
The series of events in the process of inflammation are:
- Vasodilation: leads to greater blood flow to the area of inflammation, resulting in redness and heat.
- Vascular permeability: endothelial cells become “leaky” from either direct endothelial cell injury or via chemical...
What triggers an inflammatory response?
Nov 15, 2021 · Acute Inflammation is a general pattern of immune response to Cell Injury characterized by rapid accumulation of immune cells at the site of injury. The acute inflammatory response is initiated by both immune and parenchymal cells at the site of injury and is coordinated by a wide variety of soluble mediators.
How to dramatically reduce inflammation?
Also asked, what does acute inflammation mean? Acute inflammation is a short-term process occurring in response to tissue injury, usually appearing within minutes or hours. It is characterized by five cardinal signs: pain, redness, immobility (loss of function), swelling and heat. What are three signs of the inflammatory response? The four cardinal signs of inflammation …
What are the three phases of the inflammatory response?
Apr 13, 2022 · The inflammatory response (Fig. 1) consists of changes in blood flow, increased permeability of blood vessels, and the migration of fluids, proteins and white blood cells from the circulation to the site of tissue damage. Table of Contents What causes inflammation in the body? How is inflammation in the body measured? What causes inflammation?
What is the difference between acute and chronic inflammation?
Apr 14, 2022 · Acute inflammation is the early (almost immediate) response of a tissue to injury. It is nonspecific and may be evoked by any injury short of one that is immediately lethal. Acute inflammation may be regarded as the first line of defense against injury and is characterized by changes in the microcirculation: exudation of fluid and emigration of leukocytes from blood …
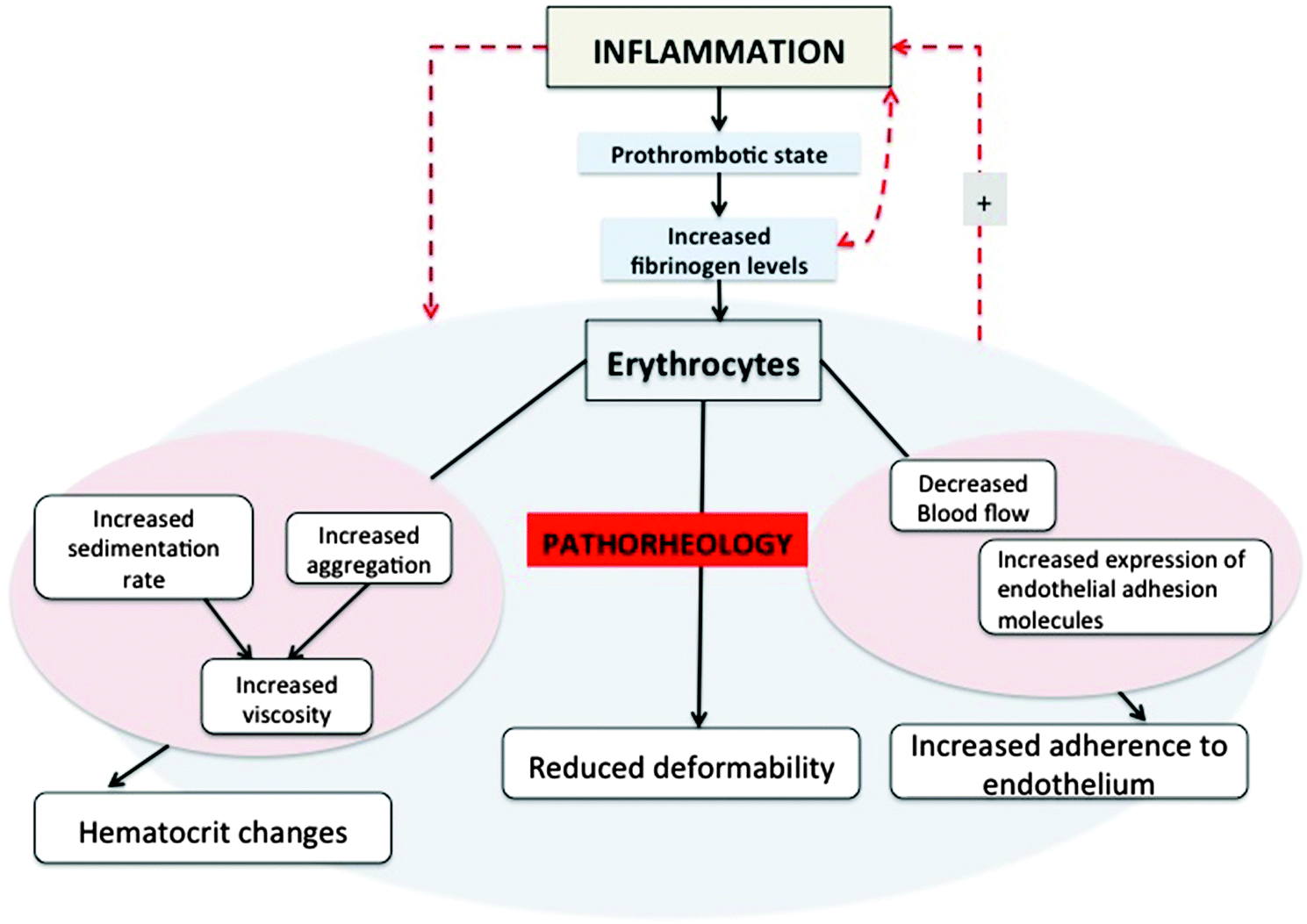
What is an acute inflammatory process?
Acute inflammation: The response to sudden body damage, such as cutting your finger. To heal the cut, your body sends inflammatory cells to the injury. These cells start the healing process. Chronic inflammation: Your body continues sending inflammatory cells even when there is no outside danger.Jul 28, 2021
What are the 4 steps of the inflammatory response?
The inflammatory response has four phases: inflammatory inducers (infection or tissue damage), inflammatory sensors (mast cells and macrophages), inflammatory mediators (cytokines, chemokines, etc.) and the tissues that are affected. Each phase has many options that are triggered based on the type pathogen introduced.
What are the 3 stages of inflammatory response?
The are three main stages of inflammation which can each vary in intensity and duration: Acute -swelling stage. Sub-acute – regenerative stage. Chronic – scar tissue maturation and remodelling stage.
What are the events of inflammatory response?
At the tissue level, inflammation is characterized by redness, swelling, heat, pain, and loss of tissue function, which result from local immune, vascular and inflammatory cell responses to infection or injury [5].
What are the 5 steps of the inflammatory response?
Inflammation is how your body responds to infection. Five cardinal signs characterize this response: pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Not all five cardinal signs are present in every case of inflammation.Jan 12, 2022
What are the signs of inflammation?
The five cardinal signs of inflammation are: 1. Rubor – Rubor or a redness of the injured or infected area is caused by increased blood flow. 2.
How long does it take for inflammation to subside?
Products are typically combined with carrier oils or other base ingredients. If inflammation symptoms don’t subside within 48 hours, it is wise to check with a healthcare professional to see if further treatment is needed. If untreated, acute inflammation may develop into chronic inflammation.
How to treat inflammation in the body?
Cannabis may provide relief in ingested or topical forms: 1 Ingested – Hemp or marijuana may be smoked, eaten in edibles, or used in teas and tinctures. 2 Topical – Topical hemp treatments are a good way to get relief from acute inflammation without some of the side-effects that may be present in NSAIDs and narcotic pain relievers. Hemp topicals can be found in creams, massage oil, or serum form. Hemp topicals made from the root of the hemp plant are especially effective at treating inflammatory pain, with the use of hemp root dating back to ancient China. It is important to note that hemp oil or any essential oil should not be placed directly on the skin. Products are typically combined with carrier oils or other base ingredients.
How to treat swelling and inflammation?
One of these natural ways you can treat inflammation pain and swelling is to elevate the area and apply an ice pack. It is also a good idea to drink plenty of water to help the healing progress. Diet also plays a role in natural inflammation pain relief.
What is the body's response to injury?
Acute inflammation is the body’s normal tissue response to injuries, foreign bodies and other outside factors. It is the defense mechanism of body tissue reacting to kick start the healing process. 1. Physical – Some of the physical causes of inflammation include frostbite, burns and injuries. 2.
What causes redness and inflammation?
4. Psychological – Blushing is a form of inflammation. It is usually caused by embarrassment, but other types of nervousness or emotional responses may also cause redness and inflammation.
What herbs help with inflammation?
Many of the culinary herbs such as cinnamon, cloves, oregano, and nutmeg help to fight inflammation. Cannabis is another plant that has been found to reduce inflammation and pain significantly. o Hemp/Marijuana – Both hemp and marijuana have both been found to reduce pain and inflammation.
What are the characteristics of acute inflammation?
The main characteristics of acute inflammation are the exudation of fluid, plasma proteins, and emigration of leukocytes (predominantly neutrophils) from blood into inflammatory site. On the other hand, chronic inflammation is of longer duration and is associated with the presence of lymphocytes and macrophages. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is the purpose of inflammation?
ADVERTISEMENTS: The main purpose of inflammation is to attract and accumulate leukocytes at the site of tissue injury (such as bacterial infection of a finger), leading to phagocytosis and killing of bacteria.
What is the function of the vascular endothelium?
Normally the vascular endothelium permits free exchange of water and small molecules between blood and tissue spaces; but limits the passage of plasma proteins (whose molecular sizes are large) from the blood into tissue spaces. But after tissue injury, the permeability of blood vessels in the injured area increases.
What is the role of phagocytosis in leukocytes?
Phagocytosis stimulates numerous intracellular events in leukocytes, such as burst in oxygen consumption, increased glucose oxidation and production of reactive oxygen metabolites (such as hydrogen peroxide and superoxide ion (O 2 -)}. In presence of a halide like Cl –, the H 2 O 2 is converted into HOCl – through an enzyme called myeloperoxidase. HOCl – is a powerful oxidant and antimicrobial agent capable of killing bacteria, fungus, protozoa, and virus. This mechanism is known as H 2 O 2 myeloperoxidase-halide system or myeloperoxidase- dependent killing.
What is the cytoplasm of a leukocyte?
Killing or Degradation of Bacteria: The cytoplasm of the leukocyte has numerous vesicles called lysosomes and the lysosomes contain a variety of hydrolytic enzymes (like acid phosphatase, glucoranidase, sulfatase, ribonuclease, and collagenase) capable of breaking down most proteins and carbohydrates.
