
Just four weeks after conception, the neural tube along your baby's back is closing. The baby's brain and spinal cord will develop from the neural tube. The heart and other organs also are starting to form.
Full Answer
What are the stages of development of a fetus?
Dates and staging are also "ideal", and there is significant biological variability in the general timing of events. Week 1 to Week 8 (GA10)are considered the embryonicperiod of development. Week 9 to week 37 (GA11-39) or birthare considered the fetalperiod of development. First month (4 weeks) after birth is the neonatalperiod of development.
What happens in the womb at 4 weeks?
In weeks 4 to 5 of early pregnancy, the embryo grows and develops within the lining of your womb. The outer cells reach out to form links with your blood supply. The inner cells form into 2, and then later into 3 layers. Each of these layers will grow to be different parts of your baby's body:
How long does it take for an embryo to develop?
Within 24 hours after fertilization, the egg that will become your baby rapidly divides into many cells. By the eighth week of pregnancy, the embryo develops into a fetus. There are about 40 weeks to a typical pregnancy. These weeks are divided into three trimesters.
What is the timing of the embryonic stage of pregnancy?
"Timing" refers to days from fertilization or post conception age (PC), not the clinical or gestational age ( GA) calculated from LMP (add 2 weeks). Dates and staging are also "ideal", and there is significant biological variability in the general timing of events. Week 1 to Week 8 ( GA 10)are considered the embryonic period of development.
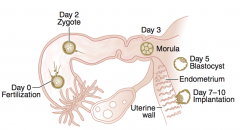
What happens in the first 4 weeks of fetal development?
The fertilized egg and your uterus are making contact this week in a process called implantation, as the blastocyst you'll one day call your baby begins to attach itself to the uterine lining. Up to 25 percent of the time, implantation bleeding will occur as that bundle of cells burrows its way into the uterine wall.
What does a fetus have at 4 weeks?
Baby at Week 4 During week 4 of pregnancy, the ball of cells is splitting into the embryo (your future child) and placenta. Baby's neural tube, the building block of the spine, brain and backbone, is already formed. The amniotic sac and fluid are forming into protective cushioning for baby.
What are the 4 stages of embryonic development in order?
The correct sequence of embryogenesis is Fertilization- cleavage- gastrulation- differentiation.
What happens to the embryo in the first week of pregnancy?
Baby: Now that your egg is fertilized, it burrows into the lining of your uterus. This is called implantation. It may happen up to 4 days after fertilization. Mom-to-be: You're probably expecting your period this week, and if it doesn't occur, it might be one of the first signs that you're pregnant.
Does a 4 week fetus have a heartbeat?
A fetal heartbeat may first be detected by a vaginal ultrasound as early as 5 1/2 to 6 weeks after gestation. That's when a fetal pole, the first visible sign of a developing embryo, can sometimes be seen. But between 6 1/2 to 7 weeks after gestation, a heartbeat can be better assessed.
Can you see a baby at 4 weeks?
Your baby is no longer a zygote or a single cell. The cells have multiplied rapidly and now the embryo is taking shape. There is not yet a clear sac on ultrasound scan. A Guide to each week of your pregnancy, with details on your baby's growth, your body and symptoms to look out for.
What occurs first during embryonic development?
The early stages of embryonic development begin with fertilization. The process of fertilization is tightly controlled to ensure that only one sperm fuses with one egg. After fertilization, the zygote undergoes cleavage to form the blastula.
What are the early stages of embryonic development?
The early stages of embryonic development, such as fertilization, cleavage, blastula formation, gastrulation, and neurulation, are crucial for ensuring the fitness of the organism. Fertilization is the process in which gametes (an egg and sperm) fuse to form a zygote.
What occurs during the embryonic stage of development?
During the embryonic stage, the heart begins to beat and organs form and begin to function. At 22 days after conception, the neural tube forms along the back of the embryo, developing into the spinal cord and brain.
What happens in the first 2 weeks of pregnancy?
Your weeks of pregnancy are dated from the first day of your last period. This means that in the first 2 weeks or so, you are not actually pregnant – your body is preparing for ovulation (releasing an egg from one of your ovaries) as usual. Your "getting pregnant" timeline is: day 1: the first day of your period.
What's happening at 3 weeks pregnant?
Implantation happens this week Your developing baby has travelled down the fallopian tube and is starting to implant itself in the lining of your uterus. At this time, 15 to 25 percent of women experience implantation bleeding, which is a light bleeding that happens about six to 12 days after conception.
What happens when you are 3 weeks pregnant?
We have an embryo! Your soon-to-be fetus is still a cluster of cells that are growing and multiplying. It's about the size of a pinhead. It takes about four days for your fertilized egg — now dubbed a blastocyst — to reach your uterus and another two to three days to implant.
Can you see anything in a 4 week ultrasound?
Stage Two: This is usually at four to five weeks after a pregnant woman's last period. The ultrasound commonly shows a small collection of fluid within the lining of the uterus that represents the early development of the gestational sac.
What week Does the fetus have a heartbeat?
A baby's cardiovascular system begins developing five weeks into pregnancy, or three weeks after conception. The heart starts to beat shortly afterward.
When does an embryo become a fetus?
At the end of the 10th week of pregnancy, your baby is no longer an embryo. It is now a fetus, the stage of development up until birth.
What week does the placenta begin to form?
Week 4 - implantation After some time, they will form the placenta (afterbirth). The inner group of cells will develop into the embryo. These inner cells form three layers at first.
Weeks 1 and 2: Getting Ready
It might seem strange, but you're not actually pregnant the first week or two of the time allotted to your pregnancy. Yes, you read that correctly!...
Week 3: Fertilization
The sperm and egg unite in one of your fallopian tubes to form a one-celled entity called a zygote. If more than one egg is released and fertilized...
Week 4: Implantation
The rapidly dividing ball of cells — now known as a blastocyst — has begun to burrow into the uterine lining (endometrium). This process is called...
Week 5: Hormone Levels Increase
The fifth week of pregnancy, or the third week after conception, the levels of HCG hormone produced by the blastocyst quickly increase. This signal...
Week 6: The Neural Tube Closes
Growth is rapid this week. Just four weeks after conception, the neural tube along your baby's back is closing. The baby's brain and spinal cord wi...
Week 7: Baby's Head Develops
Seven weeks into your pregnancy, or five weeks after conception, your baby's brain and face are growing. Depressions that will give rise to nostril...
Week 8: Baby's Nose Forms
Eight weeks into your pregnancy, or six weeks after conception, your baby's lower limb buds take on the shape of paddles. Fingers have begun to for...
Week 9: Baby's Toes Appear
In the ninth week of pregnancy, or seven weeks after conception, your baby's arms grow and elbows appear. Toes are visible and eyelids form. Your b...
Week 10: Baby's Elbows Bend
By the 10th week of pregnancy, or eight weeks after conception, your baby's head has become more round.Your baby can now bend his or her elbows. To...
Week 11: Baby's Genitals Develop
At the beginning of the 11th week of pregnancy, or the ninth week after conception, your baby's head still makes up about half of its length. Howev...
How long does it take for the respiratory system to develop?
The respiratory system begins forming at the very end of the fourth week, around 26 days after conception. First, the 2 primary lung buds grow. These lung buds become the left and right lung. By 4 ½ weeks, the major airways to the left and right lungs, called bronchi, have grown. These bronchi divide into three major lobes on the right and two major lobes on the left. 8 In the fifth week, the airways start branching repeatedly. This continues over the next ten to twelve weeks, until the airways have branched at least 17 times. After birth, these airways connect the alveoli, where air is exchanged in the lungs, to the windpipe and the external air. 9
What is the brain's function at the end of the fifth week?
By the end of the fifth week, the brain has separate right and left cerebral hemispheres, 4 and a cerebellum. The cerebral hemispheres will direct speech, decision making, movement, balance, vision, memory, and many other functions. The cerebellum will control muscle coordination.
What organs have started to form?
Almost all major organs have started to form, including the lungs, liver, kidneys, stomach, and pancreas.
When does the face become more recognizable?
The face becomes more recognizable in the fifth week after conception. Outgrowths from the forebrain become the optic nerve and the back of the eye. These cells interact with the outer surface of the embryo and form the eye’s lens. 5 The nose gets a pair of little depressions that will become the baby’s nostrils. The early mouth and tongue start taking shape. 6
When do lungs develop?
Illustration of the stages of lung development. The lungs start developing around the fourth week after conception. The lungs become progressively more branched and more able to exchange gases with the blood, so that the full-term newborn baby can breathe unaided. At birth, the baby will have developed 300 to 600 million alveoli, or about 1000 per alveolar sac. (Image Credit: Science Source)
Who wrote the book The Development and Shaping of the Brain?
Sandra Ackerman , The Development and Shaping of the Brain, Discovering the Brain (National Academies Press (US), 1992), https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK234146/.
How long does it take for a neuropore to close?
Neural - rostral (or cephalic) neuropore closes within a few hours; closure is bidirectional, it takes place from the dorsal and terminal lips and may occur in two areas simultaneously. The two lips, however, behave differently.
What is stage 11 thyroid?
Stage 11. thyroid - thyroid median endodermal thickening in the floor of pharynx. neural - rostral (or cephalic) neuropore closes within a few hours; closure is bidirectional, it takes place from the dorsal and terminal lips and may occur in two areas simultaneously. The two lips, however, behave differently.
What is stage 10 neural crest?
Stage 10. neural crest - differentiation at spinal cord level from day 22 until day 26. neural - neural folds begin to fuse near the junction between brain and spinal cord, when neural crest - cells are arising mainly from the neural ectoderm. neural crest - trigeminal, facial, and postotic ganglia components visible.
What is the fourth week of embryonic development?
These notes cover the fourth week of embryonic development, which is the beginning of organogenesis, (specific tissues and systems are beginning to differentiate) from the trilaminar embryo. On the embryo surface sensory placodes and limb buds appear. Sensory placodes (otic, lens, nasal) will form specific components of the ear, eye and nose.
Where do neural folds begin to fuse?
Neural - neural folds begin to fuse near the junction between brain and spinal cord, when Neural Crest - cells are arising mainly from the neural ectoderm
When should I reach out to my healthcare provider about a new pregnancy?
Most healthcare providers will have you wait to come in for an appointment until you have had a positive home pregnancy test. These tests are very accurate once you have enough hCG circulating throughout your body. This can be a few weeks after conception. It’s best to call your healthcare provider once you have a positive pregnancy test to schedule your first appointment.
How does conception work?
Each month, your body goes through a reproductive cycle that can end in one of two ways. You will either have a menstrual period or become pregnant. This cycle is continuously happening during your reproductive years — from puberty in your teen years to menopause around age 50.
What happens right after conception?
Within 24 hours after fertilization, the egg begins rapidly dividing into many cells. It remains in the fallopian tube for about three days after conception. Then the fertilized egg (now called a blastocyte) continues to divide as it passes slowly through the fallopian tube to the uterus. Once there, its next job is to attach to the endometrium. This is called implantation.
How early can I know I’m pregnant?
It’s also the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. Even though this hormone is there from the beginning, it takes time for it to build within your body. It typically takes three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for the hCG to increase enough to be detected by pregnancy tests.
What happens to the oocytes during pregnancy?
In a cycle that ends with pregnancy, there are several steps. First, a group of eggs (called oocytes) gets ready to leave the ovary for ovulation (release of the egg). The eggs develop in small, fluid-filled cysts called follicles. Think of these follicles as small containers for each immature egg. Out of this group of eggs, one will become mature and continue on through the cycle. This follicle then suppresses all the other follicles in the group. The other follicles stop growing at this point.
What does 38 6/7 mean?
This stands for how many days you currently are in the gestational week. So, if you see 38 6/7, it means that you are on day 6 of your 38th week. The last few weeks of pregnancy are divided into the following groups:
How long does it take for a baby to develop a ball?
Within three weeks, the blastocyte cells ultimately form a little ball, or an embryo. By this time, the baby’s first nerve cells have formed. Your developing baby has already gone through a few name changes in the first few weeks of pregnancy.
How does the placenta help the baby?
Cells from the placenta grow deep into the wall of the womb, establishing a rich blood supply. This ensures the baby receives all the oxygen and nutrients it needs.
What is the outer layer of the embryo?
the outer layer becomes the brain and nervous system, the eye lenses, tooth enamel, skin and nails. In these early weeks of pregnancy, the embryo is attached to a tiny yolk sac that provides nourishment. A few weeks later, the placenta will be fully formed and take over the transfer of nutrients to the embryo.
What is Start4Life about?
The Start4Life site has more about you and your baby at 4 weeks of pregnancy. You can sign up for Start4Life's weekly emails for expert advice, videos and tips on pregnancy, birth and beyond.
How to close a modal window?
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
How do you know if you are pregnant at 4 weeks?
In the first 4 weeks of pregnancy, you probably will not notice any symptoms. The first thing most women notice is that their period does not arrive, or they may have other signs and symptoms of pregnancy, such as breast tenderness. Most women confirm the pregnancy with a pregnancy test. You can work out the date when your baby is due.
What are the layers of a baby's body?
Each of these layers will grow to be different parts of the baby's body: the inner layer becomes the breathing and digestive systems, including the lungs, stomach, gut and bladder. the middle layer becomes the heart, blood vessels, muscles and bones. the outer layer becomes the brain and nervous system, the eye lenses, tooth enamel, skin and nails.
What are the different layers of the human body?
Each of these layers will grow to be different parts of the baby's body: 1 the inner layer becomes the breathing and digestive systems, including the lungs, stomach, gut and bladder 2 the middle layer becomes the heart, blood vessels, muscles and bones 3 the outer layer becomes the brain and nervous system, the eye lenses, tooth enamel, skin and nails
What happens at the end of the proliferative phase?
At the end of the proliferative phase, the Graafian follicle ruptures under the influence of luteinizing hormone, releasing the secondary oocyte. Recall that oocytes are immobile and consequently rely on the fimbriae of the fallopian tubes to sweep it into the ampulla. Several things occur during this period: 1 The walls of the Graafian follicle involute and form the corpus luteum. 2 Increased progesterone secreted from the corpus luteum results in engorgement of the epithelial glands of the endometrial lining. 3 The secondary oocyte enters the ampulla of the fallopian tube, where it awaits fertilization. Whether or not fertilization occurs, the oocyte moves toward the uterine cavity via peristaltic forces of the tube.
What is the primary oocyte?
The primary oocytes are also enclosed within a thin layer of flat cells known as granulosa (follicular) cells. These cells are responsible for stalling the meiotic process until the onset of puberty. The primary oocyte and granulosa layer are collectively referred to as the primordial follicle.
Which axis of the uterus is responsible for oocyte maturation?
The hypothalamic – pituitary – gonadal axis not only promotes oocyte maturation, but it also acts on the endometrial lining of the uterus in order to prepare it for possible implantation. This is a cyclical process that occurs each month and is characterised by proliferation and shedding of the endometrial lining. The overall process is called the menstrual or endometrial cycle.
Which axis influences the maturation of the follicle and oocyte?
The hypothalamic – pituitary – gonadal axis also influences the maturation of the follicle and oocyte. Primary follicle (histological slide) The primary oocyte only completes meiosis I after ovulation has occurred (i.e. the oocyte has been extruded from the follicle.
How long does the period last?
Menstrual phase. Day one of the cycle is marked by shedding of the inner lining of the uterus and usually lasts for about 5 to 7 days. This occurs as a result of a reduction in progesterone in cases where fertilization does not occur.
How many follicles are there in a female?
At birth, there are roughly 2 million primordial follicles within the ovaries of the female infant. About 98% of these follicles will be reabsorbed during childhood; and of the remaining 2%, only about 400 primordial follicles will mature over the reproductive lifespan of the individual (i.e. from menarche to menopause). Also note that the use of chemical contraceptive methods (pills, patches, injections) significantly reduces the amount of follicles that mature.
What is the difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
There are staunch differences between spermatogenesis (the development of male gametes ) and oogenesis (development of female gametes). Spermatogenesis commences at the onset of puberty with the aid of hormones from the hypothalamic – pituitary – gonadal axis. The chief hormone that stimulates spermatogenesis is testosterone. It is produced by Leydig cells within the testes and acts on the sertoli cells within the seminiferous tubules (also in the testes).
What is the Y shape of the hip bones?
In the acetabulum the three hip bones are separated by a Y-shaped cartilage until after puberty. In this cartilage between the ilium and pubis the "os acetabuli" appears between the ninth and twelfth years. This bone, variable in size, forms a greater or less part of the pubic portion of the articular cavity.
What is clinical week?
Clinical weeks (shown in brackets) or Gestational Age GA) is from the first day of the Last Menstrual Period (LMP). "Stages" refer to the Carnegie stages of development. "Timing" refers to days from fertilization or post conception age (PC), not the clinical or gestational age (GA) calculated from LMP (add 2 weeks).
Where is the epiphysis of the first metatarsal?
The epiphysis of the 1st metatarsal appears at the proximal end of the bone: the other epiphyses arise at the distal ends of the metatarsals. There may be a distal epiphysis in the first metatarsal also.2In some instances a proximal epiphysis is formed on the tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal (Gruber).
When does ossification occur?
Ossification begins generally in the 13th - 14th years, and may not take place until after middle life (Thilenius). For table of relative frequency in the embryo and adult see p. 385. Days and weeks refer to the prenatal, years to the postnatal period. M= male F= female.
Is the iliac body discoid?
Iliac body is discoid. The growth rate was greater in the ilium than in the sacrum-coccyx, pubis, and ischium. 23. Articulation of the pubic symphysis, connection of the articular column in the sacrum, and Y-shape connection of the three parts of the hip bones to the acetabulum.
