
What Happens To Acetyl Coa After Beta Oxidation. Acetyl-CoA generated by the beta-oxidation pathway enters the mitochondrial TCA cycle, where is further oxidized to generate NADH and FADH2. The NADH and FADH2 produced by both beta oxidation and the TCA cycle are used by the mitochondrial electron transport chain to produce ATP
What happens to acetyl CoA in cellular respiration?
In Cellular Respiration Citric acid cycle: Acetyl-CoA reacts with oxaloacetate to form citrate, which is then oxidized to CO2 in the cycle. Fatty acid metabolism Acetyl-CoA is produced by the breakdown of both carbohydrates (by glycolysis) and lipids (by β-oxidation).
What happens to acetyl CoA in the citric acid cycle?
Acetyl-CoA then enters the citric acid cycle, where the acetyl group is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, and the energy released is captured in the form of 11 ATP and one GTP per acetyl group. GTP is the equivalent of ATP and they can be interconverted by Nucleoside-diphosphate kinase.
How does beta oxidation end in acyl CoA?
In the case of even-numbered acyl-CoA chains, beta oxidation ends after a four-carbon acyl-CoA chain is broken down into two acetyl-CoA units, each one containing two carbon atoms. Acetyl-CoA molecules enter the citric acid cycle to yield ATP.
What happens when acetyl CoA reacts with FADH2?
This reaction releases acetyl-CoA, FADH2 and NADH, the three of which then enter another metabolic process called citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, in which ATP is produced to be used as energy. Beta oxidation goes on until two acetyl-CoA molecules are produced and the acyl-CoA chain has been completely broken down.
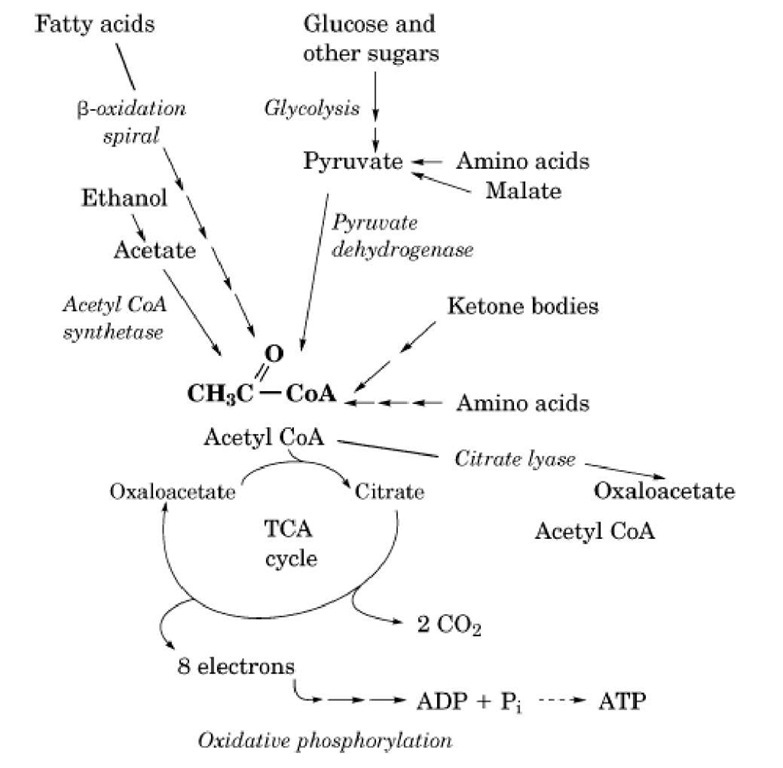
What happens when acetyl-CoA is oxidized?
In the presence of oxygen, acetyl CoA delivers its acetyl group to a four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, to form citrate, a six-carbon molecule with three carboxyl groups; this pathway will harvest the remainder of the extractable energy from what began as a glucose molecule.
What happens at the end of beta-oxidation?
At the end of each β-oxidation cycle, two new molecules are formed, an acetyl-CoA and an acyl-CoA that is two carbons shorter. Additionally, during β-oxidation NADH and FADH2 are formed. One FADH2 is produced during the reaction catalyzed by acyl-CoA dehydrogenase.
Does beta-oxidation make acetyl-CoA?
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, and NADH and FADH2, which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport ...
How many acetyl-CoA will be produced after the last repetition of β-oxidation?
β-oxidation continues until two acetyl-CoA molecules are produced in the final step.
Where do the products of beta-oxidation go?
Acetyl-CoA generated by the beta-oxidation pathway enters the mitochondrial TCA cycle, where is further oxidized to generate NADH and FADH2. The NADH and FADH2 produced by both beta oxidation and the TCA cycle are used by the mitochondrial electron transport chain to produce ATP.
What is removed in beta-oxidation?
During beta-oxidation, fatty acid molecules are broken down by removing two-carbon units from the carboxyl end of a fatty acid molecule to produce acetyl-CoA.
What processes occurs during beta-oxidation?
Inside mitochondria beta oxidation of fatty acids takes place in which two carbon atoms are removed in the form of acetyl-CoA from acyl-CoA at the carboxyl terminal. The bond is broken between the second carbon/beta carbon and the third carbon/gamma carbon, hence the name beta oxidation.
How many moles of acetyl-CoA are produced in beta-oxidation?
In each round of β-oxidation, 1 molecule of acetyl-CoA, 1 molecule of NADH, and 1 molecule of FADH2 are produced.
Can acetyl-CoA be oxidized?
Acetyl-CoA then enters in the TCA cycle where it is oxidized for energy production.
How many molecules of acetyl-CoA are produced from the β-oxidation of a saturated C 18 fatty acid?
Beta oxidation of an 18-carbon fatty acid yields 9 molecules of acetyl-CoA.
How many acetyl-CoA are produced during beta-oxidation of stearic acid?
Beta-oxidation of fatty acids results in the formation of Acetyl-CoA and reduced electron carriers such as NADH and FADH2 N A D H a n d F A D H 2 . For an 18-Carbon saturated fatty acid (stearic acid), it will produce 9 Acety-CoA.
How many ATP are produced by complete oxidation of acetyl-CoA?
Each acetyl CoA enters into citric acid cycle and yields 3 NADH2 (9 ATP), 1 FADH2 (2 ATP) and 1 GTP (1 ATP). Therefore, altogether 12 ATP molecules will be produced from each mole of acetyl-CoA.
What does the ending of the beta test mean?
In the end, Jordan requested Caroline to kill him as he saw a pair of scissors in her hand. However, Caroline forgave her, and Jordan looked at her for a moment and deciphered that she had cheated on him too. Even she got a letter from Johnny, and she filled it.
What is the end product of oxidation?
Combustion involves complete oxidation reaction where biomass reacts with excess oxygen at high temperature (700–1400°C) to generate heat in the form of steam and other gaseous by-products such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
What happens at the end of beta-oxidation of odd chain fatty acids?
Oxidation of Odd-Chain Fatty Acids Oxidation of fatty acids with odd numbers of carbons ultimately produces an intermediate with three carbons called propionyl-CoA, which cannot be oxidized further in the beta-oxidation pathway. Metabolism of this intermediate is odd.
What is the end product of even chain fatty acid beta-oxidation?
two acetyl-CoA moleculesExplanation: During beta oxidation of fatty acids, carbons are removed from the fatty acid chain two at a time. So when a fatty acid is composed of an even number of carbons (as most are) 4 carbons will be left at the end. This will be cleaved into two separate 2 carbon molecules - two acetyl-CoA molecules.
What is the source of acetyl-CoA?
Melatonin synthesis. Acetylation. Acetyl-CoA is also the source of the acetyl group incorporated onto certain lysine residues of histone and nonhistone proteins in the posttranslational modification acetylation. This acetylation is catalyzed by acetyltransferases.
What is the term for the occurrence of high levels of ketone bodies in the blood during starvation?
The occurrence of high levels of ketone bodies in the blood during starvation, a low-carbohydrate diet, prolonged heavy exercise, and uncontrolled type-1 diabetes mellitus is known as ketosis , and in its extreme form in out-of-control type-1 diabetes mellitus, as ketoacidosis.
What enzyme converts fatty acids into acyl-coa?
Acyl-CoA is then degraded in a four-step cycle of oxidation, hydration, oxidation and thiolysis catalyzed by four respective enzymes, namely acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, enoyl-CoA hydratase, 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, and thiolase.
What is the name of the process that converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA?
Pyruvate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation in which it loses its carboxyl group (as carbon dioxide) to form acetyl-CoA, giving off 33.5 kJ/mol of energy. The oxidative conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA is referred to as the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction. It is catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
What happens to the citrate produced by the tricarboxylic acid cycle?
At high glucose levels, glycolysis takes place rapidly , thus increasing the amount of citrate produced from the tricarboxylic acid cycle. This citrate is then exported to other organelles outside the mitochondria to be broken into acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate by the enzyme ATP citrate lyase (ACL). This principal reaction is coupled with the hydrolysis of ATP.
How is acetyl-coa produced?
Fatty acid metabolism. Acetyl-CoA is produced by the breakdown of both carbohydrates (by glycolysis) and lipids (by β-oxidation ). It then enters the citric acid cycle in the mitochondrion by combining with oxaloacetate to form citrate.
What is the acetyl group in CoASH?
Coenzyme A (CoASH or CoA) consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to the vitamin pantothenic acid (B5) through an amide linkage and 3'-phosphorylated ADP. The acetyl group (indicated in blue in the structural diagram on the right) of acetyl-CoA is linked to the sulfhydryl substituent of the β-mercaptoethylamine group.
What is Beta Oxidation?
Eating good food is one of the simple pleasures in life. A piece of decadent chocolate cake, a perfectly cooked steak, or a slice of freshly baked bread can add a touch of extravagance to an otherwise ordinary day. However, food is not eaten simply for enjoyment. Humans and all other living organisms need to ingest food to make energy.
Where does Beta Oxidation Occur?
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that lack membrane-bound organelles. Bacteria and archaea are examples of prokaryotic organisms. Because prokaryotes do not have organelles, all of their reactions occur in the cytosol, including beta-oxidation.
Beta Oxidation Cycle
Now that we have discussed the location of and preparatory steps for beta-oxidation, let us now look at the actual process of beta-oxidation. In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, a round of beta-oxidation consists of four reactions. Briefly, the steps are as follows:
What is the oxidation of acetyl CoA?
The acetate of acetyl CoA undergoes a stepwise oxidation to carbon dioxide and water in a cyclic pathway, the citric acid cycle, shown in Figures 5.17 and 5.18. This pathway is sometimes known as the Krebs cycle, after its discoverer, Sir Hans Krebs.
What is the precursor to gluconeogenesis?
Although, as discussed below (section 5.7), oxaloacetate is the precursor for gluconeogenesis, fatty acids and other compounds that give rise to acetyl CoA ...
What is the citric acid cycle?
Although it appears complex at first sight, the citric acid cycle is a simple pathway. A four-carbon compound, oxaloacetate, reacts with acetyl CoA to form a six-carbon compound, citric acid. The cycle is then a series of steps in which two carbon atoms are lost as carbon dioxide, followed by a series of oxidation and other reactions, ...
What is the oxidation of the hydroxyl group?
Oxidation of the hydroxyl group, linked to reduction of NAD+, to yield an oxo-group.
Does Gaba produce succinate?
In turn, GABA can undergo further metabolism to yield succinate. This pathway (sometimes called the GABA shunt) thus provides an alternative to a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in thiamin deficiency, so that oxidation of acetyl CoA and formation of ATP can continue. The sequence of reactions between succinate and oxaloacetate is chemically ...
Can oxaloacetate be withdrawn from gluconeol?
Therefore, when acetyl CoA is the substrate, there is no increase in the pool of citric acid cycle intermediates, and therefore oxaloacetate cannot be withdrawn for gluconeogenesis.
Does thiamin deficiency affect citric acid?
However, thiamin deficiency does not have a significant effect on the citric acid cycle, because, as shown in Figure 5.19, a-ketoglutarate can undergo transamination to yield glutamate, which is decarboxylated to y-aminobutyric acid (GABA). In turn, GABA can undergo further metabolism to yield succinate. This pathway (sometimes called the GABA ...
