What are the symptoms of dying from diabetes?
- Urinate (pee) a lot, often at night
- Are very thirsty
- Lose weight without trying
- Are very hungry
- Have blurry vision
- Have numb or tingling hands or feet
- Feel very tired
- Have very dry skin
- Have sores that heal slowly
- Have more infections than usual
What are the end stage of diabetes?
Diabetes at the end-of-life can lead to several life affecting complications but being able to recognize the signs of high and low blood glucose (blood sugars) can help avoid these complications. If you recognize any of the following end-of-life diabetes signs, please contact the patient’s primary care physician or hospice care provider.
Can you die from diabetes?
Yes, they may. If not managed properly and in time, diabetes may lead to may complications, increasing the chances of death. 1. Hypoglycemia Fluctuating blood sugar levels and resulting symptoms are often what diabetics present with.
What is it like to be a diabetic?
Constant hunger or thirst can be early signs of type 2 diabetes. People with diabetes often do not get enough energy from the food they eat. The digestive system breaks food down into a simple sugar called glucose, which the body uses as fuel. In people with diabetes, not enough of this glucose moves from the bloodstream into the body’s cells.
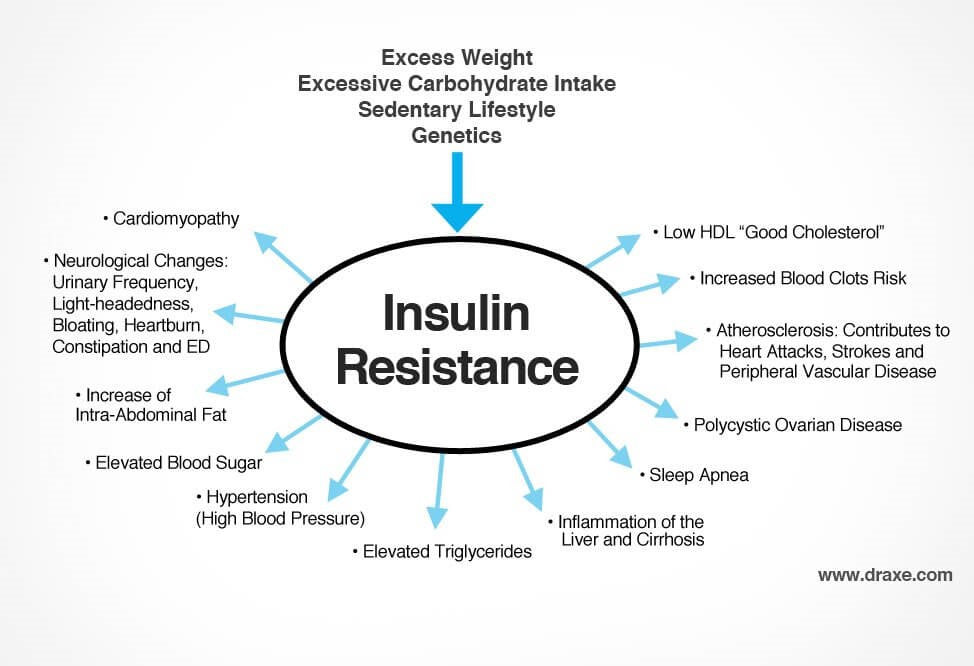
What happens when someone has diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, stroke and narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis). If you have diabetes, you're more likely to have heart disease or stroke. Nerve damage (neuropathy).
What are the six symptoms of diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes SymptomsUrinate (pee) a lot, often at night.Are very thirsty.Lose weight without trying.Are very hungry.Have blurry vision.Have numb or tingling hands or feet.Feel very tired.Have very dry skin.More items...
What are complications of diabetes mellitus?
What are the major complications of diabetes?Eye problems (retinopathy) ... Diabetes foot problems are serious and can lead to amputation if untreated. ... Heart attack and stroke. ... Kidney problems (nephropathy) ... Nerve damage (neuropathy) ... Gum disease and other mouth problems. ... Related conditions, like cancer.More items...
What mellitus means?
Excerpt. Diabetes mellitus is taken from the Greek word diabetes, meaning siphon - to pass through and the Latin word mellitus meaning sweet. A review of the history shows that the term "diabetes" was first used by Apollonius of Memphis around 250 to 300 BC.
What are the 3 signs of diabetes mellitus?
The main symptoms of diabetes are described as the three polys - polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia. Individuals with high risk for developing diabetes should be alert to these symptoms and seek medical attention if they notice the above symptoms.
What causes diabetes mellitus?
What causes type 1 diabetes? Type 1 diabetes occurs when your immune system, the body's system for fighting infection, attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. Scientists think type 1 diabetes is caused by genes and environmental factors, such as viruses, that might trigger the disease.
What are the 4 most common complications of diabetes?
Here are the four most common complications associated with diabetes:Heart disease. A diabetic has twice a non-diabetic's likelihood of dying of heart disease, including stroke. ... Foot problems. Diabetes reduces circulation. ... Kidney disease. Diabetes is the foremost cause of kidney disease. ... Eye problems.
What is the difference between diabetes and diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is more commonly known simply as diabetes. It's when your pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin to control the amount of glucose, or sugar, in your blood.
How does diabetes affect the body?
Diabetes affects your body’s ability to produce or use insulin, a hormone that allows your body to turn glucose (sugar) into energy. Here’s what symptoms may occur to your body when diabetes takes effect. Share on Pinterest. Diabetes can be effectively managed when caught early.
What happens if you smoke and you are at risk of diabetes?
If you smoke, consider quitting if you’re at risk of diabetes. Smoking increases your risk of cardiovascular problems and restricted blood flow. Your doctor can help you create a quit plan.
What is the term for a diabetic with high blood glucose levels?
Diabetic hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome (HHS) occurs in type 2 diabetes. It involves very high blood glucose levels but no ketones.
Why does my pancreas stop working?
This is a result of poor lifestyle, dietary, and exercise habits. With type 2 diabetes, your pancreas stops using insulin effectively. This causes issues with being able to pull sugar from the blood and put it into the cells for energy. Eventually, this can lead to the need for insulin medication.
How many types of diabetes are there?
The effects of diabetes on your body also depends on the type you have. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Why do people have type 2 diabetes?
Most people are diagnosed as a child or young adult. Type 2 is related to insulin resistance. It used to occur in older populations, but now more and more younger populations are being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. This is a result of poor lifestyle, dietary, and exercise habits.
What does it mean when you hear the word "diabetes"?
When you hear the word “diabetes,” your first thought is likely about high blood sugar. Blood sugar is an often-underestimated component of your health. When it’s out of whack over a long period of time, it could develop into diabetes. Diabetes affects your body’s ability to produce or use insulin, a hormone that allows your body to turn glucose ...
What are the symptoms of type 1 diabetes?
Some of the signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes are: Presence of ketones in the urine (ketones are a byproduct of the breakdown of muscle and fat that happens when there's not enough available insulin) Frequent infections, such as gums or skin infections and vaginal infections.
What age does diabetes develop?
Type 2 diabetes, the more common type, can develop at any age, though it's more common in people older than 40.
Why does gestational diabetes cause low blood sugar?
Sometimes babies of mothers with gestational diabetes develop low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) shortly after birth because their own insulin production is high. Prompt feedings and sometimes an intravenous glucose solution can return the baby's blood sugar level to normal.
What causes diabetes and prediabetes?
In prediabetes — which can lead to type 2 diabetes — and in type 2 diabetes, your cells become resistant to the action of insulin, and your pancreas is unable to make enough insulin to overcome this resistance.
Why can't my pancreas keep up with my insulin?
When this happens, too little glucose gets into your cells and too much stays in your blood, resulting in gestational diabetes.
What is the risk of developing type 1 diabetes?
The presence of damaging immune system cells (autoantibodies). Sometimes family members of people with type 1 diabetes are tested for the presence of diabetes autoantibodies. If you have these autoantibodies, you have an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes. But not everyone who has these autoantibodies develops diabetes.
Why is glucose important for the body?
Glucose is vital to your health because it's an important source of energy for the cells that make up your muscles and tissues. It's also your brain's main source of fuel.
How Does Diabetes Affect The Body?
Tweet Knowing how diabetes affects your body can help you look after your body and prevent diabetic complications from developing. Many of the effects of diabetes stem from the same guilty parties; namely high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels and a lack of blood glucose control. Signs of diabetes When undiagnosed or uncontrolled, the effects of diabetes on the body can be noticed by the classic symptoms of diabetes, namely: Increased thirst Frequent need to urinate Fatigue Blurred vision and Tingling or pain in the hands, feet and/or legs Long term effects of diabetes on the body In addition to the symptoms, diabetes can cause long term damage to our body. The long term damage is commonly referred to as diabetic complications. Diabetes affects our blood vessels and nerves and therefore can affect any part of the body. However, certain parts of our body are affected more than other parts. Diabetic complications will usually take a number of years of poorly controlled diabetes to develop. Complications are not a certainty and can be kept at bay and prevented by maintaining a strong level of control on your diabetes, your blood pressure and cholesterol. These can all be helped by keeping to a healthy diet, avoiding cigarettes and alcohol, and incorporating regular activity into your daily regime in order to keep blood sugar levels within recommended blood glucose level guidelines. The effect of diabetes on the heart Diabetes and coronary heart disease are closely related. Diabetes contributes to high blood pressure and is linked with high cholesterol which significantly increases the risk of heart attacks and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes and strokes Similar to how diabetes affects the heart, high blood pressure and cholesterol raises the risk of strokes. How dia Continue reading >>
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Here are some key points about diabetes. More detail and supporting information is in the main article. Diabetes is a long-term condition that causes high blood sugar levels. In 2013 it was estimated that over 382 million people throughout the world had diabetes (Williams textbook of endocrinology). Type 1 Diabetes - the body does not produce insulin. Approximately 10% of all diabetes cases are type 1. Type 2 Diabetes - the body does not produce enough insulin for proper function. Approximately 90% of all cases of diabetes worldwide are of this type. Gestational Diabetes - this type affects females during pregnancy. The most common diabetes symptoms include frequent urination, intense thirst and hunger, weight gain, unusual weight loss, fatigue, cuts and bruises that do not heal, male sexual dysfunction, numbness and tingling in hands and feet. If you have Type 1 and follow a healthy eating plan, do adequate exercise, and take insulin, you can lead a normal life. Type 2 patients need to eat healthily, be physically active, and test their blood glucose. They may also need to take oral medication, and/or insulin to control blood glucose levels. As the risk of cardiovascular disease is much higher for a diabetic, it is crucial that blood pressure and cholesterol levels are monitored regularly. As smoking might have a serious effect on c Continue reading >>
What Happens When Diabetic Eats Sugar?
In diabetics, the body lacks enough insulin to help absorb glucose in the bloodstream, or doesn't respond to insulin at all. Glucose levels in diabetics can build up and cause health complications. Video of the Day Insulin in People without Diabetes Insulin, a hormone produced and secreted by the beta cells in the pancreas, has a special role in the regulation of glucose levels in the blood. When blood glucose levels rise above the normal concentration, the body responds by secreting insulin, which plays a significant role in relocating the glucose transporter Glut4 next to the cells for absorption of glucose, so the body can use it for energy. According to the National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, or NDIC, the normal glucose level in the blood of people without diabetes is between 70 to 120 mg/ dl before a meal. After a meal, the blood glucose level should rise, but should drop back to the normal range one to two hours later. Insulin in People with Type 1 Diabetes A person with type 1 diabetes has dysfunctional beta cells because the “body’s immune system has attacked and destroyed them,” according to the NDIC, thus the body can’t produce insulin. When a type 1 diabetic forgets an insulin injection or doesn’t get enough insulin, eating a meal can raise the level of sugar significantly in the bloodstream, thereby inducing hyperglycemia. Insulin in People with Type 2 Diabetes The NDIC explains that people with type 2 diabetes begin with normal functional pancreatic beta cells, but over time, the fat, muscle and liver cells can no longer respond to insulin properly. To bring the blo Continue reading >>
How do you know if you have diabetes?
What are the symptoms of diabetes? Symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst and urination increased hunger fatigue blurred vision numbness or tingling in the feet or hands sores that do not heal unexplained weight loss Symptoms of type 1 diabetes can start quickly, in a matter of weeks. Symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly—over the course of several years—and can be so mild that you might not even notice them. Many people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms. Some people do not find out they have the disease until they have diabetes-related health problems, such as blurred vision or heart trouble. What causes type 1 diabetes? Type 1 diabetes occurs when your immune system, the body’s system for fighting infection, attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. Scientists think type 1 diabetes is caused by genes and environmental factors, such as viruses, that might trigger the disease. Studies such as TrialNet are working to pinpoint causes of type 1 diabetes and possible ways to prevent or slow the disease. What causes type 2 diabetes? Type 2 diabetes—the most common form of diabetes—is caused by several factors, including lifestyle factors and genes. Overweight, obesity, and physical inactivity You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are not physically active and are overweight or obese. Extra weight sometimes causes insulin resistance and is common in people with type 2 diabetes. The location of body fat also makes a difference. Extra belly fat is linked to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and heart and blood vessel disease. To see if your weight puts you at risk for type 2 diabetes, check out these Body Mass Index (BMI) charts. Insulin resistance Type 2 diabetes usually begins with insulin resista Continue reading >>
How long does it take for diabetes to progress?
Swallowing pills, checking your blood sugar all the time, or sticking yourself with needles full of insulin probably doesn't sound like your idea of a good time. But taking steps to keep your diabetes under control is your best shot at preventing a slew of frightening complications. If you don't take care of yourself, "diabetes complications typically start within 5 years; within 10 to 15 years, the majority of patients will progress to have multiple health issues," says Betul Hatipoglu, MD, an endocrinologist at Cleveland Clinic. Fortunately, eating a nutritious diet, exercising, and taking your medication may not only stop complications from progressing, but can also reverse them, she says. Need motivation to stick to your treatment plan? Here's what can happen when you slack off. With type 1 diabetes, your body stops producing insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar; with type 2 diabetes, your body can't properly use the insulin you do produce. In turn, your HDL (or "good") cholesterol lowers, and your levels of harmful blood fats called triglycerides rise. Insulin resistance also contributes to hardened, narrow arteries, which in turn increases your blood pressure. As a result, about 70% of people with either type of diabetes also have hypertension—a risk factor for stroke, heart disease, and trouble with thinking and memory. (Add these 13 power foods to your diet to help lower blood pressure naturally.) Failing to control high blood pressure and high cholesterol, either with diet and exercise alone or by adding medications, accelerates the rate at which all your other complications progress, says Robert Gabbay, MD, PhD, chief medical officer at Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston. More than 4 million people with diabetes have some degree of retinopathy, or dam Continue reading >>
How does glucose work?
Here's how normal glucose metabolism works, and what happens when you have diabetes — a disease where your body either can't produce enough insulin or it can't use insulin properly. The food you eat consists of three basic nutrients: carbohydrates, protein and fat. During digestion, chemicals in your stomach break down carbohydrates into glucose, which is absorbed into your bloodstream. Your pancreas responds to the glucose by releasing insulin. Insulin is responsible for allowing glucose into your body's cells. When the glucose enters your cells, the amount of glucose in your bloodstream falls. If you have type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesn't secrete insulin — which causes a buildup of glucose in your bloodstream. Without insulin, the glucose can't get into your cells. If you have type 2 diabetes, your pancreas secretes less insulin than your body requires because your body is resistant to its effect. With both types of diabetes, glucose cannot be used for energy, and it builds up in your bloodstream — causing potentially serious health complications. Continue reading >>
How do you know if you have diabetes?
Symptoms of diabetes include. increased thirst and urination. increased hunger. fatigue. blurred vision. numbness or tingling in the feet or hands. sores that do not heal. unexplained weight loss. Symptoms of type 1 diabetes can start quickly, in a matter of weeks.
What causes type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes —the most common form of diabetes—is caused by several factors, including lifestyle factors and genes.
What causes insulin resistance?
Hormonal diseases. Some hormonal diseases cause the body to produce too much of certain hormones, which sometimes cause insulin resistance and diabetes. Cushing’s syndrome occurs when the body produces too much cortisol —often called the “stress hormone.”. Acromegaly occurs when the body produces too much growth hormone.
What is monogenic diabetes?
Monogenic diabetes is caused by mutations, or changes, in a single gene. These changes are usually passed through families, but sometimes the gene mutation happens on its own. Most of these gene mutations cause diabetes by making the pancreas less able to make insulin. The most common types of monogenic diabetes are neonatal diabetes and maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY). Neonatal diabetes occurs in the first 6 months of life. Doctors usually diagnose MODY during adolescence or early adulthood, but sometimes the disease is not diagnosed until later in life.
What is the cause of insulin resistance in Type 2 diabetes?
Insulin resistance. Type 2 diabetes usually begins with insulin resistance, a condition in which muscle, liver, and fat cells do not use insulin well. As a result, your body needs more insulin to help glucose enter cells. At first, the pancreas makes more insulin to keep up with the added demand.
What are the causes of gestational diabetes?
Hormonal changes, extra weight, and family history can contribute to gestational diabetes.
How do genes affect diabetes?
Genes also can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes by increasing a person’s tendency to become overweight or obese.
How long does it take for a diabetic to develop symptoms?
People who have type 1 diabetes may also have nausea, vomiting, or stomach pains. Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop in just a few weeks or months and can be severe. Type 1 diabetes usually starts when you’re a child, teen, or young adult but can happen at any age.
When does type 2 diabetes start?
Type 2 diabetes usually starts when you’re an adult, though more and more children and teens are developing it. Because symptoms are hard to spot, it’s important to know the risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Make sure to visit your doctor if you have any of them.
What is untreated diabetes?
Untreated diabetes is when your high blood sugar level isn’t properly controlled. This is not always a result of someone deciding not to manage their diabetes. It can also happen to those who have diabetes but have not been diagnosed.
How does diabetes affect the urine?
With diabetes, excess glucose ends up in the urine, where it pulls more water and results in more urine. How Type 2 Diabetes Affects the Urinary Tract.
How to tell if you have diabetes?
High Blood Sugar Level. One of the signs of untreated diabetes is high blood sugar. When you visit your doctor, they will measure your blood sugar and let you know what range your blood glucose should fall in. Healthy blood sugar levels are usually between 70 and 130 mg/dL before meals and below 180 mg/dl two hours after meals.
How often do diabetics urinate?
Another common symptom of untreated diabetes is increased urination (polyuria). A person is diagnosed with polyuria when they urinate a minimum of 3 L daily. It is different from urinary frequency, which is the number of times someone pees in a day.
What is the cause of diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when your blood sugar, also called blood glucose, is too high (also known as hyperglycemia ). Blood glucose is your main source of energy and comes from the food you eat.
Why is my vision blurry?
Blurred Vision. High blood sugar levels in uncontrolled diabetes can damage small blood vessels, including those in your eyes. This can affect the blood vessels connected to the retina, a layer of tissue at the back of your eyeball that is responsible for eyesight, resulting in blurred vision .
How to tell if blood sugar is high?
High blood sugar is also often associated with a number of symptoms. If you notice any of the following symptoms, contact your doctor right away about getting your blood glucose checked: 3 1 Increased thirst or hunger 2 Blurred vision 3 Frequent urination 4 Headaches 5 Fatigue 6 Weight loss 7 Skin infections 8 Slow-healing cuts and sores
What happens if you have diabetes?
Uncontrolled diabetes increases your chances of developing several eye conditions, including: glaucoma, which happens when pressure builds up in your eye. cataracts, which occur when the lens of your eye becomes cloudy. retinopathy, which develops when blood vessels in the back of your eye become damaged.
What are the complications of diabetes?
Skin conditions. Uncontrolled diabetes can cause an increased risk of bacterial and fungal skin infections. Diabetes-related complications can cause one or more of the following skin symptoms: pain. itchiness. rashes, blisters, or boils. styes on your eyelids.
Why is high blood glucose dangerous?
That’s because high blood glucose can damage your cardiovascular system. People with diabetes are two to four times more likely to die from heart disease than people who don’t have diabetes. They’re also one and a half times more likely to experience a stroke. The warning signs of stroke include:
How to manage diabetes complications?
These complications can potentially lower your quality of life and increase your chances of early death. Fortunately, you can take steps to manage diabetes and lower your risk for complications. A treatment plan may include lifestyle changes, such as a weight loss program or increased exercise.
How to maintain your eyesight after diabetes?
Fortunately, early diagnosis and treatment can help you maintain your eyesight. In addition to following your recommended diabetes treatment plan, make sure to schedule regular eye exams. If you notice changes in your vision, make an appointment with your eye doctor. 3.
How old do you have to be to get Type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes usually develops in people over age 45, but, in recent years, more young adults, teens, and children have been diagnosed with the disease. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 34 million. Trusted Source. people in the United States have diabetes.
Why is it important to keep your blood glucose and blood pressure in check?
To lower your risk of heart disease and stroke, it’s important to keep your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels in check.
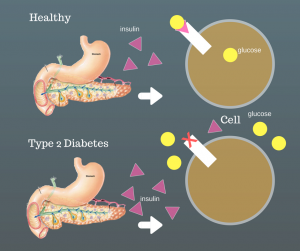
What Is It?
Symptoms
- Diabetes initially might not cause any symptoms. It can sometimes be caught early with a routine blood test before a person develops symptoms. When diabetes does cause symptoms, they may include: 1. excessive urination 2. excessive thirst, leading to drinking a lot of fluid 3. weight loss. People with diabetes also have an increased susceptibility to infections, especially yeast (Candi…
Diagnosis
- Diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests that detect the level of glucose in the blood. 1. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test. A blood sample is taken in the morning after you fast overnight. A normal fasting blood sugar level is between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Diabetes is diagnosed if the fasting blood sugar level is 126 mg/dL or higher. 2. Oral glucose tolerance tes…
Expected Duration
- Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong illness. Usually, type 2 diabetes is also life-long. However, people with type 2 diabetes can sometimes restore their blood sugar levels to normal just by eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and losing weight. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after childbirth. However, women with gestational diabetes are at high risk for developing type 2 diab…
Prevention
- Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented. You can decrease your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. If a close relative—particularly, a parent or sibling—has type 2 diabetes, or if your blood glucose test shows "pre-diabetes" (defined as blood glucose levels between 100 and 125 mg/dL), you are at increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes. You can help to prevent type 2 diabetes by 1. main…
Treatment
- Type 1 diabetes is always treated with insulin injections. In most cases, type 2 diabetes treatment begins with weight reduction through diet and exercise. A healthy diet for a person with diabetes is low in total calories, free of trans fats and nutritionally balanced, with abundant amounts of whole grains, fruits and vegetables, and monounsaturated fats. Most people with type 2 diabete…
When to Call A Professional
- If you have diabetes, see your doctor regularly. People with high blood sugar levels have a higher risk of dehydration. Contact your doctor immediately if you develop vomiting or diarrhea and are not able to drink enough fluids. Monitor your blood sugar as advised by your health care team. Report any significant deviations in blood sugar levels.
Additional Info
- American Diabetes Association www.diabetes.org/ Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics www.eatright.org Diabetes Health Information National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases http://diabetes.niddk.nih.gov/
Further Information
- Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. Medical Disclaimer
Prognosis
Causes
- Normally after you eat or drink, your body will break down sugars from your food and use them for energy in your cells. To accomplish this, your pancreas needs to produce a hormone called insulin. Insulin is what facilitates the process of pulling sugar from the blood and putting it in the cells for use, or energy. If you have diabetes, your pancreas either produces too little insulin or n…
Overview
- The effects of diabetes on your body also depends on the type you have. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1, also called juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is an immune system disorder. Your own immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, destroying your bodys ability to make insulin. With type 1 diabetes, you mu…
Diagnosis
- Type 2 is related to insulin resistance. It used to occur in older populations, but now more and more younger populations are being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. This is a result of poor lifestyle, dietary, and exercise habits.
Results
- With type 2 diabetes, your pancreas stops using insulin effectively. This causes issues with being able to pull sugar from the blood and put it into the cells for energy. Eventually, this can lead to the need for insulin medication.
Prevention
- Earlier phases like prediabetes may be effectively managed with diet, exercise, and careful monitoring of blood sugars. This can also prevent the full development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes can be controlled. In some cases it can even go into remission if proper lifestyle changes are made.
Symptoms
- Moist, warm folds in the skin are susceptible to fungal, bacterial, or yeast infections. These tend to develop between fingers and toes, the groin, armpits, or in the corners of your mouth. Symptoms include redness, blistering, and itchiness. In most cases, gestational diabetes is easily controlled and glucose levels return to normal after the baby is born. Symptoms are similar to ot…
Risks
- High-pressure spots under your foot can lead to calluses. These can become infected or develop ulcers. If you do get an ulcer, see your doctor immediately to lower the risk of losing your foot. You may also be more prone to boils, folliculitis (infection of the hair follicles), sties, and infected nails. If you develop gestational diabetes, your baby may have a higher birth weight. This can ma…