What causes a longer luteal phase?
A long phase means that the body continues to produce high levels of progesterone for more than 16 days past ovulation. Here are two common causes of a long luteal phase. Pregnancy; If your secretory phase is longer than 16 days, you may want to take a pregnancy test.
What is the difference between the luteal phase and ovulation?
The luteal phase and ovulation are both different parts of a woman's monthly cycle. A luteal phase is the time period ranging from the first day of ovulation to the day before the menstrual period starts. Ovulation occurs once a month when a woman releases an egg from her ovarian follicle, which travels through the fallopian tube.
Is a 10 day luteal phase too short?
When the luteal phase lasts for 10 days or less, it is known as a short luteal phase or a luteal phase defect. A woman with a short luteal phase may have a harder time getting or staying pregnant. Her body will not have as much progesterone as a woman with a longer luteal phase.
Is a very long luteal phase bad?
Most women experience a luteal phase between 10-16 days, with 14 days being very common. A long luteal phase is when the body continues to produce increased levels of progesterone for more than 16 days after ovulation. Long luteal phases are very rare, but can affect fertility and conception planning.
Can you get pregnant during the luteal phase?
Can you get pregnant in the luteal phase? Yes, however, once you've ovulated the egg can only survive for 12-24 hours, you can only get pregnant in the first day of the luteal phase.
What happens to hormone levels during luteal phase?
Luteal Phase This part of the Ovulation Cycle lasts approximately 14 days. In this phase, the dominant hormone of the Follicular Phase estrogen declines and progesterone levels increase.
What does discharge look like during luteal phase?
It's filled with fluid and cells that are being shed from the vagina and may even look slightly yellow at times. This part of your menstrual cycle is called the luteal phase. It's when the hormone progesterone peaks in your body. When estrogen is the dominant hormone, discharge tends to be clear, stretchy, or watery.
What are symptoms of the luteal phase?
Luteal phasebloating.breast swelling, pain, or tenderness.mood changes.headache.weight gain.changes in sexual desire.food cravings.trouble sleeping.
Which day is the progesterone level the highest?
Progesterone levels rise after ovulation and peak five to nine days after your luteal phase–which occurs during the second half of the menstrual cycle, after ovulation occurs–so progesterone level is usually checked six to eight days after you ovulate (about day 21 of a day 28 cycle).
When is a woman's testosterone highest?
Estrogen and testosterone peak around the 14th day of the cycle (when most women are ovulating), when you'll probably feel frisky because Mother Nature's ultimate goal is to get you pregnant.
When is estrogen highest in cycle?
Estrogen levels rise and fall twice during the menstrual cycle. Estrogen levels rise during the mid-follicular phase and then drop precipitously after ovulation. This is followed by a secondary rise in estrogen levels during the mid-luteal phase with a decrease at the end of the menstrual cycle.
When does estrogen drop in your cycle?
The PMS cycle Estrogen rises during the first half of the menstrual cycle and drops during the second half. In some women, serotonin levels stay mostly steady. But in women with PMS, serotonin drops as estrogen drops. This means serotonin is lowest in the 2 weeks before the period.
When does the luteal phase end?
The luteal phase begins as the egg starts traveling down the fallopian tube. This phase ends when your next period begins.
How long does luteal phase last?
Trusted Source. , the luteal phase lasts 12 to 14 days. Your luteal phase is considered to be short if it lasts less than 10 days. In other words, you have a short luteal phase if you get your period 10 days or less after you ovulate.
What does it mean when your luteal phase is short?
A short luteal phase can be a sign of a condition called luteal phase defect ( LPD). In LPD, the ovary produces less progesterone than usual. Or, the uterine lining doesn’t grow in response to progesterone like it should. LPD can lead to infertility and miscarriage.
Why does BBT go up when you ovulate?
When you ovulate, your BBT will go up because progesterone stimulates heat production in your body. Once you’re in the luteal phase of your cycle, your basal body temperature should be about 1°F higher than it was during the follicular phase.
Why do women have a short luteal phase?
In one study, women with a short luteal phase were more likely to smoke than those with a longer phase. Smoking might shorten this phase by reducing your body’s estrogen and progesterone production.
What is the second half of the menstrual cycle?
The luteal phase is the second half of your menstrual cycle. It starts after ovulation and ends with the first day of your period. Once the follicle has released its egg, the egg travels down the fallopian tube, where it may come in contact with sperm and be fertilized. The follicle itself then changes.
What happens to the follicle when it is empty?
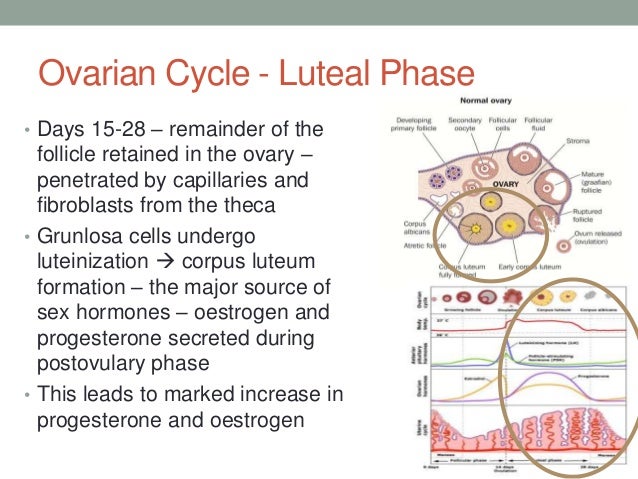
The follicle itself then changes. The empty sac closes off, turns yellow, and transforms into a new structure called the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum releases progesterone and some estrogen. Progesterone thickens the lining of your uterus so that a fertilized egg can implant.
What is the menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle is the cycle of hormones that control our periods (and lots of other things in our bodies)
What are the different phases of our menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle can be divided in various ways. This depends on whether you are looking at what is happening in the uterus (womb) or the ovaries. The different names for the different phases can get very confusing and very ‘medical’ so we are going to try and avoid that.
The luteal phase
The luteal phase follows ovulation and ends when your next period starts. It is often referred to as the “second half” of the cycle. The luteal phase is often the part of the cycle when people notice the most symptoms. These can be physical or psychological and are caused by the hormonal changes.
What next?
Hopefully, you now have a better idea of what is happening during your menstrual cycle. The more we know about how our bodies work then the easier it is to manage the tricky symptoms they throw at us.
Katherine Maslowski
Katherine is a junior doctor from New Zealand who has experience working in Obstetrics and Gynaecology and is currently studying an MSc in Women’s Health. She is passionate about women’s health and empowering women to learn about their bodies and understand how they work.
Be the first one to know when we launch!
We can help you work out if your hormones are working against you, and support you to get them back on your side. Sign up to be the first one to know when we launch!
What are the phases of the menstrual cycle?
Your menstrual cycle has two phases: the follicular phase and the luteal phase. Follicles mature during the first stage and one follicle starts dominating, (usually) culminating in the release of one egg during ovulation. The follicular phase is controlled by FSH, follicle stimulating hormone. While follicles compete for domination, the lining of the uterus also grows in order to provide a cushy environment for the egg if it is fertilized.
How many periods do women have?
They're mildly annoying for some, and devastatingly annoying to those who have to take painkillers and call in sick every month. The average woman has about 300 menstrual periods in her lifetime. Most of us have a rough idea of the length of our menstrual cycles, and we also know that we ovulate somewhere between two periods. Most of all, though, we know that we don't really like menstruating.
What hormone is triggered by ovulation?
Ovulation is triggered by LH, luteinizing hormone. This hormone is suppressed by estradiol during the follicular phase, but when that hormone reaches certain levels estrogen starts dominating instead. This, in turn, triggers the release of LH from the pituitary gland. The LH surge signifies the start of ovulation, and it's this surge that you detect if you use ovulation predictor kits. Once it takes place, you have 12 to 24 hours before the egg starts disintegrating.
Can you get pregnant in the luteal phase?
The luteal phase is the second half of that cycle. When you're in your luteal phase, you can't get pregnant — yet knowing all about it can help you plan for pregnancy more accurately.
How Long is the Luteal Phase?
While the follicular phase, or first half, of the menstrual cycle can vary in length, in most women, the luteal phase is consistently about 14 days long.
What is the role of the embryo in the development of the placenta?
The early embryo begins to make human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), which maintains the corpus luteum and progesterone production . The corpus luteum will sustain the uterine lining and pregnancy until the placenta develops.
Which organ secretes progesterone and estrogen?
The corpus luteum secretes progesterone and estrogen that cause the uterine lining, or endometrium, to thicken and be able to nourish a fertilized egg.
What happens if an embryo is not fertilized?
If the egg is not fertilized and an embryo does not implant, the corpus luteum deteriorates, and progesterone levels will fall. Without progesterone, the endometrium isn’t maintained and the uterus will start to shed its lining, resulting in menstruation.
How Long Is The Luteal Phase?
The average luteal phase is 12 to 14 days long, but it can last 10 to 17 days. You’ll often read that 14 days is normal. This standard is based on a 28-day cycle, but menstrual cycles vary greatly.
What Are the Luteal Phase Signs And Symptoms?
When progesterone levels drop during the luteal phase, some women experience physical and mental symptoms. These issues are better known as premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms and include:
What Is A Luteal Phase Defect?
A luteal phase deficiency or defect is when uterine lining doesn’t thicken properly. It’s a potential fertility problem because an egg cannot implant if the lining isn’t thick enough. This can happen if:
What hormones are needed for luteal phase?
Knowing as much as possible about your menstrual cycle is essential. The chart above shows different hormone levels throughout your cycle. Progesterone is crucial for the luteal phase. For women trying to conceive (TTC), it’s important to know about progesterone levels because:
What phase of menstruation follows ovulation?
The luteal phase of your menstrual cycle immediately follows ovulation. Below you’ll learn all about:
How long does a menstrual cycle last?
This standard is based on a 28-day cycle, but menstrual cycles vary greatly. Some medical sources say cycles may last 21 to 35 days long. Others state 21 to 45 days is normal. This makes it hard to know how long your luteal phase is and when the phase occurs.
When does progesterone peak?
Progesterone peaks halfway through the luteal phase. The corpus luteum dissolves if there is no fertilized egg or implantation. This causes progesterone levels to drop ( learn more on your period and progesterone here ). The luteal phase ends when your period begins. The first day of your period is the first day of the follicular phase, ...
What happens during the menstrual cycle?
During each menstrual cycle, an egg develops and is released from the ovaries. The lining of the uterus builds up. If a pregnancy doesn’t happen, the uterine lining sheds during a menstrual period. Then the cycle starts again. A woman’s menstrual cycle is divided into four phases: menstrual phase. follicular phase.
How many phases are there in the menstrual cycle?
A woman’s menstrual cycle is divided into four phases: menstrual phase. follicular phase. ovulation phase. luteal phase. The length of each phase can differ from woman to woman, and it can change over time.
What hormones are released during ovulation?
Ovulation phase. Rising estrogen levels during the follicular phase trigger your pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone (LH). This is what starts the process of ovulation. Ovulation is when your ovary releases a mature egg. The egg travels down the fallopian tube toward the uterus to be fertilized by sperm.
What happens when a follicle matures?
The maturing follicle sets off a surge in estrogen that thickens the lining of your uterus. This creates a nutrient-rich environment for an embryo to grow.
Why does my period shed blood?
Because pregnancy hasn’t taken place, levels of the hormones estrogen and progesterone drop. The thickened lining of your uterus, which would support a pregnancy, is no longer needed, so it sheds through your vagina. During your period, you release a combination of blood, mucus, and tissue from your uterus.
How many follicles do ovaries produce?
This hormone stimulates your ovaries to produce around 5 to 20 small sac s called follicles. Each follicle contains an immature egg. Only the healthiest egg will eventually mature. (On rare occasions, a woman may have two eggs mature.) The rest of the follicles will be reabsorbed into your body.
Why does my period stop?
These noncancerous growths in your uterus can make your periods longer and heavier than usual. Eating disorders. Anorexia, bulimia, and other eating disorders can disrupt your menstrual cycle and make your periods stop. Here are a few signs of a problem with your menstrual cycle:
