
Beginning at puberty, the brain is reshaped. Neurons (gray matter) and synapses (junctions between neurons) proliferate in the cerebral cortex and are then gradually pruned throughout adolescence. Eventually, more than 40% of all synapses are eliminated, largely in the frontal lobes. Meanwhile, the white insulating coat of myelin on the axons ...
How to trigger puberty?
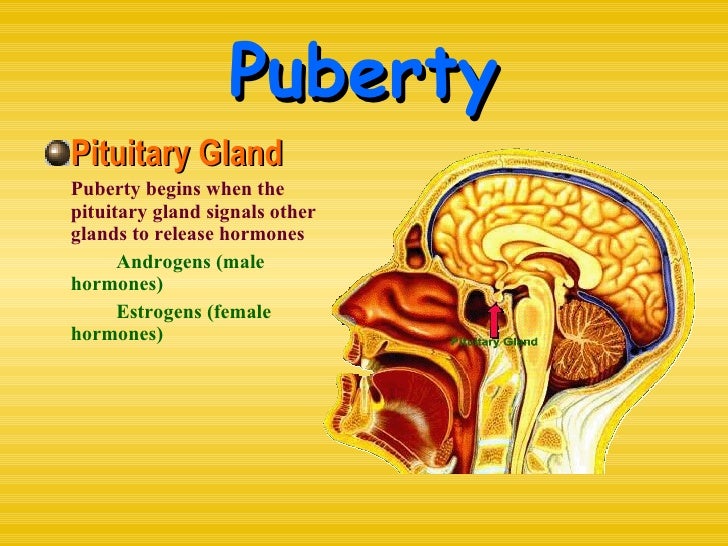
Puberty's trigger lies in a small part of the brain called the hypothalamus, a gland that secretes gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). GnRH stimulates the pituitary gland, a pea-sized organ connected to the bottom of the hypothalamus, to emit two hormones: luteinizing (pronounced LOO-tee-uh-nize-ing ) hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating ...
How to hit puberty quicker?
Tips To Hit Puberty Faster
- Stay Healthy – Eat Healthy. For your child to hit puberty around the same time as his friends, he has to eat healthy and nutritious food.
- Be Active – Participate in Sports. Sports has a very important role to play in physical and mental development of the child. ...
- Stay Positive – Enjoy Your Childhood. Delayed puberty is normal in some children. ...
- Sleep Well. ...
What happens when Boys hit puberty?
Puberty in boys begins when the pituitary gland sends a signal to the testicles that it’s time to start making testosterone. Testosterone is the male hormone that changes your body during puberty. The first signs of puberty in boys is that your testicles (balls) begin to get bigger.
What are the effects of puberty?
The signs of puberty include 1:
- Growth of pubic hair, other body hair, and facial hair
- Enlargement of testicles and penis
- Muscle growth
- Growth spurt
- Acne
- Deepening of the voice
What part of the brain shuts down during puberty?
Although the development of the prefrontal cortex is the last step on the development checklist, teenagers undergo major changes in their limbic system—the area of the brain that controls emotions—at the onset of puberty, which is typically around the ages of 10 to 12.
Does the brain get bigger during puberty?
Thus, the brain does not grow in size much during adolescence. However, the creases in the brain continue to become more complex until the late teens. The biggest changes in the folds of the brain during this time occur in the parts of the cortex that process cognitive and emotional information.
Do you get smarter during puberty?
“The first is that performance on intelligence tests increases during adolescence. The second is that processing speed”—the brain taking in and using new stimuli or information—“as measured by tests of mental speed also increases during adolescence.”
At what age is your brain fully developed?
age 25Brain Maturity Extends Well Beyond Teen Years Under most laws, young people are recognized as adults at age 18. But emerging science about brain development suggests that most people don't reach full maturity until the age 25.
At what age is the brain 95 developed?
The human brain reaches 95% of its adult size by the time a child turns three years old1. Although there is consistent growth via neural connections well into adulthood, the structures of the brain are present at birth. The functionality of the brain changes as children experience the world around them.
Are girls brains more developed?
Sex differences in the brain are reflected in the somewhat different developmental timetables of girls and boys. By most measures of sensory and cognitive development, girls are slightly more advanced: vision, hearing, memory, smell, and touch are all more acute in female than male infants.
Does puberty affect memory?
Human brains aren't fully developed at birth. As our brain develops in infancy and early childhood, so does our capacity to remember. There are changes in the brain's prefrontal cortex during puberty and adolescence, with corresponding changes in our memory abilities.
Does the brain develop until 25?
The rational part of a teen's brain isn't fully developed and won't be until age 25 or so. In fact, recent research has found that adult and teen brains work differently. Adults think with the prefrontal cortex, the brain's rational part.
How did mice learn to find a treat?
The study involved training two groups of mice to find a treat that was associated with a certain scent. Some mice had puberty induced by injection of estradiol and progesterone, while other mice had their ovaries removed to prevent puberty from occurring. The mice who were induced into puberty, had very different electrical patterns in the front part of the brain, where it’s believed plasticity is controlled. In addition, when the learned task of finding the treat was changed, and the mice had to use “higher-order learning strategies” like trial and error to find it, the mice who were given puberty hormones were not as quick to learn how to find the treat and adapt to the changes in the task. The study design showed that it wasn’t just age or experience that impacted learning, but hormonal changes that caused the brain’s plasticity to be altered. Wilbrecht compared the introduction of puberty hormones to a switch in the frontal cortex.
What is Wilbrecht's study?
Wilbrecht compared the introduction of puberty hormones to a switch in the frontal cortex. The study used only female mice, so more work is needed to see if the results occur in males as well. The research is published in the journal Current Biology. The video below talks more about the study and how puberty can have a definite effect on the brain, ...
Why is it easier for kids to learn a second language?
It’s well-known that young children have more flexibility in how they learn. Neuroscientists call this “brain plasticity” and it’s why it’s easier for younger children to pick up a second language, learn to read and tackle other academic learning. Once the hormones kick in however, there is a shift in the kind of learning ...
Why do girls grow up so fast?
This head start could be a problem in terms of learning and brain plasticity. Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley have published a study, using female mice, that shows once the puberty hormones start to flow, the focus of learning shifts. This change might even impact the ability to learn academic subjects because the hormonal shifts impact areas of the brain that process knowledge, memory, reading and mathematical calculation.
How does hormonal change affect learning?
This change might even impact the ability to learn academic subjects because the hormonal shifts impact areas of the brain that process knowledge, memory, reading and mathematical calculation.
Why is puberty occurring earlier and earlier in girls in modern urban settings?
Puberty onset is occurring earlier and earlier in girls in modern urban settings -- driven by such factors as stress and the obesity epidemic -- and has been associated with worse outcomes in terms of school and mental health.".
What do children do in puberty?
For children beginning puberty, they start to look around at their social environment and use their brain power on managing relationships and fitting in with the trends of the peers like fashion and pop culture. Of course academic learning doesn’t stop with puberty, but it’s just a bit harder for the pubescent brain to shift from thinking about ...
How do gonadal steroid hormones affect the body?
The gonadal steroid hormones estrogen and testosterone, as well as their weaker adrenal counterparts, influence the physical appearance of the body. They also affect the brain and behavior. These effects are hypothesized to occur via two relatively distinct processes: organization and activation [Schulz et al., 2009; Sisk and Foster, 2004]. Organizational effects occur pre‐ and perinatally, with waves of testosterone masculinizing and defeminizing neural circuits in males, and the absence of testosterone resulting in a female neural phenotype. Activational effects occur at puberty, as gonadal steroid hormones act on dormant neural circuits to elicit adult reproductive behaviors in context; a recent modernization of this dichotomy suggests that the hormonal events of puberty also organize neural circuits for adult social and reproductive behaviors [Schulz et al., 2009; Sisk and Foster, 2004]. Indeed, based on findings from nonhuman animal studies, it is suggested that the hormonal events of puberty trigger a second period of structural reorganization and plasticity in the brain [Sisk and Foster, 2004]. In humans, however, there is very little understanding of the specific relationships between puberty and adolescent brain development.
How does puberty affect neural development?
Relatively little is known about the relationship between puberty and neural development in humans. However, a wealth of evidence from nonhuman animal studies indicates that the hormonal events of puberty exert profound effects on brain maturation and behavior [Cahill, 2006; Sisk and Foster, 2004; Spear, 2000]. These changes mould the perceptions, motivations, and behavioral repertoire of an individual, enabling reproductive behavior and independence [Sato et al., 2008]. In recent years, a small but growing number of human behavioral and neuroimaging studies, including in populations with endocrine disruptions, have provided tentative evidence that pubertal hormones might influence the structure and function of the developing human brain.
How does white matter development differ between sexes?
One study reported a positive relationship between LH concentration and white matter density at age nine; this relationship did not differ between the sexes [Peper et al., 2009a]. However, it has been shown that during adolescence, developmental trajectories of white matter volume, as well as the MTR, differ between the sexes. Recent studies by Perrin et al. [2008, 2009] have investigated whether this difference may be due to puberty hormones downstream from LH. Perrin et al. [2008] investigated the relationship between expression levels of a gene encoding the androgen (testosterone) receptor, and white matter development, in males. The results showed that variance in trajectories of white matter development in males was indeed related to gene expression levels, suggesting that effects of testosterone may be responsible for the sexually dimorphic relationship between age and white matter volume. In Perrin et al. [2009], evidence was presented for sexual dimorphism in the mechanism underlying adolescent increases in white matter volume.
What is the period of physical and psychological development between childhood and adulthood?
Adolescence refers to the period of physical and psychological development between childhood and adulthood. The beginning of adolescence is loosely anchored to the onset of puberty, which brings dramatic alterations in hormone levels and a number of consequent physical changes. Puberty onset is also associated with profound changes in drives, motivations, psychology, and social life; these changes continue throughout adolescence. There is an increasing number of neuroimaging studies looking at the development of the brain, both structurally and functionally, during adolescence. Almost all of these studies have defined development by chronological age, which shows a strong—but not unitary—correlation with pubertal stage. Very few neuroimaging studies have associated brain development with pubertal stage, and yet there is tentative evidence to suggest that puberty might play an important role in some aspects of brain and cognitive development. In this paper we describe this research, and we suggest that, in the future, developmental neuroimaging studies of adolescence should consider the role of puberty. Hum Brain Mapp, 2010. © 2010 Wiley‐Liss, Inc.
What is the period of physical, cognitive, and social maturation between childhood and adulthood?
Adolescence is the period of physical, cognitive, and social maturation between childhood and adulthood [Lerner and Steinberg, 2004; Sisk and Foster, 2004]. The beginning of adolescence occurs around the onset of puberty and is therefore marked by dramatic changes in hormone levels and in physical appearance (including rapid physical growth, ...
What is the most common measure of puberty?
A commonly used measure of puberty is Tanner Stage . Tanner staging categorizes individuals along an ordinal puberty scale from 1 to 5, on the basis of pubic hair and breast development in females, and pubic hair and genital development in males [Tanner, 1971; Tanner and Whitehouse, 1976]. Tanner staging by physical exam should be carried out by a trained clinician. There are several limitations to Tanner staging. The scale was developed with reference to a single ethnic group (there may be cross‐ethnic differences) and in a relatively small sample of 200 children. Overweight girls will tend to be inaccurately staged, due to the reliance of the staging on breast development, which can be erroneously over‐estimated in a purely visual examination. Despite these limitations, Tanner staging has historically been considered the gold standard for puberty measurement [Dorn, 2006].
What are the changes that can be seen in MRI?
Developmental changes that have been delineated using MRI include alterations in the amount of gray and white matter, and changes in white matter microstructure.
How does puberty affect boys?
Scientists have found that brain networks develop differently in males and females at puberty, with boys showing an increase in connectivity in certain brain areas, and girls showing a decrease in connectivity as puberty progresses. These analyses were focused on brain regions previously ...
What is the role of brain imaging in mental health?
May 9, 2018 — Brain regions that help process what we see may play a key role in mental health. Researchers used brain imaging to identify patterns of brain connectivity -- the ability of brain regions to talk to ...
Do boys have brain networks?
Scientists have found that brain networks develop different ly in male s and females at puberty, with boys showing an increase in connectivity in certain brain areas, and girls showing a decrease in connectivity as puberty progresses. These analyses were focused on brain regions previously identified as conferring risk for mood problems in adolescents, suggesting an association, although this needs to be tested. This work is presented at the ECNP Congress in Copenhagen, and is based on a recent peer-reviewed publication.
Do boys and girls have opposite brain activity?
Collectively these findings indicate that there are opposite changes of brain activity in boys and in girls as they go through puberty, and this male/female developmental pattern can be a key factor in in the role of pubertal development in the emergence of mood disorders. The next critical next step is to examine the role of these brain connectivities in the development of depression as these adolescents get older, using a longitudinal design."
Does depression affect the brain?
Through this study, researchers found that depression has different effects on the brain activity of male and female ... Jan. 13, 2017 — A multiregional brain-on-a-chip that models the connectivity between three distinct regions of the brain has been revealed by researchers.
Does the brain develop differently in boys and girls?
According to lead researcher, Dr Monique Ernst (National Institute of Mental Health / NIH, Bethesda, Maryland, USA), "In our study, we showed that certain brain regions develop differently in boys and girls at puberty. Functional connectivity increases in boys and decreases in girls over puberty. Our next set of studies will aim to clarify the significance of these communication changes in the maturing brain, and to identify if the changes are protective or if they increase vulnerability."
Do women have depression during puberty?
We know that mood upsets, particularly anxiety and depression, occur disproportionately in girls, and that women are twice likely as men to suffer from depression following the trend emerging during puberty. We found that the puberty period is associated with significant brain changes in these mood-related brain areas; however, ...
What Happens During Puberty?
The shape, size, and composition of our bodies change as we progress toward sexual maturity, which is the ability of an organism to reproduce. Our moods and behaviors change as a result of puberty as well. The same hormones that cause changes in our bodies also help shape the structure and organization of our brains. Through puberty, our brains strengthen and fine-tune the connections that allow for mature ways of thinking, feeling, and behaving [ 2 ].
What hormones are involved in the brain?
Even before birth, testosterone and estrogen are involved in early brain development, helping to create new neurons and guide them as they form the brain’s structure. During puberty, these hormones then act to permanently change the organization and structure of the brain into its mature form ( Figure 3 ).
How do hormones affect puberty?
Hormones help our bodies become taller, change shape, and even grow hair. Although hormones act on different parts of the body (like bones, muscles, or skin), several crucial hormones for puberty are actually made in the brain. Scientists are learning more about the ways hormones affect how the brain grows and changes, and in turn, ...
How does pubertal hormone affect the brain?
Pubertal Hormones Change Brain Structure and Function. Puberty is a dynamic transition period that prepares us for the adult world. Yet, even as adults, life is constantly in flux and our brains need ways of adapting to these ongoing changes.
How does the brain change?
There are several ways that brain structure can be altered. One is neuron growth or death , which changes the overall size of brain regions. In animals and healthy humans, pubertal hormones are necessary for proper growth of brain structures like the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and amygdala. Since the hypothalamus and pituitary gland are crucial for life-long hormone regulation, improper growth of these brain regions during puberty can lead to long-term health consequences, such as disorders of sleep or metabolism. Klinefelter syndrome, which is a genetic disorder caused by an extra X chromosome, leads to a shortage of testosterone and a significantly decreased amygdala volume in adolescence. These hormonal and brain structure changes may contribute to the social and emotional problems these individuals face, including social anxiety and difficulty expressing feelings.
Why are androgens important?
Androgen hormones like testosterone and DHEA, as well as estrogen hormones like estradiol, are especially important for the proper development of parts of the brain involved in learning and memory, sexual behaviors, and emotion processing. Using animal models together with studies of healthy humans as well as those with hormonal disorders, scientists are starting to get a better picture of how the pubertal hormones change the structure and the function of the brain.
What does it mean when you have a change in appearance?
Changes in appearance caused by increasing sex hormones during puberty that are different in males and females and symbolize the completion of sexual development. . For girls, this includes wider hips, larger breasts, and the start of menstruation.
Why is puberty accelerating?
There is a lot of speculation around the reasons why human puberty might be accelerating, but one theory is that it is related to diet.
What are the changes in the brain during adolescence?
There are dramatic changes in neural circuits, particularly in frontal cortical and basal ganglia circuits during adolescence. We believe that these changes adjust and tune the brain in order to sculpt learning and decision-making at these different life stages. People often deride the function of the frontal cortex in teenagers.
Why are adolescents in the middle of learning?
Adolescents have so much less experience and they are in the middle of gathering all sorts of experience in order to adjust into adult roles. We believe that there may be unrecognised aspects to learning that help people to become independent from their parents and to develop their independent identity.
What changes in structure occur in the mPFC during puberty?
Alongside changes in the brain and hormones, ...
What is SFN short course?
Bell, Cecilia Flores, Joshua Gulley, Jari Willing, and Matthew J. Paul. Short Courses are daylong scientific trainings on emerging neuroscience topics and research techniques held the day before SfN’s annual meeting.
Which brain circuit is essential for changes to how the brain perceives social interactions and reward during adolescence?
Second, the mesocorticolimbic dopamine pathway is the brain circuit that is essential for changes to how the brain perceives social interactions and reward during adolescence.
Which circuit plays a large role in receiving and regulating rewarding stimuli?
The circuit that plays a large role in receiving and regulating rewarding stimuli is the mesocorticolimbic dopamine pathway. In rodents and primates, this pathway undergoes extensive changes during adolescence.
What is the transition from childhood to adulthood?
Adolescence — the transition from childhood to adulthood — is a time of great change in the brain and behavior. In addition to sexual maturity, individuals also develop social and emotional skills during this time that will serve them as adults. Traditionally, researchers trying to understand this period have focused on a mismatch in ...
What is the name of the area of the brain that increases dopamine?
One of the most striking changes is the steady, linear increase in dopaminergic neural projections that happens in both males and females in the brain area known as the medial prefrontal cortex, or mPFC. In addition to the increase in projections, the brain regions involved in this circuit also increase the expression of dopamine receptors ...
How do humans and rodents change?
Alongside changes in the brain and hormones, adolescent humans and rodents experience changes in how they respond to social structure that can, in turn, drive changes in neural circuitry. In humans, adolescents start to rely more on their peers for social support and, in doing so, learn behaviors that will serve them as adults.
How does the brain affect adolescent development?
The adolescent brain pours out adrenal stress hormones, sex hormones, and growth hormone, which in turn influence brain development. The production of testosterone increases 10 times in adolescent boys. Sex hormones act in the limbic system and in the raphe nucleus, source of the neurotransmitter serotonin, which is important for the regulation ...
What happens to the brain during puberty?
Beginning at puberty, the brain is reshaped . Neurons (gray matter) and synapses (junctions between neurons) proliferate in the cerebral cortex and are then gradually pruned throughout adolescence. Eventually, more than 40% of all synapses are eliminated, largely in the frontal lobes. Meanwhile, the white insulating coat of myelin on the axons that carry signals between nerve cells continues to accumulate, gradually improving the precision and efficiency of neuronal communication — a process not completed until the early 20s. The corpus callosum, which connects the right and left hemispheres of the brain, consists mostly of this white matter.
How do addictions start?
Most addictions get their start in adolescence, and there is evidence that adolescent and adult brains respond differently to drugs. In both human beings and laboratory rats, studies have found that adolescents become addicted to nicotine faster and at lower doses.
Why do teenagers have trouble with their parents?
Adolescents need to assert their independence and explore their limits, taking risks, breaking rules, and rebelling against their parents while still relying on them for support and protection. ("What's the matter with the older generation?") They have to cope with disconcerting new sexual impulses and romantic feelings. Cultural change heightens incompatibility between the generations. Now scientific research is suggesting a new reason for the clashes between teenagers and their environment. Unsettled moods and unsettling behavior may be rooted in uneven brain development.
Why are animal experiments limited?
Animal experiments have limited value because laboratory animals do not undergo a lengthy human childhood. And human brain development does not unfold automatically and uniformly. There is much individual variation that reflects experience as well as genetic programming.
What is the Iowa gambling task?
Another revealing psychological experiment is the Iowa gambling task. Subjects can choose from one of two decks of cards in the hope of picking a card that provides a reward. The "good" deck contains many cards that provide some reward; the "bad" one, many cards that provide nothing and insufficient compensation in the form of a few that hold a jackpot. The choices of adults correspond fairly well to their tested reasoning capacity. In adolescence, the correlation is much weaker.
Which part of the brain is responsible for emotional learning?
Among the last connections to be fully established are the links between the prefrontal cortex, seat of judgment and problem-solving, and the emotional centers in the limbic system, especially the amygdala. These links are critical for emotional learning and high-level self-regulation. Beginning at puberty, the brain is reshaped.
How do you know if your son is in puberty?
The first sign of puberty actually begins with the growth of your son's testicles and scrotum, which will more than double in volume. 6 His penis and testicles will begin to grow as he enters puberty too, as will his pubic hair.
Why does puberty start later than normal?
If your son has a chronic illness like sickle cell disease, inflammatory bowel disease, or cystic fibrosis, puberty may also begin later than normal. A small number of boys have a condition called isolated gonadotropin deficiency (IGD), which means that they don't produce adequate amounts of the hormones LH and FSH.
How old do boys have to be to get testicle size?
14 In boys, this can be defined as having no increase in testicle size by the age of 14 years old or continuing undergo puberty for more than five years after the start.
How to make your boyfriend feel comfortable?
Stay connected to his interests and talk to him about sports, school, or whatever he enjoys. This will help him feel comfortable about coming to you when he needs to talk about something important.
What are the biggest changes for a boy?
Sweating, Hair, and Acne. Personal hygiene is probably one of the biggest changes for young boys. It may have been hard to get him to wash his hands or take a shower, but now he will need to pay attention to these things as he starts to sweat more and develop body odor.
Why does my son's voice change?
Your son's voice will change around the time that his growth spurt has begun to slow down a bit. This occurs because his vocal chords and voice box (larynx) gain mass too. Before his voice changes completely, it may crack and soar, going from high to low quickly. 9 This can be embarrassing for him, so be mindful of this.
What changes do boys go through during puberty?
A boy goes through many important changes during puberty. His body beefs up, his voice cracks as it changes, he becomes stronger, and he begins to mature sexually. 1
