Definition of Cellular Respiration
- Aerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP.
- Anaerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen. It is also called fermentation.
What are the four steps in aerobic respiration?
The steps of aerobic cellular respiration are:
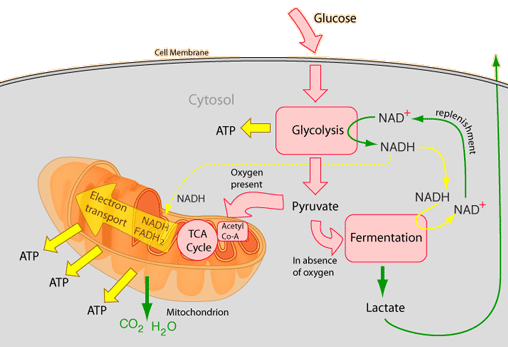
- Glycolysis (the break down of glucose)
- Link reaction.
- Krebs cycle.
- Electron transport chain, or ETC.
What are the 4 stages of aerobic respiration?
what are the stages of aerobic respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration, Glycolysis, Prep Steps
- Cellular Respiration (UPDATED)
- The stages of aerobic respiration
What are the different steps of aerobic respiration?
What are the 5 phases of respiration?
- Pulmonary Ventilation. …
- External Respiration. …
- Transport of gases through blood vessels. …
- Internal Respiration. …
- Cellular Respiration.
What does aerobic respiration start with?
When the breakdown of glucose food occurs with the use of oxygen, it is called aerobic respiration. In aerobic respiration, the glucose food is completely broken down into carbon dioxide and water with the use of oxygen, and energy is released.

What do you understand by aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is the process involved in the production of energy in the presence of oxygen.
What are the different stages of aerobic respiration?
The different stages of aerobic respiration are: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Citric acid cycle Electron Transport Chain
What are the end products of aerobic respiration?
The end products of aerobic respiration include 6 molecules of carbon dioxide, 6 molecules of water and 30 molecules of ATP.
Where does aerobic and anaerobic respiration take place?
Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondrial matrix of the cell. On the contrary, anaerobic respiration occurs in the fluid portion of the cytop...
What is the importance of aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration provides energy to the living organisms to perform all the essential functions of life. That is why aerobic respiration is impo...
What are the different types of aerobes?
The different types of aerobes include: Obligate aerobes that strictly need oxygen to grow. Facultative aerobes can grow in the presence as well as...
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a biological process in which food glucose is converted into energy in the presence of oxygen. The chemical equation of aerobic respiration is as given below-
Why is aerobic respiration important?
Aerobic respiration provides energy to the living organisms to perform all the essential functions of life. That is why aerobic respiration is important.
What is the process of utilisation of oxygen to breakdown glucose, amino acids, fatty acids to produce ATP?
Aerobic respiration is the process of utilisation of oxygen to breakdown glucose, amino acids, fatty acids to produce ATP. The pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA in the mitochondrial matrix. The Kreb’s cycle occurs twice per glucose molecule.
What is the third step of aerobic respiration?
The third step in aerobic respiration is the citric acid cycle , which is also called the Krebs cycle. In this stage of Aerobic respiration, the oxaloacetate combines with the acetyl-coenzyme A and produces citric acid. The citric acid cycle undergoes a series of reactions and produces 2 molecules of carbon dioxide, 1 molecule of ATP, ...
How many ATP molecules are produced in the last step of aerobic respiration?
In this phase, the large amounts of ATP molecules are produced by transferring the electrons from NADH and FADH. A single molecule of glucose creates a total of 34 ATP molecules.
What are the two types of respiration?
Respiration is of two types, aerobic respiration, and anaerobic respiration . Aerobic Respiration: It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals.
What is the energy released during the process of breaking the glucose molecule?
The 2900 kJ of energy is released during the process of breaking the glucose molecule and in turn, this energy is used to produce ATP – Adenosine Triphosphate molecules which are used by the system for various purposes. Aerobic respiration process takes place in all multicellular organisms including animals, plants and other living organisms.
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a process in which the cells utilize oxygen for the degradation of primary metabolites and release energy. It takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell and produces ATP ( Adenosine Triphosphate ).
Why is aerobic respiration important?
Aerobic respiration plays a significant role in releasing a lot of energy which helps in the survival of life. These are the following importance of aerobic respiration: It releases a large amount of energy in comparison to anaerobic respiration. It carries out a complete breakdown of glucose into carbon dioxide.
What are the two types of cellular respiration?
The cellular respiration is of two types, i.e. aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration . Aerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP. Anaerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen.
What is the process of breaking down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP?
Cellular respiration is the process where a cell breaks down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP. Cellular respiration can take place in the presence or absence of molecular oxygen. Aerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic respiration is a type ...
How does the cell get ATP?
Cellular respiration is the process where a cell breaks down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP.
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
It takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell and produces ATP ( Adenosine Triphosphate ).
What is the process of breakdown of primary metabolites in the cell with the release of energy in the form of?
The process of breakdown of primary metabolites (like glucose, protein, fatty acids, etc.) in the cell with the release of energy in the form of ATP is called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration takes place in the living cells of organisms.
What are the stages of aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration has four stages: Glycolysis, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain.
What is the process of respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a biological process that takes energy from glucose and other organic compounds to create a molecule called Adenosine TriPhosphate (ATP). ATP is then used as energy by nearly every cell in the body -- the largest user being the muscular system.
Where does glycolysis take place?
This step takes place within the cytosol of the cell, and is actually anaerobic, meaning it does not need oxygen. During glycolysis, which means breakdown of glucose, glucose is separated into two ATP and two NADH molecules, which are used later in the process of aerobic respiration. Advertisement.
How many turns of the citric acid cycle are needed to break down the original acetyl coenzy?
Two turns of the citric acid cycle are required to break down the original acetyl coenzyme A from the single glucose molecule. These two cycles create an additional two ATP molecules, as well as six NADH and two FADH molecules, all which are used later. Advertisement.
What is aerobic cellular respiration?
Aerobic cellular respiration refers to the process by which living organisms convert nutrients into energy for the body to use via the oxidization of nutrients. During aerobic respiration, catabolic reactions convert larger complex organic molecules into ATP, the chemical ...
Why is aerobic respiration important?
Aerobic respiration is fundamental as it allows for the production of ATP, the molecule that drives every physiological process in every known living organism. The high energy yield of aerobic respiration allows for complex multicellular life and is occurring all the time in every cell of the body.
What is the most basic metabolic pathway found in eukaryotic organisms?
Others hold that it is the body’s ability to stabilize levels of free radicals that determine lifespan, as free radicals are signaling molecules used for maintaining normal cell functioning. Aerobic cellular respiration is the most basic metabolic pathway found in eukaryotic organisms. Aerobic respiration is fundamental as it allows for ...
How many ATP molecules are produced by oxidation of NADH?
In actual cells though, energy is always lost due to heat dissipation and proton leakage, making the average total yield around 29-30 molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose. Oxidative phosphorylation marks the terminal point of the cellular respiration and the main sequence that accounts for the high ATP yield of aerobic cellular respiration.
How is pyruvate formed?
Once pyruvate is formed from glycolysis, the body still needs to process the pyruvate to access the chemical energy stored in its bonds. In the second step of cellular respiration, pyruvate molecules produced by glucose are transported to the cell’s mitochondria and are oxidized to produce acetyl-CoA, an enzyme the provides the acetyl base for ...
What is the first step in the chain of catabolic reactions?
Glycolysis is the first step in the chain of catabolic reactions the comprise the process of cellular respiration. During glycolysis, monosaccharides (simple sugars) such as glucose, sucrose, or fructose are converted into pyruvic acid. Incidentally, the word “glycolysis” literally means “splitting sugar.” The whole sequence of glycolysis is comprised out of 10 individual reactions, each of which is catalyzed by a different enzyme. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm, the jelly-like substance that fills the inside of cells. For every 1 molecule of glucose, glycolysis produces 2 molecules of pyruvate, 2 molecules of NADH, and 2 molecules of ATP.
What is the process of respiration?
In other words, respiration is the key way that a cell gets chemical energy to drive cellular activity. The process of aerobic respiration involves 4 main steps: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Each step involves the conversion of one or more chemical substances to utilize ...
Where does respiration occur?
The first stages of respiration occur in the cytoplasm of plant and animal cells, but most of the stages of respiration that release energy happen in the mitochondria. Microorganisms do not have mitochondria - they carry out respiration only in the cytoplasm.
Which organisms can respire anaerobically?
Some plants, microorganisms and fungi such as yeast can respire anaerobically - it's preferable to release less energy and make less ATP but remain alive.
Can anaerobic respiration occur without oxygen?
Anaerobic respiration. Most organisms cannot respire without oxygen but some organisms and tissues can continue to respire if the oxygen runs out. In conditions of low or no oxygen the process of anaerobic respiration occurs. The 'an' in 'anaerobic' means without.
How do cells get energy?
All cells need energy to survive. They obtain this energy by carrying a series of chemical reactions that are collectively known as respiration.
Is carbon dioxide a waste product of aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration breaks down glucose and combines the broken down products with oxygen, making water and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide is a waste product of aerobic respiration because cells do not need it.
Is glucose released during anaerobic respiration?
During anaerobic respiration, the oxidation of glucose is incomplete - not all of the energy can be released from the glucose molecule as it is only partially broken down. The reaction therefore releases much less energy than aerobic respiration - around only a nineteenth of the energy released during aerobic respiration. This means that fewer molecules of ATP can be made.
What is aerobic respiration?
Aerobic Respiration is the process by which the energy from glucose is released in the presence of oxygen. It takes place only if oxygen is available. ADVERTISEMENTS: For instance, if glucose were oxidized, the result would be energy, carbon dioxide and water. Take a look at the chemical formula given below.
What is the energy released during aerobic respiration?
In this stage of aerobic respiration, remaining energy from the glucose will be released by the electron transport chain. The network of electrons carrying proteins to the inner membrane of the cell is known as electron transport chain. Eventually, in this stage the electrons along with the protons will be added to oxygen.
What is the next stage of the cellular respiratory cycle?
This is the next stage of aerobic cellular respiratory. In Krebs cycle, private molecules are processed to release the energy that is stored between their molecular bonds. The energy is released in the form of ATP. This cycle is also called as the citric acid cycle.
How many stages of aerobic respiration are there?
There are three stages of aerobic respiration as given below:
What is the process of adding protons and electrons to oxygen?
Actually, when the protons are moved across the cell membrane, ATP is produced. This process is called as chemiosis. Cellular Respiration. Various Types of Cells (Bacterial Cells and Fungi Cell) | Biology.
