
Overview of the Stages of Meiosis
- Interphase. There are two stages or phases of meiosis: meiosis I and meiosis II. ...
- Prophase I. Chromosomes condense and attach to the nuclear envelope. ...
- Metaphase I. Tetrads align at the metaphase plate. ...
- Anaphase I. Chromosomes move to the opposite cell poles. ...
- Telophase I. ...
- Prophase II. ...
- Metaphase II. ...
- Anaphase II. ...
- Telophase II. ...
- Stages of Meiosis: Daughter Cells. ...
What are the 10 stages of meiosis?
Meiosis consists of two divisions, both of which follow the same stages as mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) Meiosis is preceded by interphase, in which DNA is replicated to produce chromosomes consisting of two sister chromatids. A second growth phase called interkinesis may occur between meiosis I and II, however no DNA ...
What are the five steps of meiosis?
- Interphase 1 (definition) Chromosomes are in a threadlike form.
- Prophase 1 (definition) Each chromosome is made up of 2 chromatids.
- Metaphase 1 (definition)
- Anaphase 1 (definition)
- Telophase 1 (definition)
- Cytokinesis 1 (definition)
- Prophase 2 (definition)
- Metaphase 2 (definition)
What occurs during the different stages of meiosis?
What are the 8 stages of meiosis in order?
- prophase I. the chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase I. pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase I.
- Telophase I and Cytokinesis.
- Prophase II.
- Metaphase II.
- Anaphase II.
- Telophase II and Cytokinesis.
What is the Order of events in meiosis?
What are the stages of meiosis in order?
- Prophase I. The chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase I. Pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase I.
- Telophase I and Cytokinesis.
- Prophase II.
- Metaphase II.
- Anaphase II.
- Telophase II and Cytokinesis.
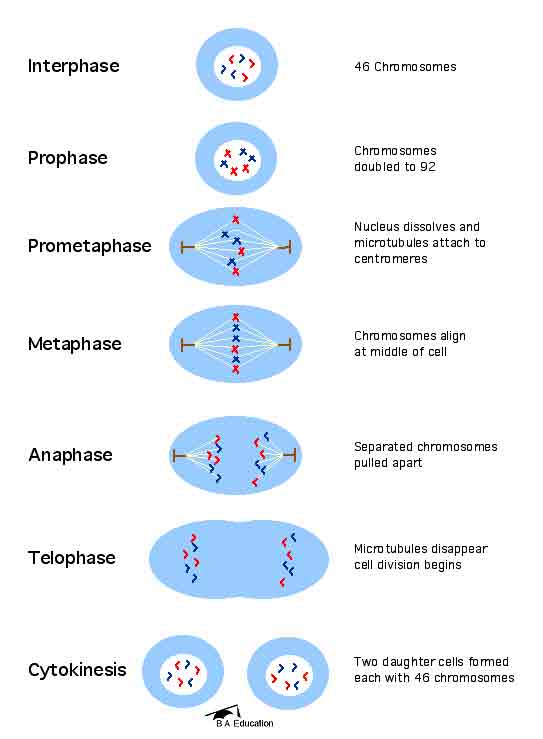
What happens in each stage of meiosis 1?
In meiosis 1 the homologous chromosomes separate from each other, whereas, in meiosis 2 the sister chromatids separate. In meiosis 1 two diploid daughter cells are produced, whereas, in meiosis 2 four haploid daughter cells are produced.
What happens in the 5 stages of meiosis?
Mitosis has five different stages: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. The process of cell division is only complete after cytokinesis, which takes place during anaphase and telophase. Each stage of mitosis is necessary for cell replication and division.
What are the 7 stages of meiosis in order?
Therefore, meiosis includes the stages of meiosis I (prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I) and meiosis II (prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II).
What are the 8 stages of meiosis in order?
In this video Paul Andersen explains the major phases of meiosis including: interphase, prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, cytokinesis, interphase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II.
What happens in each stage of meiosis 1 and 2?
However, Meiosis I begins with one diploid parent cell and ends with two haploid daughter cells, halving the number of chromosomes in each cell. Meiosis II starts with two haploid parent cells and ends with four haploid daughter cells, maintaining the number of chromosomes in each cell.
What is the 4 stages of meiosis?
The 4 Mitosis Phases: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase.
What happens during each of the four phases of mitosis?
1) Prophase: chromatin into chromosomes, the nuclear envelope break down, chromosomes attach to spindle fibres by their centromeres 2) Metaphase: chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate (centre of the cell) 3) Anaphase: sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell 4) Telophase: nuclear envelope ...
What happens in G1 phase?
Initially in G1 phase, the cell grows physically and increases the volume of both protein and organelles. In S phase, the cell copies its DNA to produce two sister chromatids and replicates its nucleosomes. Finally, G2 phase involves further cell growth and organisation of cellular contents.
What are the 5 stages of meiosis 1?
Meiotic prophase I is subdivided into five stages: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
What are the 8 stages of meiosis quizlet?
Terms in this set (8)prophase I. the chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down. ... Metaphase I. pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell.Anaphase I. ... Telophase I and Cytokinesis. ... Prophase II. ... Metaphase II. ... Anaphase II. ... Telophase II and Cytokinesis.
What are the 8 phases of mitosis?
prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. metaphase, prometaphase, prophase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis.
What happens before entering meiosis?
Before entering meiosis I, a cell must first go through interphase. As in mitosis, the cell grows during G phase, copies all of its chromosomes during S phase, and prepares for division during G phase.
What is the process of meiosis?
To put that another way, meiosis in humans is a division process that takes us from a diploid cell—one with two sets of chromosomes—to haploid cells—ones with a single set of chromosomes. In humans, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs.
What phase of meiosis is haploid?
In meiosis II, the sister chromatids separate, making haploid cells with non-duplicated chromosomes. Phases of meiosis II. Prophase II: Starting cells are the haploid cells made in meiosis I. Chromosomes condense. Metaphase II: Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate.
What happens to homologues in anaphase I?
In anaphase I, the homologues are pulled apart and move apart to opposite ends of the cell. The sister chromatids of each chromosome, however, remain attached to one another and don't come apart. Finally, in telophase I, the chromosomes arrive at opposite poles of the cell.
How are sister chromatids captured?
The two sister chromatids of each chromosome are captured by microtubules from opposite spindle poles. In metaphase II, the chromosomes line up individually along the metaphase plate. In anaphase II, the sister chromatids separate and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell.
Why do chromosomes become haploid in meiosis?
The number of chromosomes becomes haploid in meiosis I, because the actual sister chromatids are not pulled apart by spindle fibers. For example, if a cell was undergoing meiosis, and had a total of 4 chromosomes in it, then 2 of them would go to one daughter cell, and 2 of them would go to the other daughter cell.
Where do homologues attach to microtubules?
Each chromosome attaches to microtubules from just one pole of the spindle, and the two homologues of a pair bind to microtubules from opposite poles. So, during metaphase I, homologue pairs—not individual chromosomes—line up at the metaphase plate for separation. The phases of meiosis I.
What happens in metaphase 1 of meiosis?
In metaphase I of meiosis, the alleles are separated, allowing for this phenomenon to happen. In meiosis II, they will be separated into individual gametes. In mitosis, all the chromosomes line up on their centromeres, and the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate into new cells.
Where does meiosis occur?
Human meiosis occurs in the sex organs. Male testis produce sperm and female ovaries produce eggs. Before these gametes are made, however, the DNA must be reduced. Humans have 23 distinct chromosomes, existing in homologous pairs between maternal and paternal DNA, meaning 46 chromosomes.
What is the first step in meiosis?
Prophase I , the first step in meiosis I, is similar to prophase in mitosis in that the chromosomes condense and move towards the middle of the cell. The nuclear envelope degrades, which allows the microtubules originating from the centrioles on either side of the cell to attach to the kinetochores in the centromeres of each chromosome.
Why is meiosis necessary?
Meiosis is necessary for many sexually-reproducing animals to ensure the same number of chromosomes in the offspring as in the parents. The act of fertilization includes two cells fusing together to become a new zygote. If the number of alleles of each gene is not reduced to 1 in the gametes that produce the zygote, ...
Why do gametes fuse?
The gametes can then meet, during reproduction, and fuse to create a new zygote. Because the number of alleles was reduced during meiosis, the combination of two gametes will yield a zygote with the same number of alleles as the parents. In diploid organisms, this is two copies of each gene.
What is the process of reducing the number of chromosomes in a cell before reproduction?
What is Meiosis ? Meiosis is the process in eukaryotic, sexually-reproducing animals that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell before reproduction. Many organisms package these cells into gametes, such as egg and sperm.
Where do homologous chromosomes line up in meiosis?
In metaphase I of meiosis I, the homologous pairs of chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate, near the center of the cell. This step is referred to as a reductional division. The homologous chromosomes that contain the two different alleles for each gene are lined up to be separated. As seen in the diagram above, while the chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate with their homologous pair, there is no order upon which side the maternal or paternal chromosomes line up. This process is the molecular reason behind the law of segregation.
What are the stages of meiosis?
Stages of Meiosis 1 and 2 (With Pictures) Meiosis is the type of cell division that is seen during the formation of gametes (sex cells). It consists of two successive divisions which are meiosis 1 and meiosis 2. In meiosis 1, the number of chromosomes is reduced by one-half and for this reason, it is called reduction division.
What are the two divisions of meiosis?
Each of the two meiotic divisions is divided into interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Each stage is followed by 1 or 2 indicating whether it belongs to meiosis 1 or 2. Here are list of stages of meiosis 1 and meiosis 2 as below:
How do homologous chromosomes form?
This stage is manifested by the chromosomes becoming visible as distinct bodies as they get shorter and thicker and centrioles become arranged at opposite sides of the nucleus. As prophase progresses, homologous chromosomes lie side by side and become intertwined rather like a zipper forming pairs called bivalents in a process called synapsis. Chromosomes may become coiled around each other and their chromatids may remain in contact at points called chiasmata. During synapsis, homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material between one another. This exchange is called crossing over.
Why do homologous chromosomes migrate to the opposite poles?
This is because the spindle fibres shorten and thus the chromosomes are pulled. It is important to note that sister chromatids do not separate at this stage.
What is the difference between meiosis 1 and 2?
In meiosis 1, the number of chromosomes is reduced by one-half and for this reason, it is called reduction division. Meiosis 2 results in separation the sister chromatids and for this reason, it is known as equatorial division. Each of the two meiotic divisions is divided into interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
What happens to the chromosomes in the nuclear membrane?
Nuclear membrane disappears completely making the chromosomes free in the cytoplasm. The spindles are already fully formed. Each pair of the homologous chromosomes moves to the equator of the spindle and attach to the spindles by their centromeres such that the two homologous chromosomes orientate towards opposite poles.
How many daughter cells are there in meiosis?
The cytoplasm divides across the middle. Thus meiosis results into four daughter cells each having a haploid number of chromosomes.
What is meiosis?
Meiosis is, along with mitosis, one of the two major types of cell division. Unlike the mitotic division, which takes place in all the cells of our body (to understand it better, we will focus from now on the human being, but it happens in all organisms with sexual reproduction), meiosis only happens in germ cells.
In what phases is meiosis divided?
Biologically speaking, meiosis is more complex than mitosis. More than anything because, although the mitotic division consisted of a single division (with a total of 7 phases), meiosis requires two consecutive divisions with their particularities.
Meiosis I
Meiosis I is, broadly speaking, the stage of mitotic division in which we start from a diploid germ cell and end up having two daughter cells that are also diploid but have undergone chromosomal crossover. The goal of the first mitotic division is to give genetic diversity.
Interface
The interface spans the entire life span of the germ cell prior to entry into meiosis. When it is time to carry out the meiotic division, the cell, which, remember, is diploid (2n), duplicates your genetic material. At this time, we have two homologous chromosomes of each. When chromosomal duplication has taken place, meiosis proper is entered.
Prophase I
In prophase I, which is the first stage of meiosis, tetrads are formed, which now we will see what they are. After the duplication of genetic material happened at the interface, the homologous chromosomes come together.
Metaphase I
Metaphase I is the stage of the first mitotic division in which the mitotic spindle forms two units known as centrosomes, two organelles that move, each one of them, to opposite poles of the cell. Microtubules are born from these centrosomes that move towards the equatorial plane, joining the centromeres of the sister chromatids.
Anaphase I
In anaphase I, homologous chromosomes separate. As we have already commented, each one of them is anchored to an opposite pole of the cell, therefore, when the microtubules stretch from the centromere, each chromosome migrates to a different pole and inevitably they separate.
What are the stages of meiosis 2?
The four aspects of Meiosis 2 are Prophase 2 , Metaphase 2, Anaphase 2 and Telophase 2. The stages of meiosis 2 are as follows: Prophase 2: Here, we see the nucleoli and nuclear membrane disappear again. The chromatids get shorter and thicker.
What is the longest phase of meiosis?
Prophase 1 is the longest phase of meiosis where three primary aspects are taking place. First is the condensation of chromatin into chromosomes, the second aspect is the physical contact between homologous chromosomes, and the third aspect is the transmission of genetic information between synapsed chromosomes.
What is the process of a chromosome moving up the equator called?
In this meiosis phase, the pairs of homologous chromosomes move up the equator of the cell and line up on the metaphase plate. The process is called random assorting where maternal and paternal chromosomes line up in random order, aligning themselves on either side of the equator, which leads to genetic diversity among offspring.
What are the five subphases of prophase 1?
The following are the five sub-phases under prophase 1: Leptotene: The chromosomes start to condense and attach to the cell membrane through a ‘cap’ like structure at the end of chromosomes called telomeres. Zygotene: Here the chromosomes start pairing and synapsis between homologous chromosomes begins.
How are synapses formed?
Pachytene: Here, the synapse is formed, by a chromatid of one pair attaching to the chromatid in a homologous chromosome and the crossing over begins. After some time, the synapses snap, finishing the process of crossing over of the genetic information.
Where do the separated chromatids move?
These separated chromatids move to the opposite ends of the cell. The chromatids are now called sister chromosomes as they are at the equator of the cell. This stage is similar to the telophase 1 stage in Meiosis 1.
Which phase of meiosis is the process where the plasma membrane is divided into two daughter cells?
4) Telophase 1: In this meiosis phase, the chromosomes decondense, later the chromosomes are completely separated and the nuclear envelope forms. Cytokinesis is the process where the plasma membrane is divided into two daughter cells.
