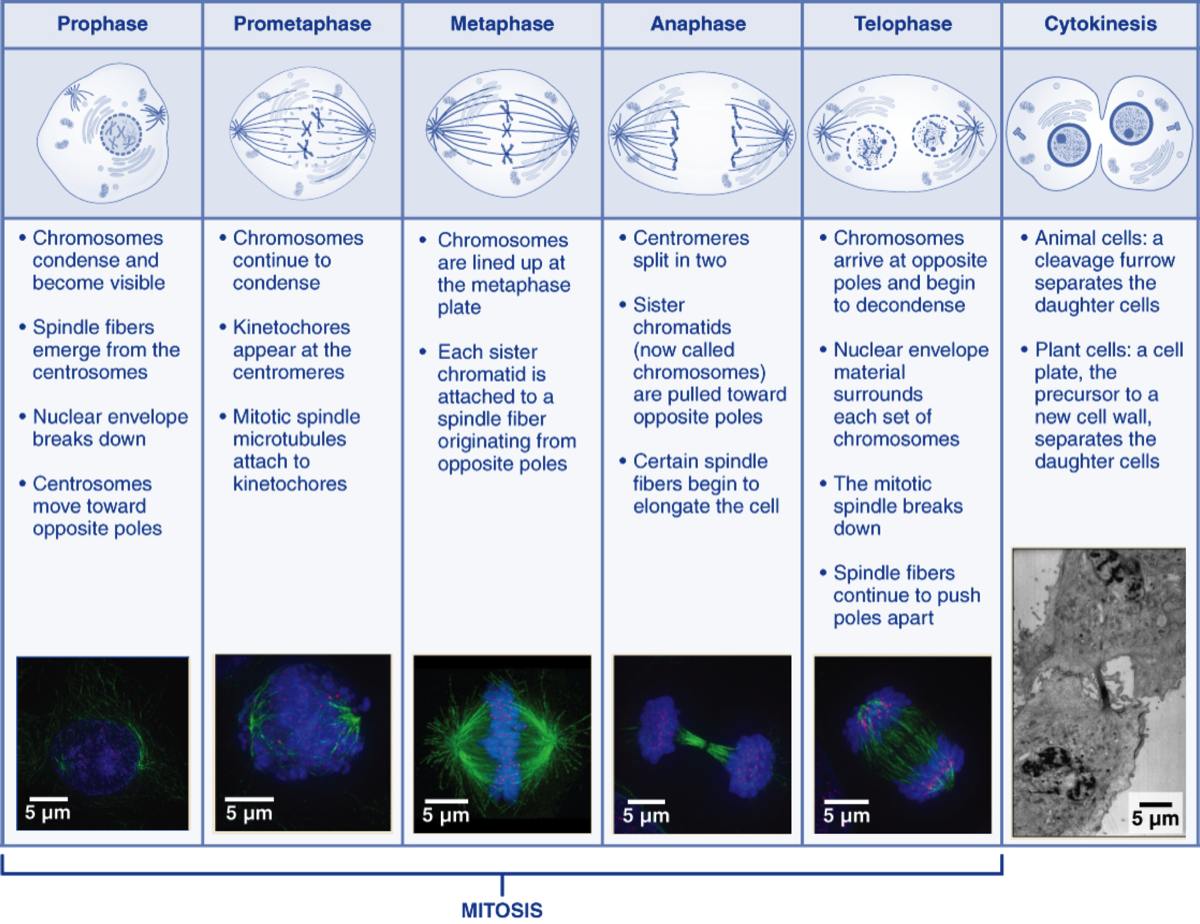
What happens during each of the four phases of mitosis? 1) Prophase: chromatin into chromosomes, the nuclear envelope break down, chromosomes attach to spindle fibres by their centromeres 2) Metaphase: chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate (centre of the cell) 3) Anaphase: sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell 4) Telophase: nuclear envelope …
Do mitosis pair up with chromosomes?
The stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Do homologous chromosomes pair up? No, homologous chromosomes act independently from one another during alignment in metaphase and chromatid segregation in anaphase. Does crossing over occur? No, because chromosomes do not pair up (synapsis), there is no chance for crossing ...
Which phase of mitosis would you first see chromosomes?
The first and longest phase of mitosis is prophase. During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope (the membrane surrounding the nucleus) breaks down. In animal cells, the centrioles near the nucleus begin to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Does the number of chromosomes change in mitosis?
There is no change in chromosome number in mitosis. A human cell have 46 total or 23 pairs of chromosomes. Does the number of chromosomes change in mitosis?
What pulls the chromosomes apart during meiosis?
pull the homologous pairs apart. Each pair of chromosomes separates, and the members move to opposite ends of the cell. In mitosis, the spindle fibers pull the chromatids apart. In meiosis, the spindle fibers pull the pairs of chromosomes apart, not the chromatids.
What are the 4 stages of mitosis and how do the chromosomes behave in each?
There are four stages of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Chromatin into chromosomes, the nuclear envelope break down, chromosomes attach to spindle fibres by their centromeres. Chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate (centre of the cell).
What happens to chromosomes in the prophase of mitosis?
The first and longest phase of mitosis is prophase. During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope (the membrane surrounding the nucleus) breaks down. In animal cells, the centrioles near the nucleus begin to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
What happens to chromosomes in the metaphase of mitosis?
Metaphase During metaphase, the nucleus dissolves and the cell's chromosomes condense and move together, aligning in the center of the dividing cell. At this stage, the chromosomes are distinguishable when viewed through a microscope.
What happens to the chromosomes in anaphase of mitosis?
During anaphase, each pair of chromosomes is separated into two identical, independent chromosomes. The chromosomes are separated by a structure called the mitotic spindle.
What happens to the chromosomes during telophase?
During telophase, a nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes to separate the nuclear DNA from the cytoplasm. The chromosomes begin to uncoil, which makes them diffuse and less compact.
What happens during each stage of mitosis?
Prophase – The chromosomes shorten and thicken. Metaphase – Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Anaphase – Chromatids break apart at the centromere and move to opposite poles. Telophase – Two nuclei formed after nuclear envelopes reform around each group of chromosomes.
What happens in the anaphase?
In anaphase, the sister chromatids separate from each other and are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell. The protein “glue” that holds the sister chromatids together is broken down, allowing them to separate. Each is now its own chromosome. The chromosomes of each pair are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell.
How many chromosomes are in each phase of mitosis?
At this point, nuclear division begins, and the parent cell is divided in half, forming 2 daughter cells. Each daughter cell will have half of the original 46 chromosomes, or 23 chromosomes. Each chromosome consists of 2 sister chromatids.
What happens early prophase?
early prophase - the nuclear membrane becomes more and more indistinct and the chromatin fibers become more and more packaged and condensed. It is usually not possible to follow individual threads, but the condensation of the material into individual units is becoming obvious.
What happens during telophase stage?
What Happens during Telophase? During telophase, the chromosomes arrive at the cell poles, the mitotic spindle disassembles, and the vesicles that contain fragments of the original nuclear membrane assemble around the two sets of chromosomes. Phosphatases then dephosphorylate the lamins at each end of the cell.
How are chromosomes arranged during this phase?
During metaphase, chromosomes are organized on an equatorial plate. Metaphase is the stage of eukaryotic cell division when the chromosomes align in the middle of the cell.
What happens interphase?
A cell spends most of its time in what is called interphase, and during this time it grows, replicates its chromosomes, and prepares for cell division. The cell then leaves interphase, undergoes mitosis, and completes its division.
What happens in prophase stage of mitosis?
Prophase is the first phase of mitosis, the process that separates the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell into two identical daughter cells. During prophase, the complex of DNA and proteins contained in the nucleus, known as chromatin, condenses.
Why are chromosomes thicker and shorter during the prophase stage of mitosis?
These chromatids are held together by the centromere. Throughout the process of prophase the chromosomes condense meaning they get shorten and thicken to form visibly distinct threads within the nucleus. This is brought about by the action of large proteins called condensins.
Which of the following occurs to the chromosomes during prophase stage?
During prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses, a step unique to meiosis. The paired chromosomes are called bivalents, and the formation of chiasmata caused by genetic recombination becomes apparent. Chromosomal condensation allows these to be viewed in the microscope.
How many chromosomes are in prophase of mitosis?
46 chromosomesAt this point, nuclear division begins, and the parent cell is divided in half, forming 2 daughter cells. Each daughter cell will have half of the original 46 chromosomes, or 23 chromosomes.
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a type of cell division in which one cell (the mother) divides to produce two new cells (the daughters) that are genetically identical to itself. In the context of the cell cycle, mitosis is the part of the division process in which the DNA of the cell's nucleus is split into two equal sets of chromosomes.
How many phases are there in mitosis?
Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts in anaphase or telophase.
Where do microtubules extend?
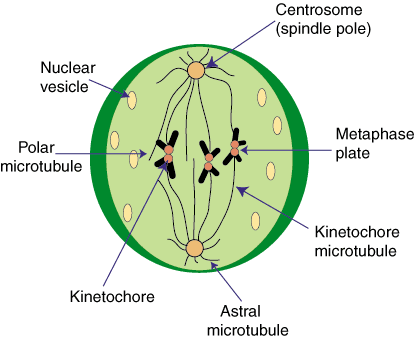
More microtubules extend from each centrosome towards the edge of the cell, forming a structure called the aster. Metaphase. Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate, under tension from the mitotic spindle. The two sister chromatids of each chromosome are captured by microtubules from opposite spindle poles.
Which phase of the cell is the sister chromatids separated from each other?
Anaphase. The sister chromatids separate from one another and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell. The microtubules that are not attached to chromosomes push the two poles of the spindle apart, while the kinetochore microtubules pull the chromosomes towards the poles.
What is the order of mitosis?
These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts in anaphase or telophase. Stages of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. Cytokinesis typically overlaps with anaphase and/or telophase. You can remember the order of the phases with ...
Why can't you see chromosomes in the nucleus?
You can’t see the chromosomes very clearly at this point, because they are still in their long, stringy, decondensed form.
Where do microtubules bind to chromosomes?
Microtubules can bind to chromosomes at the kinetochore, a patch of protein found on the centromere of each sister chromatid. ( Centromeres are the regions of DNA where the sister chromatids are most tightly connected.)
How are chromosomes held in the metaphase plate?
Chromosomes are held at the metaphase plate by the equal forces of the polar fibers pushing on the centromeres of the chromosomes.
What is the phase of the cell cycle where chromosomes are evenly divided between two cells?
Mitosis is the phase of the cell cycle where chromosomes in the nucleus are evenly divided between two cells. When the cell division process is complete, two daughter cells with identical genetic material are produced.
How do chromosomes move?
Chromosomes move randomly until they attach (at their kinetochores) to polar fibers from both sides of their centromeres.
When do diploid cells begin to form?
It begins prior to the end of mitosis in anaphase and completes shortly after telophase/mitosis. At the end of cytokinesis, two genetically identical daughter cells are produced. These are diploid cells, with each cell containing a full complement of chromosomes.
What happens during prophase?
In prophase, the chromatin condenses into discrete chromosomes. The nuclear envelope breaks down and spindles form at opposite poles of the cell. Prophase (versus interphase) is the first true step of the mitotic process. During prophase, a number of important changes occur:
What is the S phase in biology?
S phase: The period during which DNA is synthesized. In most cells, there is a narrow window of time during which DNA is synthesized. The S stands for synthesis.
Why do centrioles move away from each other?
The two pairs of centrioles (formed from the replication of one pair in Interphase) move away from one another toward opposite ends of the cell due to the lengthening of the microtubules that form between them.
At which phase does the migration of chromosome happen?
During anaphase, the sister chromatids at the equatorial plane are split apart at the centromere. Each chromatid, now called a chromosome, is pulled rapidly toward the centrosome to which its microtubule was attached.
What happens to the chromosomes and where do they move in anaphase?
Metaphase leads to anaphase, during which each chromosome’s sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Where do chromosomes migrate to?
In anaphase, sister chromatids (now called chromosomes) are pulled toward opposite poles. In telophase, chromosomes arrive at opposite poles, and nuclear envelope material surrounds each set of chromosomes.
How many chromosomes are moving to each pole during anaphase of mitosis?
Anaphase I: In anaphase I, the attachment of the spindle fibers is complete. The homologous chromosomes are pulled apart and move towards opposite ends of the cell. Do not confuse this with the pulling apart of sister chromatids! This is the point in which reduction occurs with 23 chromosomes moving to each pole.
What event occurs during anaphase?
In anaphase, the sister chromatids separate from each other and are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell. The protein “glue” that holds the sister chromatids together is broken down, allowing them to separate. Each is now its own chromosome. The chromosomes of each pair are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell.
What happens in G1 G2 and S phase?
Initially in G1 phase, the cell grows physically and increases the volume of both protein and organelles. In S phase, the cell copies its DNA to produce two sister chromatids and replicates its nucleosomes. Finally, G2 phase involves further cell growth and organisation of cellular contents.
What occurs during the G1 phase?
In G1, cells accomplish most of their growth; they get bigger in size and make proteins and organelles needed for normal functions of DNA synthesis. Here, proteins and RNAs are synthesized, and, more especially the centromere and the other components of the centrosomes are made.
