
What are the major causes of type 2 diabetes?
What causes type 2 diabetes?
- Overweight, obesity, and physical inactivity. You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are not physically active and are overweight or obese.
- Insulin resistance. Type 2 diabetes usually begins with insulin resistance, a condition in which muscle, liver, and fat cells do not use insulin well.
- Genes and family history. ...
What to do when you have type 2 diabetes?
- Don't beat yourself up about it. It's natural to ask yourself—"What did I do?" The important part is to move past this. ...
- Don't panic. Many people are horrified when they hear the word diabetes. ...
- Don't be too rigid about treatment options. You may feel that you never want to take oral medication or insulin. ...
What is the best treatment for type 2 diabetes?
Which Foods Fight Diabetes?
- Dark green leafy vegetables. They’re low in calories and carbs, and high in nutrition. ...
- Berries. To satisfy your sweet tooth, pick berries. ...
- Fatty fish. Aim to eat fish twice a week. ...
- Beans. They’re good for your heart -- and your diabetes. ...
- Milk and yogurt. Dairy products provide vitamin D, which may help your insulin work better. ...
- Citrus fruits. ...
What should I eat if I have type 2 diabetes?
You should:
- eat a wide range of foods – including fruit, vegetables and some starchy foods like pasta
- keep sugar, fat and salt to a minimum
- eat breakfast, lunch and dinner every day – do not skip meals
See more
What actually happens in type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is an impairment in the way the body regulates and uses sugar (glucose) as a fuel. This long-term (chronic) condition results in too much sugar circulating in the bloodstream. Eventually, high blood sugar levels can lead to disorders of the circulatory, nervous and immune systems.
What is the difference between type 2 diabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease. It is characterized by high levels of sugar in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is also called type 2 diabetes mellitus and adult-onset diabetes. That's because it used to start almost always in middle- and late-adulthood.
What is the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus?
The pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by peripheral insulin resistance, impaired regulation of hepatic glucose production, and declining β-cell function, eventually leading toβ -cell failure.
What is Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications?
Type 2 diabetes is a disease that prevents someone from properly regulating their blood glucose levels. The pancreas produces a hormone called insulin, which regulates the level of glucose in a person's blood. Insulin helps glucose present in the blood enter cells in the body.
Can Type 2 diabetes mellitus be reversed?
According to recent research, type 2 diabetes cannot be cured, but individuals can have glucose levels that return to non-diabetes range, (complete remission) or pre-diabetes glucose level (partial remission) The primary means by which people with type 2 diabetes achieve remission is by losing significant amounts of ...
What is the mechanism of diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is a syndrome with disordered metabolism and inappropriate hyperglycemia due to either a deficiency of insulin secretion or to a combination of insulin resistance and inadequate insulin secretion to compensate.
Which of the following is characteristic of type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss.
What is the disease process of diabetes mellitus?
With diabetes, your body doesn't make enough insulin or can't use it as well as it should. When there isn't enough insulin or cells stop responding to insulin, too much blood sugar stays in your bloodstream. Over time, that can cause serious health problems, such as heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease.
What is difference between diabetes and diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is more commonly known simply as diabetes. It's when your pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin to control the amount of glucose, or sugar, in your blood. Diabetes insipidus is a rare condition that has nothing to do with the pancreas or blood sugar.
What does mellitus mean in diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease, involving inappropriately elevated blood glucose levels. DM has several categories, including type 1, type 2, maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY), gestational diabetes, neonatal diabetes, and secondary causes due to endocrinopathies, steroid use, etc.
What are the 3 types of diabetes mellitus?
There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant).Type 1 Diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake). ... Type 2 Diabetes. ... Gestational Diabetes.
What is the meaning of mellitus?
: a variable disorder of carbohydrate metabolism caused by a combination of hereditary and environmental factors and usually characterized by inadequate secretion or utilization of insulin, by excessive urine production, by excessive amounts of sugar in the blood and urine, and by thirst, hunger, and loss of weight — ...
What is the most common type of diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) accounts for around 90% of all cases of diabetes. In T2DM, the response to insulin is diminished, and this is defined as insulin resistance. During this state, insulin is ineffective and is initially countered by an increase in insulin production to maintain glucose homeostasis, but over time, insulin production decreases, resulting in T2DM. T2DM is most commonly seen in persons older than 45 years. Still, it is increasingly seen in children, adolescents, and younger adults due to rising levels of obesity, physical inactivity, and energy-dense diets.
How to diagnose diabetes?
Diabetes can be diagnosed either by the hemoglobin A1C criteria or plasma glucose concentration (fasting or 2-hour plasma glucose).
Why is T2DM a fetal condition?
T2DM is caused due to duel defects in insulin resistance and insulin secretion. Gestational diabetes is associated with maternal as well as fetal complications. Exercise and a healthy diet are beneficial in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
What is monogenic diabetes?
A single genetic mutation in an autosomal dominant gene causes this type of diabetes. Examples of monogenic diabetes include conditions like neonatal diabetes mellitus and maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY). Around 1 to 5% of all diabetes cases are due to monogenic diabetes. MODY is a familial disorder and usually presents under the age of 25 years.
What percentage of diabetes is T1DM?
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) accounts for 5% to 10% of DM and is characterized by autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the islets of the pancreas. As a result, there is an absolute deficiency of insulin.
What is DM in medical terms?
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by persistent hyperglycemia. It may be due to impaired insulin secretion, resistance to peripheral actions of insulin, or both.
What are the risk factors for GDM?
Even after birth, such infants may have respiratory distress syndrome and subsequent childhood and adolescent obesity. Older age, obesity, excessive gestational weight gain, history of congenital anomalies in previous children, or stillbirth, or a family history of diabetes are risk factors for GDM. Monogenic Diabetes.
What Is It?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease. It is characterized by high levels of sugar in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is also called type 2 diabetes mellitus and adult-onset diabetes. That's because it used to start almost always in middle- and late-adulthood. However, more and more children and teens are developing this condition. Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1 diabetes, and is really a different disease. But it shares with type 1 diabetes high blood sugar levels, and the complications of high blood sugar.
Why is glucose important for the body?
Glucose is a critically important source of energy for the body's cells. To provide energy to the cells, glucose needs to leave the blood and get inside the cells. To continue reading this article, you must log in.
Does Harvard Health Publishing have archived content?
As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Is type 2 diabetes more common than type 1 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1 diabetes, and is really a different disease. But it shares with type 1 diabetes high blood sugar levels, and the complications of high blood sugar. During digestion, food is broken down into basic components.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes?
Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas that acts like a key to let blood sugar into the cells in your body for use as energy. If you have type 2 diabetes, cells don’t respond normally to insulin; this is called insulin resistance. Your pancreas makes more insulin to try to get cells to respond. Eventually your pancreas can’t keep up, and your blood sugar rises, setting the stage for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar is damaging to the body and can cause other serious health problems, such as heart disease , vision loss, and kidney disease.
How long does it take for Type 2 diabetes to show up?
Type 2 diabetes symptoms often develop over several years and can go on for a long time without being noticed (sometimes there aren’t any noticeable symptoms at all). Because symptoms can be hard to spot, it’s important to know the risk factors and to see your doctor to get your blood sugar tested if you have any of them.
How to check blood sugar?
Recognize the signs of high or low blood sugar and what to do about it. If needed, give yourself insulin by syringe, pen, or pump. Monitor your feet, skin, and eyes to catch problems early. Buy diabetes supplies and store them properly.
How does diabetes affect children?
Childhood obesity rates are rising, and so are the rates of type 2 diabetes in youth. More than 75% of children with type 2 diabetes have a close relative who has it, too. But it’s not always because family members are related; it can also be because they share certain habits that can increase their risk. Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family: 1 Drinking more water and fewer sugary drinks 2 Eating more fruits and vegetables 3 Making favorite foods healthier 4 Making physical activity more fun
How many children with diabetes have a close relative?
More than 75% of children with type 2 diabetes have a close relative who has it, too. But it’s not always because family members are related; it can also be because they share certain habits that can increase their risk. Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family:
How can parents help prevent diabetes?
Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family: Drinking more water and fewer sugary drinks. Eating more fruits and vegetables. Making favorite foods healthier. Making physical activity more fun.
Can you take insulin if you have diabetes?
You may be able to manage your diabetes with healthy eating and being active, or your doctor may prescribe insulin, other injectable medications, or oral diabetes medicines to help manage your blood sugar and avoid complications. You’ll still need to eat healthy and be active if you take insulin or other medicines. It’s also important to keep your blood pressure and cholesterol close to the targets your doctor sets for you and get necessary screening tests.
Who is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes?
You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are age 45 or older, have a family history of diabetes, or are overweight or obese. Diabetes is more common in people who are African American, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian, Asian American, or Pacific Islander.
How do health care professionals diagnose type 2 diabetes?
Your health care professional can diagnose type 2 diabetes based on blood tests. Learn more about blood tests for diabetes and what the results mean.
How can I manage my type 2 diabetes?
Managing your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol, and quitting smoking if you smoke, are important ways to manage your type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes that include planning healthy meals, limiting calories if you are overweight, and being physically active are also part of managing your diabetes. So is taking any prescribed medicines. Work with your health care team to create a diabetes care plan that works for you.
What health problems can people with diabetes develop?
Following a good diabetes care plan can help protect against many diabetes-related health problems. However, if not managed, diabetes can lead to problems such as
How to reduce risk of diabetes type 2?
Here are some things you can do to lower your risk: Lose weight if you are overweight, and keep it off.
How to reduce calories in diabetics?
Choosing foods with less fat is another way to reduce calories. Drink water instead of sweetened beverages. Ask your health care team what other changes you can make to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes. Most often, your best chance for preventing type 2 diabetes is to make lifestyle changes that work for you long term.
What are the problems that can be caused by diabetes?
However, if not managed, diabetes can lead to problems such as. heart disease and stroke. nerve damage. kidney disease. foot problems. eye disease. gum disease and other dental problems. sexual and bladder problems. Many people with type 2 diabetes also have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
How to reduce risk of diabetes type 2?
If you have prediabetes, losing a small amount of weight if you’re overweight and getting regular physical activity can lower your risk for developing type 2 diabetes. A lifestyle change program offered through the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program can help you make those changes—and make them stick.
What are the factors that increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes?
Diabetes Factors. If you have type 2 diabetes, your body doesn’t use insulin well and can’t keep blood sugar at normal levels. We don’t know exactly why this happens, but we do know factors that may increase a person’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes. You may be at risk if you: Have prediabetes. Are overweight.
Why is visceral fat important?
Having too much visceral fat may increase the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
How much does a type 2 diabetes test lower your risk?
Through the program, you can lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes by as much as 58% (71% if you’re aged 60 years or older). Take the 1-minute test to see if you may be at risk of prediabetes.
What happens if you have too much visceral fat?
Having too much visceral fat may increase the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
How old do you have to be to be at risk for diabetes?
You may be at risk if you: Have prediabetes. Are overweight. Are 45 years or older. Have a parent, brother, or sister with type 2 diabetes. Are physically active for less than 150 minutes a week. Have ever had gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy) or given birth to a baby who weighed more than 9 pounds.
What is DSMES in diabetes?
If you have diabetes, getting support and education is critical. Diabetes self-management education and support (DSMES) services can help you stay healthy and thrive with diabetes.
Why is high blood glucose dangerous?
That’s because high blood glucose can damage your cardiovascular system. People with diabetes are two to four times more likely to die from heart disease than people who don’t have diabetes. They’re also one and a half times more likely to experience a stroke. The warning signs of stroke include:
How to manage diabetes complications?
These complications can potentially lower your quality of life and increase your chances of early death. Fortunately, you can take steps to manage diabetes and lower your risk for complications. A treatment plan may include lifestyle changes, such as a weight loss program or increased exercise.
How to lower your risk of skin conditions?
To lower your risk of skin conditions, follow your recommended diabetes treatment plan and practice good skincare. A good skincare routine includes: keeping your skin clean and moisturized. routinely checking your skin for injuries. If you develop symptoms of a skin condition, make an appointment with your doctor. 2.
What are the complications of diabetes?
Skin conditions. Uncontrolled diabetes can cause an increased risk of bacterial and fungal skin infections. Diabetes-related complications can cause one or more of the following skin symptoms: pain. itchiness. rashes, blisters, or boils. styes on your eyelids.
What happens if you have diabetes?
Uncontrolled diabetes increases your chances of developing several eye conditions, including: glaucoma, which happens when pressure builds up in your eye. cataracts, which occur when the lens of your eye becomes cloudy. retinopathy, which develops when blood vessels in the back of your eye become damaged.
What hormones are produced in the pancreas?
Overview. Insulin is a hormone that’s produced in the pancreas. If you have type 2 diabetes, your body’s cells do not correctly respond to insulin. Your pancreas then produces additional insulin as a response. This causes your blood sugar to rise, which can cause diabetes.
How to maintain your eyesight after diabetes?
Fortunately, early diagnosis and treatment can help you maintain your eyesight. In addition to following your recommended diabetes treatment plan, make sure to schedule regular eye exams. If you notice changes in your vision, make an appointment with your eye doctor. 3.
How to tell if you have diabetes?
High Blood Sugar Level. One of the signs of untreated diabetes is high blood sugar. When you visit your doctor, they will measure your blood sugar and let you know what range your blood glucose should fall in. Healthy blood sugar levels are usually between 70 and 130 mg/dL before meals and below 180 mg/dl two hours after meals.
How does diabetes affect the urine?
With diabetes, excess glucose ends up in the urine, where it pulls more water and results in more urine. How Type 2 Diabetes Affects the Urinary Tract.
How often do diabetics urinate?
Another common symptom of untreated diabetes is increased urination (polyuria). A person is diagnosed with polyuria when they urinate a minimum of 3 L daily. It is different from urinary frequency, which is the number of times someone pees in a day.
What is untreated diabetes?
Untreated diabetes is when your high blood sugar level isn’t properly controlled. This is not always a result of someone deciding not to manage their diabetes. It can also happen to those who have diabetes but have not been diagnosed.
What is the cause of diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when your blood sugar, also called blood glucose, is too high (also known as hyperglycemia ). Blood glucose is your main source of energy and comes from the food you eat.
Why is my vision blurry?
Blurred Vision. High blood sugar levels in uncontrolled diabetes can damage small blood vessels, including those in your eyes. This can affect the blood vessels connected to the retina, a layer of tissue at the back of your eyeball that is responsible for eyesight, resulting in blurred vision .
How to tell if blood sugar is high?
High blood sugar is also often associated with a number of symptoms. If you notice any of the following symptoms, contact your doctor right away about getting your blood glucose checked: 3 1 Increased thirst or hunger 2 Blurred vision 3 Frequent urination 4 Headaches 5 Fatigue 6 Weight loss 7 Skin infections 8 Slow-healing cuts and sores
Why does diabetes lower insulin levels?
As your blood sugar level returns to normal, so does the secretion of insulin from your pancreas. Diabetes drastically lowers insulin's effects on your body. This may be because your pancreas is unable to produce insulin (type 1 ...
How long does it take for hyperglycemia to show?
Symptoms of hyperglycemia develop slowly over several days or weeks. The longer blood sugar levels stay high, the more serious the symptoms become. However, some people who've had type 2 diabetes for a long time may not show any symptoms despite elevated blood sugar levels.
Why is it important to treat hyperglycemia?
It's important to treat hyperglycemia, because if left untreated, hyperglycemia can become severe and lead to serious complications requiring emergency care, such as a diabetic coma. In the long term, persistent hyperglycemia, even if not severe, can lead to complications affecting your eyes, kidneys, nerves and heart.
What happens when blood glucose levels rise?
When the glucose level in your blood rises, it signals your pancreas to release insulin. The insulin unlocks your cells so that glucose can enter and provide the fuel your cells need to function properly. Any extra glucose is stored in your liver and muscles in the form of glycogen.
How to keep blood sugar in target range?
Prevention. The following suggestions can help keep your blood sugar within your target range: Follow your diabetes meal plan. If you take insulin or oral diabetes medication, it's important that you be consistent about the amount and timing of your meals and snacks.
Why does blood sugar rise when you have surgery?
Being injured or having surgery. Experiencing emotional stress, such as family conflict or workplace challenges. Illness or stress can trigger hyperglycemia because hormones produced to combat illness or stress can also cause your blood sugar to rise.
What is the main energy source for the body?
During digestion, your body breaks down carbohydrates from foods — such as bread, rice and pasta — into various sugar molecules. One of these sugar molecules is glucose, a main energy source for your body. Glucose is absorbed directly into your bloodstream after you eat, but it can't enter the cells of most of your tissues without the help of insulin — a hormone secreted by your pancreas.
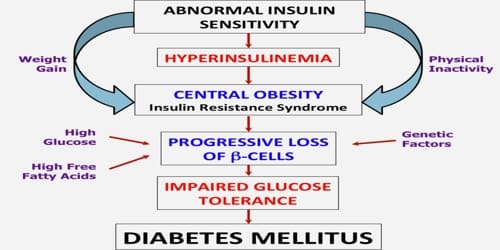
What Is It?
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Expected Duration
Prevention
- Signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly. In fact, you can be living with type 2 diabetes for years and not know it. When signs and symptoms are present, they may include: 1. Increased thirst 2. Frequent urination 3. Increased hunger 4. Unintended weight loss 5. Fatigue 6…
Treatment
When to Call A Professional
Prognosis
Additional Info