function. They involve a single base substitution that changes a codon for one amino acid into another.
What is the meaning of missense?
Definition of missense : relating to or being a gene mutation involving alteration of one or more codons so that different amino acids are determined — compare antisense, nonsense.
What is the difference between a missense mutation and a nonsense mutation?
The main difference between nonsense and missense mutation is that the nonsense mutation introduces a stop codon to the gene sequence, leading to premature chain termination whereas the missense mutation introduces a distinct codon to the gene sequence, not a stop codon, leading to a non-synonymous amino acid in the ...
What is the difference between a missense mutation and a nonsense mutation quizlet?
missense mutations change the sequence and meaning of an mRNA codon, resulting in a different amino acid. A nonsense mutation changes the codon to a stop codon.
What is the difference between a missense mutation and a silent mutation?
Nucleotide substitutions may lead to no change in the protein sequence (known as silent mutations), change the amino acid sequence (known as missense mutations), or create a stop codon (known as a nonsense mutation).
Which of the following statement is correct about missense mutation?
Answer and Explanation: The statement that is true for missense mutations is: A. A missense mutation always causes a change in the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein.
What is another name for missense mutation?
nonsynonymous substitutionA missense mutation is a nucleotide base substitution mutation that results in new amino acid, also known as nonsynonymous substitution.
How does A missense mutation cause sickle cell?
Proteins are long strings of fragments called “amino acids.” Mutation of a single nucleotide on the HBB gene causes a single amino acid mutation on the beta-globin protein. This is an example of a “missense mutation.” Sickle hemoglobin, also called hemoglobin S (HbS), is the most common form of abnormal hemoglobin.
Do missense mutations occur in genes encoding tRNA?
Yes they do. they occur in genes encoding tRNA. The altered tRNA is called suppressor tRNA.
What type of mutation occurs in sickle cell anemia?
Sickle cell disease is caused by a mutation in the hemoglobin-Beta gene found on chromosome 11. Hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. Red blood cells with normal hemoglobin (hemoglobin-A) are smooth and round and glide through blood vessels.
When would a point mutation occur?
A point mutation occurs in a genome when a single base pair is added, deleted or changed. While most point mutations are benign, they can also have various functional consequences, including changes in gene expression or alterations in encoded proteins.
How are mutations prevented during DNA replication?
The errors of DNA replication can be corrected by two mechanisms known as proofreading and strand-directed mismatch repair. Proofreading is carried out by DNA polymerase itself during the DNA synthesis. The strand-directed mismatch repair is carried out by Mut proteins just after the DNA replication.
What is a missense mutation?
A missense mutation is an alteration in the DNA that results in a different amino acid being incorporated into the structure of a protein. At a mol...
What is the difference between a nonsense mutation and a missense mutation?
Nonsense mutations replace an amino acid codon with an early stop codon, which prematurely signals the ribosome to stop building a protein. Unlike...
What causes a missense mutation?
Missense mutations can happen spontaneously or be induced by various kinds of mutagens. Mutagens include physical agents, like UV rays and chemical...
What conditions are caused by a missense mutation?
The most common condition associated with a missense mutation is sickle cell disease, also known as drepanocytosis. With sickle cell disease, the h...
What are the most important facts to know about a missense mutation?
A missense mutation is an alteration in the DNA sequence that results in a different amino acid being incorporated into the structure of a protein....
Why is Sickle Cell a missense mutation?
Sickle Cell anemia is a missense mutation because a point mutation in the beta-globin leads to a valine being added to the protein instead of a glu...
What is difference between missense and nonsense mutation?
A missense mutation occurs when a change in the DNA sequence results in the substitution of a different amino acid in the protein. A nonsense mutat...
How do you know if a mutation is missense?
A missense mutation is identified by a sequence change in the codon that results in a different amino acid being added during translation.
What is missense mutation?
A missense mutation is a type of point mutation in which a different amino acid is placed within the produced protein, other than the original. In the process of converting DNA into protein, the language of DNA must be translated into the language of proteins. During this process, a change in the structure of DNA, or a mutation, can change the sequence of amino acids which creates a protein. If it does not change the structure or function of the protein, it may be considered a silent mutation. If it does change the protein, it is considered a missense mutation.
How does a missense mutation affect the function of a protein?
This type of missense mutation can greatly change the function of a protein, as it will likely change the shape and structure of the protein. Proteins have various levels of structure, all which depend upon the DNA. If a missense mutation changes an amino acid, it first changes the primary structure, or the basic sequence of amino acids.
What are some examples of missense mutations?
A common and well-known example of a missense mutation is sickle- cell anemia, a blood disease. People with sickle-cell anemia have a missense mutation at a single point in the DNA. This missense mutation calls for a different amino acid, and affects the overall shape of the protein produced. This, in turn, causes the entire shape of blood cells to be different. People with the disease experience symptoms of not being able acquire oxygen efficiently, and experience blood clotting. However, they are partially protected from blood borne parasites which live in blood cells. Malaria is a disease caused by these parasites, and people with sickle-cell anemia have an inherent defense against the parasite. Their sickle-shaped blood cells cannot support the life cycle of the parasite.
What happens when a missense mutation changes an amino acid?
If a missense mutation changes an amino acid, it first changes the primary structure, or the basic sequence of amino acids. The secondary structure of proteins consists of patterns and structures formed by interactions between these amino acids.
What happens when a mutation calls for the same amino acid as before the mutation?
If a mutation calls for the same amino acid as before the mutation, it is considered silent. On the other hand, several other codons also call for signals to stop and process the protein. In this case, instead of adding an amino acid, the sequence is ended and the protein is ejected from the ribosome.
How many amino acids are in a point mutation?
The DNA is read in units of three, called codons. These codons call for one of 21 amino acids, which the ribosome complex will assemble in order by reading the messenger RNA, or mRNA. If there are 3 spots in a codon, and 4 possible nucleotides to go in that spot, the codons can call for 64 different signals. Since there are only 21 amino acids, many of these codons call for the same amino acid. If a mutation calls for the same amino acid as before the mutation, it is considered silent.
What happens when a mutation does not change the structure of a protein?
If it does not change the structure or function of the protein, it may be considered a silent mutation. If it does change the protein, it is considered a missense mutation. Point mutations.
What causes a missense mutation?
Missense mutations can happen spontaneously or be induced by various kinds of mutagens. Mutagens include physical agents, like UV rays and chemical molecules, as well as bi ological agents, like certain viruses.
What are the most important facts to know about a missense mutation?
A missense mutation is an alteration in the DNA sequence that results in a different amino acid being incorporated into the structure of a protein. Depending on which amino acid it codes for, missense mutations can be conservative (i.e., the resulting protein is functional) or nonconservative (i.e., the resulting protein is non-functional).
What is the difference between a nonsense mutation and a missense mutation?
Nonsense mutations replace an amino acid codon with an early stop codon, which prematurely signals the ribosome to stop building a protein. Unlike missense mutations, nonsense mutations almost always have serious consequences.
How to think about missense mutations?
A good way to think about missense mutations is to imagine you have a sentence in which one letter was changed and the entire meaning was also changed. For example, 'I have a cat' is like your normal DNA sequence. If for some reason the 'c' was changed to an 'r', now you have 'I have a rat'. This new sentence has a very different meaning than the original. The same is true of missense mutations because the new DNA sequence will code for a different amino acid.
What is the disease called when you have a missense mutation?
While people with sickle-cell disease show many symptoms, such as pain and fatigue, this disease is caused by only a single change in a DNA sequence. You can learn more about this kind of change, called a missense mutation, in this lesson.
What is a mutation in DNA?
A mutation is a permanent change in a DNA sequence. DNA is the unit of heredity of all organisms. A missense mutation occurs when one DNA nucleotide is changed so that a different amino acid is inserted into a protein. Nucleotides are the repeating units of a DNA sequence. There are four nucleotides, each with different nitrogenous bases: thymine ...
What happens when a mutation is made in a DNA molecule?
When a missense mutation occurs in a DNA molecule, it changes one of the RNA codon sequences made during transcription. This different codon will then cause a different amino acid to be inserted into a protein during translation. Proteins made when missense mutations occur may look very different and may not even be functional.
Is mutation bad for you?
DNA is the unit of heredity of all organisms, so this means that mutations can often be passed on to offspring. You probably associate the word mutation with something that is bad, but mutations don't have to be bad. Some are beneficial, and some can have no effect. There are many different categories of mutations, ...
What is missense mutation?
Missense mutation refers to a change in one amino acid in a protein, arising from a point mutation in a single nucleotide. Missense mutation is a type of nonsynonymous substitution in a DNA sequence. Two other types of nonsynonymous substitution are ...
What are the diseases caused by missense mutations?
Missense mutations can render the resulting protein nonfunctional, and such mutations are responsible for human diseases such as Epidermolysis bullosa, sickle-cell disease, and SOD1 mediated ALS.
What mutation is c.1580G>T?
LMNA missense mutation (c.1580G>T) introduced at LMNA gene – position 1580 (nt) in the DNA sequence (CGT) causing the guanine to be replaced with the thymine, yielding CTT in the DNA sequence. This results at the protein level in the replacement of the arginine by the leucine at the position 527. This leads to destruction of salt bridge and structure destabilization. At phenotype level this manifests with overlapping mandibuloacral dysplasia and progeria syndrome .
When an amino acid may be encoded by more than one codon (so-called "degener answer?
When an amino acid may be encoded by more than one codon (so-called "degenerate coding") a mutation in a codon may not produce any change in translation; this would be a synonymous substitution and not a missense mutation.
Can a missense mutation cause a protein to change?
Not all missense mutations lead to appreciable protein changes. An amino acid may be replaced by an amino acid of very similar chemical properties, in which case, the protein may still function normally; this is termed a neutral, "quiet", "silent" or conservative mutation. Alternatively, the amino acid substitution could occur in a region ...
What is a missense mutation?
A missense mutation occurs when there is a mistake in the DNA code and oneof the DNA base pairs is changed, for example, A is swapped for C.
What is the result of a deletion mutation?
Addition or deletion mutation results in a change to a gene's reading frame
What is frameshift mutation?
A frameshift mutationoccurs when the aforementioned "addition" or "deletion" mutations result in a change to the gene's reading frame, which includes groups of three bases that encode for an amino acid. The change in the reading frame alters the grouping of the bases and subsequently changes the amino acids that are encoded. Often, the encoded protein is non-functional.
What happens when DNA is removed from a sequence?
As the title may suggest, a deletion mutation occurs when there a piece of DNA is removed from the sequence. The size of the DNA that is removed can vary in length, from a single base pair to an entire gene or several consecutive genes. The removal of the DNA can, again, compromise the function of the encoded protein.
What is genetic mutation?
A genetic mutation is a permanentchange to the nucleotide sequence of a gene. More often than not, such genetic mutations are advantageous – they enable evolution and produce new desirable traits in organisms.
What is a mistake in DNA code?
Mistake in the DNA code, one of the DNA base pairs is changed
Can genetic mutations cause disease?
However, genetic mutations can also be problematic if they result in a disease. In humans, genetic disorders are often life-limiting and incredibly tricky to treat.
