
IBD can lead to several serious complications in the intestines, including:
- Profuse intestinal bleeding from the ulcers
- Perforation, or rupture of the bowel
- Narrowing -- called a stricture -- and obstruction of the bowel; found in Crohn's
- Fistulae (abnormal passages) and perianal disease, disease in the tissue around the anus. ...
- Toxic megacolon, which is an extreme dilation of the colon that is life-threatening. ...
- Malnutrition
Is inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) fatal?
Although inflammatory bowel disease usually isn't fatal, it's a serious disease that, in some cases, may cause life-threatening complications. The exact cause of inflammatory bowel disease remains unknown.
What happens if Crohn’s disease goes untreated?
Untreated Crohn’s disease could result in inflammation that affects the digestive system and other body systems. For those who are able to cope with the signs and symptoms of the disease, the inflammation that the disease causes in the intestines may not seem like a reason to be concerned.
What is the prognosis for IBD?
IBD can be debilitating and sometimes leads to life-threatening complications. Inflammatory bowel disease symptoms vary, depending on the severity of inflammation and where it occurs. Symptoms may range from mild to severe. You are likely to have periods of active illness followed by periods of remission.
What are the long-term complications of irritable bowel disease (IBD)?
So if you have IBS alone, you shouldn’t experience some of the long-term complications associated with irritable bowel disease (IBD). These include intestinal bleeding or areas of inflamed colon that require removal through surgery. Having IBS doesn’t increase your risk for colon cancer.

Can IBD go away on its own?
No, IBD cannot be cured. There will be periods of remission when the disease is not active. Medicines can reduce inflammation and increase the number and length of periods of remission, but there is no cure.
Does IBD get worse over time?
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease. It is a progressive condition, which means that it tends to worsen gradually. But symptoms can sometimes disappear for weeks or even years.
How long can you live with inflammatory bowel disease?
RESULTS: Life expectancy in patients with IBD increased between 1996 and 2011 (females: from 75.5 to 78.4 yr, difference: 2.9 yr [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.3 to 4.5]; males: from 72.2 to 75.5 yr, difference: 3.2 yr [95% CI 2.1 to 4.4]).
What happens if I don't take medication for Crohn's?
Severe Complications of Crohn's The longer the disease goes untreated, the more dangerous symptoms become, heightening a person's risk of numerous complications, hospitalizations, disability, time lost from work, surgery, and decreased quality of life.
How serious is IBD?
Although inflammatory bowel disease usually isn't fatal, it's a serious disease that, in some cases, may cause life-threatening complications.
Is IBD a disability?
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is listed in the Social Security Administration's (SSA) impairment listing manual (more commonly called the “Blue Book”) as a condition that can qualify the patient to receive Social Security Disability benefits.
Can IBD be cured with diet?
No specific diet has been shown to prevent or treat IBD. However, some diet strategies help control symptoms.
Where is IBD pain located?
Most people with IBD experience pain at some point, though pain is not always a part of an IBD flare-up. The types of pain are not always the same, depending on your IBD diagnosis and the exact location of the pain. The pain from Crohn's disease is most often found in the RLQ or the middle of the abdomen.
Is IBD genetic?
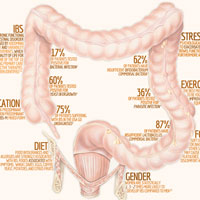
Genetic Factors Studies have shown that between 5% and 20% of people with IBD have a first-degree relative, such as a parent, child, or sibling, who also has one of the diseases. The genetic risk is greater with Crohn's disease than ulcerative colitis.
What can IBD lead to?
IBD, particularly ulcerative colitis, also increases the risk of colon cancer. IBD can also affect other organs. For example, someone with IBD may have arthritis, skin conditions, inflammation of the eye, liver and kidney disorders, or bone loss.
What does IBD flare up feel like?
What is a flare? People may also report symptoms such as fatigue, lack of appetite, joint aches, body aches, rashes, and eye problems, including pain, red- ness, or loss of vision. The symptoms of IBD vary from person to person, and may change over time.
What happens if you ignore ulcerative colitis?
If ulcerative colitis remains untreated, the inflammation can spread to the deeper layers of your colon and result in a very dangerous complication called toxic megacolon. This condition can lead to life-threatening infections, kidney failure, or a colon rupture and needs to be treated immediately.
Why are so many people getting IBD?
Most scientists believe IBD is the result of the interplay between the environment, diet, certain medications, genetic variables and an overreactive immune response against normal bacteria in the gut. If all these “planets” align the right way, an individual who may have a genetic predisposition will develop IBD.
Why is IBD increasing?
Many factors contributed to the increase in the incidence of IBD, including increased awareness, improved access to medical technology and health care providers, development of sophisticated disease surveillance systems, and environmental exposures associated with Westernization of society.
Can you suddenly develop IBD?
Signs and symptoms of Crohn's disease can range from mild to severe. They usually develop gradually, but sometimes will come on suddenly, without warning. You may also have periods of time when you have no signs or symptoms (remission).
Can IBD be cured with diet?
No specific diet has been shown to prevent or treat IBD. However, some diet strategies help control symptoms.
How to treat ulcerative colitis?
People with ulcerative colitis will use a variety of methods to keep the disease under control including medication, diet, supplements, and lifestyle modifications.
Which part of the large intestine is most at risk for disease?
Those who have disease only in the rectum (the last part of the large intestine) have the lowest amount of risk. Disease in only part of the large intestine carries an intermediate amount of risk; the greatest risk comes when the entire colon is affected by the disease (known as pan-colitis).
How long does it take to get a colonoscopy for ulcerative colitis?
For these reasons, continuing treatment for ulcerative colitis is important, as is regular screening for colorectal cancer. After eight to 10 years of having ulcerative colitis, a yearly colonoscopy might be recommended to check for polyps or colon cancer.
Does ulcerative colitis cause bone loss?
Bone Loss. People with ulcerative colitis may develop vitamin deficiencies, including a vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D is the "helper" vitamin for calcium, and an appropriate amount of calcium is needed to keep bones healthy.
Can ulcerative colitis cause shortness of breath?
Anemia. One of the hallmark symptoms of ulcerative colitis is blood in the stool. In severe cases, there may be a significant amount of bleeding. The body can’t replace this blood as fast as it is being lost. This results in anemia, which can cause fatigue, weakness, chest pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
Is colon cancer a concern?
It is a valid concern because the risk of colon cancer is higher in people who are diagnosed with ulcerative colitis than it is in people who do not live with the disease. It’s important to note that more than 90% of people diagnosed with IBD will never develop colon cancer.
Can colitis cause diarrhea?
Ulcerative colitis can cause signs and symptoms such as diarrhea, blood in the stool, nausea, fatigue, and abdominal pain. One of the goals of treatment is to stay on top of the inflammation that may contribute to these symptoms.
Why is inflammation bowel disease not a cause of IBD?
One possible cause is an immune system malfunction.
How old do you have to be to get IBD?
Age. Most people who develop IBD are diagnosed before they're 30 years old. But some people don't develop the disease until their 50s or 60s.
What is the umbrella term for inflammation of the digestive system?
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is an umbrella term used to describe disorders that involve chronic inflammation of your digestive tract. Types of IBD include:
Why does my immune system attack my digestive system?
When your immune system tries to fight off an invading virus or bacterium, an abnormal immune response causes the immune system to attack the cells in the digestive tract , too. Heredity also seems to play a role in that IBD is more common in people who have family members with the disease.
Which system is affected by Crohn's disease?
Digestive system. Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are both forms of inflammatory bowel disease. Crohn's disease most commonly affects the colon and the last part of the small intestine (ileum). Ulcerative colitis affects only the colon.
When to see a doctor for inflammatory bowel disease?
When to see a doctor. See your doctor if you experience a persistent change in your bowel habits or if you have any of the signs and symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease. Although inflammatory bowel disease usually isn't fatal, it's a serious disease that, in some cases, may cause life-threatening complications.
What medications can cause IBD?
These include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), naproxen sodium (Aleve), diclofenac sodium and others. These medications may increase the risk of developing IBD or worsen the disease in people who have IBD.
How to treat IBD?
When weight loss is severe, your doctor may recommend a special diet given via a feeding tube (enteral nutrition) or nutrients injected into a vein (parenteral nutrition) to treat your IBD. This can improve your overall nutrition and allow the bowel to rest. Bowel rest can reduce inflammation in the short term.
How to treat inflammatory bowel disease?
Limit dairy products. Many people with inflammatory bowel disease find that problems such as diarrhea, abdominal pain and gas improve by limiting or eliminating dairy products. You may be lactose intolerant — that is, your body can't digest the milk sugar (lactose) in dairy foods. Using an enzyme product such as Lactaid may help as well.
How to reduce bowels?
Even mild exercise can help reduce stress, relieve depression and normalize bowel function. Talk to your doctor about an exercise plan that's right for you. Biofeedback. This stress-reduction technique may train you to reduce muscle tension and slow your heart rate with the help of a feedback machine.
What to do if you have stricture in your bowel?
If you have a stenosis or stricture in the bowel, your doctor may recommend a low-residue diet. This will help to minimize the chance that undigested food will get stuck in the narrowed part of the bowel and lead to a blockage.
How to help Crohn's disease?
If you have trouble managing stress, try one of these strategies: Exercise. Even mild exercise can help reduce stress, relieve depression and normalize bowel function.
Can you have a capsule endoscopy for Crohn's disease?
You may still need an endoscopy with a biopsy to confirm a diagnosis of Crohn's disease. Capsule endoscopy should not be performed if there is a bowel obstruction. Balloon-assisted enteroscopy. For this test, a scope is used in conjunction with a device called an overtube.
Does Mayo Clinic treat bowel disease?
Our caring team of Mayo Clinic experts can help you with your Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) -related health concerns Start Here
How to treat IBS?
Treatment for IBS is with diet recommendations from a doctor or nutritionist, medication, and lifestyle changes like stress management and avoiding foods that trigger the condition. Treatments for IBD depend upon the type of disease, its symptoms, and health of the patient. Surgery may be necessary for some individuals.
Why do IBS and IBD cause IBS?
Researchers do not know the exact cause of either disease, but they believe that IBS may be caused and triggered by a variety of factors (foods, stress, and the nervous system of the GI tract), while IBD may be genetic or due a problem with the immune system.
What is Crohn’s disease?
Crohn's disease is a disease involving any location of the gastrointestinal tract. It frequently affects the end of the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine. In Crohn's disease, all layers of the intestine may also be involved, and there is redness and swelling in the affected parts. Other characteristics of Crohn’s disease are
What is the difference between Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis?
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are diseases that cause inflammation of part of or the entire digestive tract (GI). Crohn's affects the entire GI tract (from the mouth to the anus), while ulcerative colitis or ulcerative colitis only affects the large and small intestine and ilium.
What causes bowel obstruction?
Bowel obstruction, which is caused by the thickening of intestinal walls, can block stool or food from moving through the digestive tract. Eye inflammation. Fistulas. Gallstones and gallbladder disease, which are more likely to occur in people with Crohn’s.
Why is Crohn's disease produced in excess?
When Crohn's disease is present, TNF is produced in excess because the immune system mistakenly identifies healthy bacteria as a foreign presence.
Why does Crohn's disease happen?
Although the exact cause of Crohn’s disease is not yet known, some doctors suspect that it might happen due to a bacterial swelling, mostly due to Mycobacterium. Other causative and risk factors may include
What are some examples of IBS?
Examples include heart disease and chronic respiratory disorders. The connection between mind and body is strong when it comes to IBS. According to a study published in the journal Clinical Therapeutics, people with IBS report a lower degree of quality of life when compared to the general U.S. population.
What to do if you have bloating and constipation?
If you experience the bloating, abdominal pain, cramping, constipation, and mucus in the stool that often indicate a condition that is uncontrolled, make an appointment to talk to your primary care physician or gastroenterologist, if you have one. Making a list of your symptoms and any questions you may have in advance can help eliminate some of the discomfort in talking about your health.
What is it called when you can't push your stool out?
Fecal impaction: When stool starts to pack tightly in your rectum, you may not be able to push it out. This is known as fecal impaction . Because impaction affects the stool’s ability to move forward, you may have to seek medical attention to have the stool manually removed.
Can IBS cause colon inflammation?
IBS doesn’t cause inflammation of your colon that leads to permanent changes. So if you have IBS alone, you shouldn’t experience some of the long-term complications associated with irritable bowel disease (IBD). These include intestinal bleeding or areas of inflamed colon that require removal through surgery.
Does IBS increase your risk for colon cancer?
Having IBS doesn’t increase your risk for colon cancer. However, this doesn’t mean that you won’t ever get colon cancer — just that IBS isn’t a risk factor.
Can IBS cause anxiety?
Living with long-term abdominal pain from IBS can lead to anxiety over symptoms. Depression, or long-lasting feelings of hopelessness, can set in as a result. In addition, depression causes other symptoms, including a lack of motivation, withdrawal from others, and all-over body aches.
Can IBS affect my mental health?
Having IBS or CIC can have long-term impacts on your mental health and overall sense of well-being. People with either condition can develop a fear of going to public places, especially unfamiliar ones, due to concerns over not being able to find a bathroom or getting to a bathroom fast enough.
What is the effect of Crohn's disease on the small intestine?
If the small intestine is inflamed, it is less able to absorb nutrients from food.
How does Crohn's disease affect the body?
Crohn’s disease can affect the entire body in different ways because it affects the immune system . However, the disease is usually characterized as one that primarily affects the digestive system. Crohn’s disease can cause inflammation in any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus.
What is it called when the inside of the bowel is narrowed?
When a section of the inside of the bowel becomes narrowed, it is called a stricture . People with Crohn’s disease are at an increased risk of developing strictures 6 . A stricture may cause pain and it can also contribute to the development of bowel obstructions if food is not able to pass through the narrowed area.
Why is Crohn's disease necessary?
It is necessary to treat active Crohn’s disease because the condition not only causes ulcers in the digestive tract but is also associated with problems in the eyes, skin, joints, and other organ systems in the body.
What are the symptoms of Crohn's disease?
Ongoing Signs and Symptoms. Some of the signs and symptoms of Crohn’s disease include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stools, vomiting, nausea, and fatigue. Inflammation in the digestive tract may lead to these symptoms and others, which is why is needed.
What is the condition where food is unable to pass through the intestine?
Crohn’s disease is associated with blockages in the intestine. A blockage is when the small or the large intestine becomes partially or totally blocked and undigested food is unable to pass through it. Some of the symptoms of an obstruction include fever, abdominal distention, vomiting, constipation and/or diarrhea, and abdominal pain (sometimes severe).
What are the deficiencies in Crohn's disease?
Other vitamin and mineral deficiencies could lead to a wide range of health problems. A lack of calcium, iron, vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin K, and zinc are some of the other more common deficiencies in people who have Crohn’s disease 7 .
What happens if you don't treat ulcerative colitis?
If people do not treat ulcerative colitis, it may lead to: nutritional deficiencies. loss of appetite. swo llen abdomen. fatigue.
What does it mean when you have no symptoms?
When a person has few or no symptoms, doctors refer to it as being in remission. When symptoms suddenly get worse, they call it a flare-up.
What is the best treatment for ulcerative colitis?
Surgery: A healthcare professional may recommend surgery for people with severe or difficult-to-treat ulcerative colitis. This can involve removing part or all of a person’s colon.
What are the risks of colitis?
fever. rapid heartbeat. bleeding from the rectum. ruptur ed bowel. greater risk of colon cancer. Ulcerative colitis may also increase the risk of physical and mental health complications, such as: arthritis. skin problems. eye inflammation.
Can ulcerative colitis cause colon cancer?
In contrast, those who stop taking their medication have a five-times greater risk of relapse. For people with severe ulcerative colitis, prompt treatment can help prevent complications. Research suggests that long-term inflammation in the large intestine can lead to colonic dysplasia and even colorectal cancer.
Does ulcerative colitis get worse?
A person who believes they have ulcerative colitis should speak to a doctor. Ulcerative colitis tends to be a progressive condition that does not get better on its own. Without treatment, symptoms may persist and get worse, and inflammation may spread within the colon.
Does ulcerative colitis increase the risk of cancer?
The risk of developing cancer increases in individuals with severe ulcerative colitis and in those who have had the disease for longer.
What are the Dangers of Not Treating a Hernia?
Some people assume that just because they aren’t experiencing any significant or bothersome symptoms, the hernia they are suffering from must not be too big of a problem. Such a view may even lead these people to believe that ignoring the hernia is best.
What happens when a hernia gets bigger?
As hernias get bigger, they become more susceptible to incarceration and strangulation. The latter usually involves blood being stopped from flowing freely to the tissue, which can lead to tissue death and gangrene. Such an event can lead to parts of organs dying or rupturing—both of which will usually require emergency surgery. ...
How do you know if you have a strangulated hernia?
How do you know if you are suffering from a strangulated hernia? First of all, you will feel very sick and the symptoms you will be facing may include intense pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever . If you are experiencing one or more of these symptoms and you have a hernia, seek immediate medical attention.
Can hernias get worse?
Hernias are no different than other problems we experience in life—they tend to get worse or larger if not addressed adequately. Mild symptoms can turn into more serious ones, possibly spiraling into seriously underestimated complications.
Can a hernia grow smaller?
In some cases, hernias cease from growing, but they never get smaller. In some extreme cases, hernias can become so large that the abdominal cavity can collapse – making repair much more difficult. At any rate, it’s better to get a hernia treated while it is relatively small than to wait until it grows in size.
Can a hernia cause death?
They can cause pain and activity limitations. And the reality is that some hernias can lead to serious injury; some of them can even lead to death. It must be stressed that the hernias that ultimately cause severe harm or lead to death do so because they were not treated properly or promptly.
Can a hernia be repaired?
In other words, if hernias are managed properly and surgically repaired, life can return to normal and the risks can be minimized. The bottom line is that an untreated hernia involves more potential risks and can lead to more severe harm than treating one—as the following facts will help illustrate.
Treatment
Clinical Trials
- Inflammatory bowel disease symptoms vary, depending on the severity of inflammation and where it occurs. Symptoms may range from mild to severe. You are likely to have periods of active illness followed by periods of remission. Signs and symptoms that are common to both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis include: 1. Diarrhea 2. Fatigue 3. Abdom...
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment