Which genetic disorder can only result from nondisjunction?
Turner syndrome (TS) is a genetic disorder caused by the partial or complete absence of one X chromosome. This is called monosomy and is typically caused by chromosomal nondisjunction. It is a very common abnormality among the sex chromosome disorders, with an incidence of 1 in 2000 liveborn females. Is Down syndrome caused by nondisjunction?
What are some the main reasons of nondisjunction in mitosis?
Nondisjunction causes abnormal number chromosomes in all the cells called aneuploidy or in some cells called mosaicism. Some of the important examples are: Down’s syndrome – Trisomy of autosomes, i.e. chromosome 21. It contains one extra chromosome 21. Rarely in only 1% of cases, Down’s syndrome with mosaicism is observed.
What happens if nondisjunction occurs during meiosos?
Nondisjunction in meiosis can result in pregnancy loss or birth of a child with an extra chromosome in all cells, whereas nondisjunction in mitosis will result in mosaicism with two or more cell lines. Aneuploidy may also result from anaphase lag. Click to see full answer.
What causes nondisjunction to occur?
What are the 4 main causes of birth defects?
- Genetics. One or more genes might have a change or mutation that prevents them from working properly. …
- Chromosomal problems. …
- Exposures to medicines, chemicals, or other toxic substances. …
- Infections during pregnancy. …
- Lack of certain nutrients.

What is the result of nondisjunction in mitosis?
In mitosis, nondisjunction lead to the formation of monosomics or trisomics and all cells derived from that cell carry this mistake resulting in a population of cells, but restricted to that site or tissue only. Non-disjunction may lead to mosaicism.
What is non-disjunction in biology?
Non-disjunction is the inability or failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate in meiosis or mitosis. As a result some gamete or cells may contain an extra chromosome and others that are missing a chromosome. This is the most common reason for many syndromes or genetic defects in humans.
Why do chromosomes fail to segregate during anaphase?
A small chromosome is generated due to Robertsonian translocation and this chromosome often fails to segregate during anaphase. We will discuss this separately later. The third reason is called as non-disjunction. Non-disjunction is the inability or failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate in meiosis or mitosis.
What happens if a cell is derived from 2n+1?
All cells derived from 2n+1 may lead to population of trisomic cells. (somatic clones of trisomics) All cells derived from 2n-1 may lead to population of monosomic cells. (somatic clones of monosomics) Nondisjunction in mitosis may lead to mosaicism.
What is the condition in which a tissue may contain patches of cells with chromosome abnormality and other cells?
Mosaicism refers to the condition in which a tissue may contain patches of cells with chromosome abnormality and other cells with normal karyotype. Or Presence of different chromosome constitution within the cells of an individual is called as mosaicism. Nearly 50% with Turner syndrome exhibit mosaicism.
How many cells are formed in mitosis?
From a single cell, billions of cells are formed in an adult human being by mitosis. Even in adults, many cells like skin cells are continuously replaced by mitosis. The precision of the process is extremely important for maintaining an individual and also the maintenance of a species. But think of meiosis, gametes are formed by meiosis ...
How many chromosomes are lost in monosomy?
Monosomy is the loss of a single chromosome, represented as 2n-1. A monosomic person has 45 chromosomes
What is nondisjunction in biology?
This is one of the most common forms of chromosomal aberration that occurs in humans.
What are the effects of nondisjunction?
Effects of Nondisjunction. Nondisjunction can lead to the loss of a chromosome and give rise to a condition known as monosomy, denoted as (n – 1) or (2n – 1). It can also lead to the addition of a chromosome and is known as trisomy, denoted as (n + 1) or (2n + 1) . These abnormalities can give rise to a number of conditions.
What happens to sister chromatids in anaphase II?
In this process, separation of sister chromatids in anaphase II fails, resulting in an uneven distribution of the chromatids into the newly formed daughter cells. If this type of nondisjunction takes place, two cells have normal number of chromosomes (n), whereas in two cells, the number of chromosome has increased by one (n + 1). There is a good chance that this aneuploidy might go unnoticed in females as only one of the newly formed daughter cells develops into an ovum.
What is the name of the condition that results from the trisomy of the autosomal chromosome 21?
Down Syndrome : This results from the trisomy of the autosomal chromosome 21. The frequency of this condition is one in every thousand births. Nondisjunction is mostly of maternal origin. Individuals with this syndrome usually have a lower intelligence and poor immunity. These individuals usually have slanting eyes and experience a stunted growth. The mouth is usually small, and the tongue may be protruding. These individuals usually suffer from heart defects and thyroid abnormalities.
What percentage of aneuploidies are caused by nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction is one of the most common causes of aneuploidies, it amounts to about 25 percent of the aneuploidies that may occur in human oocytes.
How often does nondisjunction occur?
The frequency of this condition is one in every thousand births. Nondisjunction is mostly of maternal origin. Individuals with this syndrome usually have a lower intelligence and poor immunity. These individuals usually have slanting eyes and experience a stunted growth.
How many types of nondisjunction are there?
Depending on the stage in which nondisjunction has occurred, it can be classified into three types.
What happens at the end of Prophase I?
At the end of Prophase I the membrane around the nucleus in the cell dissolves away, releasing the chromosomes.
Why are sister chromatids pulled to opposite poles?
The sister chromatids are then pulled to opposite poles due to the action of the meiotic spindle.
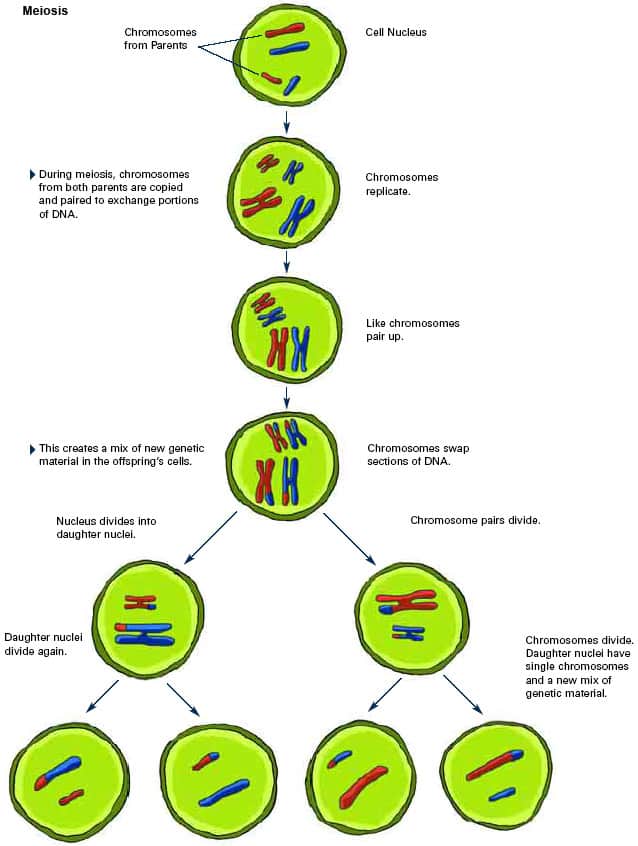
How many stages of meiosis are there?
Meiosis can be divided into nine stages. These are divided between the first time the cell divides (meiosis I) and the second time it divid
What happens when chromosomes pair up?
The chromosomes pair up so that both copies of chromosome 1 are together, both copies of chromosome 2 are together, and so on.
How many cells does one cell divide in mitosis?
During mitosis one cell? divides once to form two identical cells.
What is the process of a single cell pinching in the middle of a nucleus?
This process is known as cytokinesis.
What extends from centrosomes during interphase?
During interphase, microtubules extend from these centrosomes.
What is nondisjunction in biology?
-disjunction is a lack of junction, or a separation or breaking apart. Disjunction is a normal process for both mitosis and meiosis — the chromosomes are supposed to split apart during anaphase so each daughter cells can receive a full and complete copy of the original cell's genome. Finally, nondisjunction, the full term, means there is a lack of separation. The chromosomes stay joined together so that too many migrate to one daughter cell while the other has a deficit.
What is the process of reducing the number of chromosomes in a cell?
Meiosis is the process responsible for reducing the chromosome number; i.e. for turning a diploid cell into four haploid cells.
How many chromosomes are produced during Meiosis I?
If nondisjunction occurs during Meiosis I in humans, two gametes with extra chromosomes will be produced (24 chromosomes each, or n+1) and two gametes lacking a chromosome will be produced (22 chromosomes each, n-1 ).
How many rounds of cell division does meiosis occur?
Meiosis occurs in two rounds of cell division — Meiosis I and Meiosis II. The overall process is described in the steps below and outlined in the figure
When are sister chromatids joined?
Sister chromatids are joined together at their centromere, and will remain joined until Anaphase II during the second division in meiosis.
Can nondisjunction occur in both males and females?
Nondisjunction can occur in both males and females, so it is possible for both sperm and eggs with abnormal chromosome numbers to be produced.