What happens if you give MMR vaccine intramuscular?
Since then, data have shown that administration of MMR vaccine by IM injection generates an immune response equal to the response when the vaccine is given via the SC route, and the vaccine is also well-tolerated.
What happens if varicella vaccine is administered intramuscularly?
Response to vaccines recommended by the subcutaneous route is unlikely to be affected if the vaccines are administered by the intramuscular rather than subcutaneous route. Repeating doses of vaccine administered by the intramuscular route when recommended to be by the subcutaneous route is not necessary (10).
Is MMR given subcutaneously or intramuscular?
The dosage for both MMR and MMRV is 0.5 mL. Both vaccines are administered by the subcutaneous route. The minimum age for both MMR and MMRV is 12 months of age. The typical age for the second dose of either vaccine is at 4 to 6 years of age.
Does the MMR vaccine go into the muscle?
How is the MMR vaccine given? The MMR vaccine is given as an intramuscular injection (injected into a muscle in your thigh or upper arm).
What route is MMR given?
Each 0.5 mL dose of the M-M-R®II vaccine is administered subcutaneously into the outer part of the upper arm or into the anterolateral area of the thigh.
Can varicella be given IM?
VARIVAX is administered as an approximately 0.5-mL dose by subcutaneous injection into the outer aspect of the upper arm (deltoid region) or the anterolateral thigh. Do not administer this product intravascularly or intramuscularly.
Why is MMR given subcutaneous?
Live Attenuated Virus Vaccines Live virus vaccines have traditionally been given by subcutaneous injection as it is asserted18 that it may be less painful and associated with a lower risk of bleeding.
Where do you inject MMR?
The MMR vaccine is given as 2 doses of a single injection into the muscle of the thigh or upper arm. 2 doses of the vaccine are needed to ensure full protection.
Why are two doses of MMR needed?
During an outbreak, public health authorities may recommend an additional dose of MMR for people who belong to groups at increased risk for mumps. An additional dose can help improve protection against mumps disease and related complications.
What happens if an IM injection is given subcutaneously?
Subcutaneous injections can lead to localised cellulitis, granuloma formation and abscess. The COVID-19 vaccine has shown to have high efficacy if given correctly intramuscularly. Subcutaneous injection can happen inadvertently (figure 1), affecting efficacy of vaccination and potentiate local adverse events.
What are contraindications for MMR vaccine?
ContraindicationsSevere allergic reaction/anaphylaxis after a previous dose of MMR / MMRV or after one of the components of the vaccine (e.g., neomycin, gelatin)[5]Pregnancy or planning for it - the pregnancy should be discouraged within 28 days of vaccination due to the risk of congenital rubella. ... Immunodeficiency.More items...•
Why is the varicella vaccine given subcutaneous?
In general, vaccines containing adjuvants (a component that enhances the antigenic response) are administered IM to avoid irritation, induration, skin discoloration, inflammation, and granuloma formation if injected into subcutaneous tissue.
Is varicella vaccine subcutaneous or IM?
Dosage and Administration 2 doses (0.5 ml each) of varicella vaccine should be given subcutaneously, separated by at least 3 months. MMRV vaccine is approved for healthy children in this age group.
Why is MMR given subcutaneous?
Live Attenuated Virus Vaccines Live virus vaccines have traditionally been given by subcutaneous injection as it is asserted18 that it may be less painful and associated with a lower risk of bleeding.
Can MMR and varicella be given in same leg?
Routine administration of all age-appropriate doses of vaccines simultaneously is recommended for children for whom no specific contraindications exist at the time of the visit (7). MMR and varicella vaccine can be administered simultaneously (7).
Who Should Get MMR Vaccine?
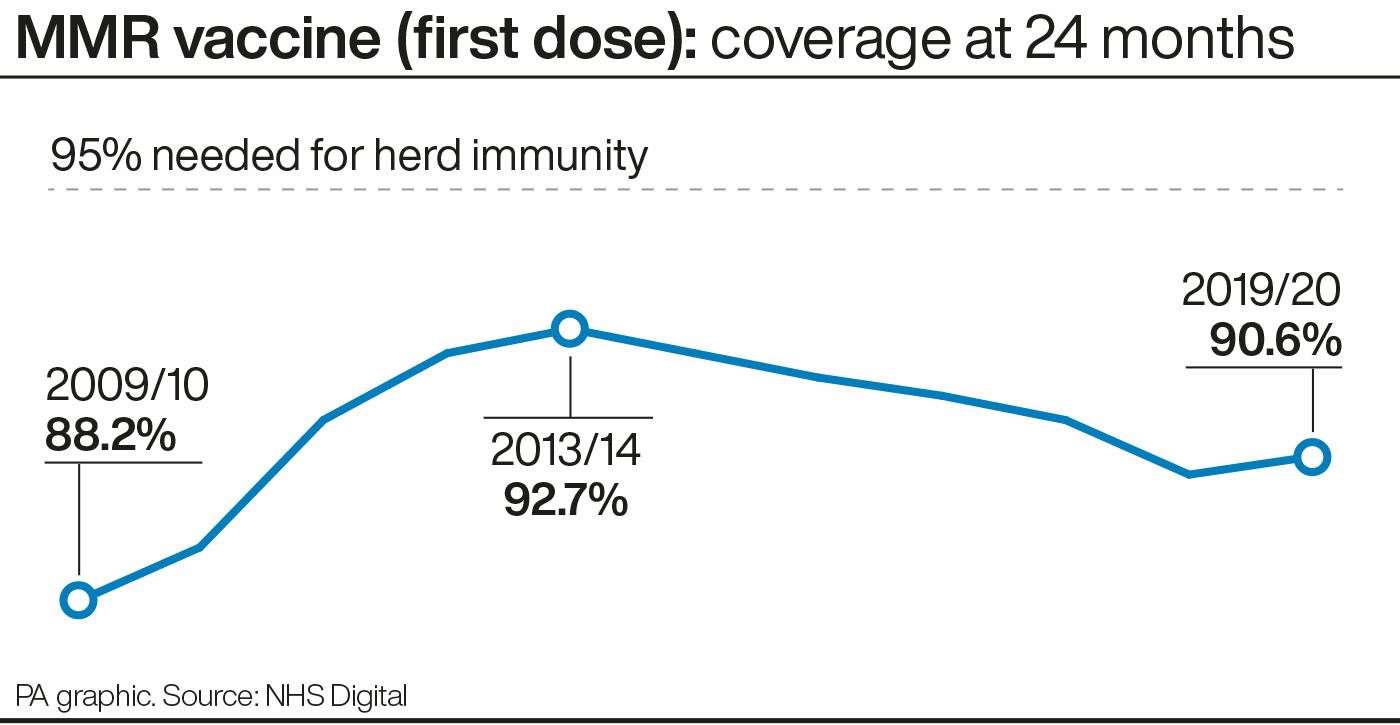
CDC recommends all children get two doses of MMR (measles-mumps-rubella) vaccine, starting with the first dose at 12 through 15 months of age, and...
Who Should Not Get MMR Vaccine?
Some people should not get MMR vaccine or should wait. 1. Anyone who has ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to the antibiotic neomycin,...
Who Does Not Need MMR Vaccine?
You do not need measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine if you meet any of these criteria for evidence of immunity: 1. You have written documenta...
How Well Does The MMR Vaccine Work?
MMR vaccine is very effective at protecting people against measles, mumps, and rubella, and preventing the complications caused by these diseases....
Should You Get Vaccinated After Being Exposed to Measles, Mumps, Or Rubella?
If you do not have immunity against measles(https://www.cdc.gov/measles/about/faqs.html#am), mumps(https://www.cdc.gov/mumps/vaccination.html#footn...
What Are The Childcare and School Requirements For MMR Vaccine?
All 50 states and the District of Columbia (DC) have state laws that require children entering childcare or public schools to have certain vaccinat...
How Can Parents Pay For MMR Vaccine?
Most health insurance plans cover the cost of vaccines. But you may want to check with your health insurance provider before going to the doctor. L...