Why does energy flow through an ecosystem?
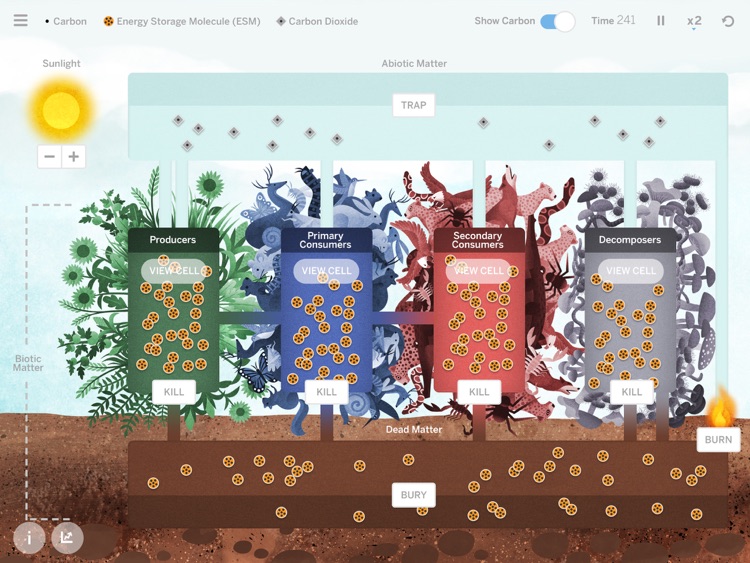
The energy flow in the ecosystem is important to maintain an ecological balance. The producers synthesise food by the process of photosynthesis. The remaining energy is utilised by the plants in their growth and development. This stored energy is transferred to the primary consumers when they feed on the producers. 294 views
What is energy through an ecosystem?
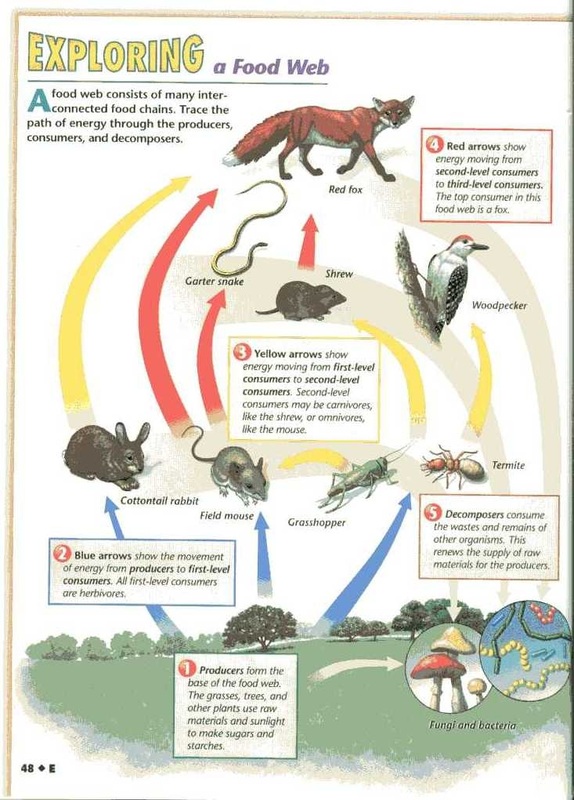
What is the flow of energy within an ecosystem? Energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. All living organisms can be organized into producers and consumers, and those producers and consumers can further be organized into a food chain. Each of the levels within the food chain is a trophic level.
How does the energy flow through the ecosystem?
The flow of energy through living organisms in most ecosystems begins with photosynthesis. This process stores energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of glucose. This energy transfers up the food chain as one organism eats another. For example, a grasshopper is a primary consumer that eats grass.
What is the flow of energy through an ecosystem called?
The study of the flow of energy through the Ecosystem is known as ecological energetics. All the power utilised by living organisms is ultimately derived from the sun. Still, as little as (1% ) of its total radiant energy is captured by green plants for distribution throughout the Ecosystem.
What happens to energy in the ecosystem?
Energy is transferred between organisms in food webs from producers to consumers. The energy is used by organisms to carry out complex tasks. The vast majority of energy that exists in food webs originates from the sun and is converted (transformed) into chemical energy by the process of photosynthesis in plants.
What happens to matter in ecosystems?
Matter is recycled and is not lost from the ecosystem. Living things need nonliving matter as well as energy. Carbon and nitrogen are examples of nutrients. Unlike energy, matter is recycled in ecosystems.
Are energy and matter recycled in an ecosystem?
Matter is cycled through the ecosystem in biogeochemical cycles. However, energy is not recycled, but it flows in the ecosystem. Energy is responsible for making the biogeochemical cycles run continuously in our ecosystem.
How do matter and energy interact within an ecosystem?
Food webs model how matter and energy are transferred among producers, consumers, and decomposers as the three groups interact within an ecosystem. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration provide most of the energy for life processes.
What happens to matter in an ecosystem quizlet?
Continual movement of the elements and compounds that make up nutrients through air, water, soil, rock, and living organisms within ecosystems. Cycle that collects, purifies, and distributes Earths's fixed supply of water. Precipitation that seeps into the ground and collects in an aquifer.
How is matter used in an ecosystem?
In ecosystems, matter and energy are transferred from one form to another. Matter refers to all of the living and nonliving things in that environment. Nutrients and living matter are passed from producers to consumers, then broken down by decomposers. Decomposers break down dead plant and animal matter.
How is matter gained or lost in an ecosystem?
Answer and Explanation: Matter is gained or lost in ecosystems because it can be transferred between different ecosystems. For example, all organisms contain energy in the form of chemical energy stored in their tissues.
How is matter conserved in an ecosystem?
Within individual organisms, food moves through a series of chemical reactions in which it is broken down and rearranged to form new molecules to support growth or to release energy. Matter is conserved during cellular respiration because atoms are conserved in physical and chemical processes.
What is the matter present in an ecosystem?
The total organic matter present in an ecosystem is hence called BIOMASS.
How does energy enter an ecosystem?
Energy enters an ecosystem when producers carry out photosynthesis, capturing energy from the sun and storing it as chemical energy in molecular bonds. During this process, matter from the environment (in the form of and ) is taken in and rearranged into organic molecules (sugars).
How are matter and energy conserved?
Energy and matter are conserved during ecosystem processes. As energy moves through an ecosystem, it changes form, but no new energy is created. Similarly, as matter cycles within an ecosystem, atoms are rearranged into various molecules, but no new matter is created.
What is the term for an organism that obtains energy by breaking down nonliving organic matter?
Decomposer. An organism that obtains energy by breaking down nonliving organic matter, such as discarded plant material, the remains of dead organisms, or animal waste. Food web. A model that shows how matter and energy are transferred among producers, consumers, and decomposers in an ecosystem. Trophic level.
How does energy move up the trophic level?
Next, energy and matter move up the trophic levels of an ecosystem as producers are eaten by primary consumers, which are then eaten by secondary consumers, and so on. Some of the organic material eaten by consumers is used for cellular respiration (again, releasing and heat), some is stored as biomass, and the rest is excreted as waste.
How do decomposers change matter?
Decomposers transform matter back into inorganic forms that can be recycled within the ecosystem. So, the energy that enters an ecosystem as sunlight eventually flows out of the ecosystem in the form of heat. In contrast, the matter in an ecosystem is continuously recycled as atoms are combined and recombined in different ways.
What is the trophic level of an ecosystem?
Trophic level. An organism’s position relative to the primary energy source (such as the sun) in a food chain. Ecological pyramid. A model that represents the relative amount of matter and energy contained within each trophic level of an ecosystem.
How many levels are there in the energy pyramid?
An energy pyramid displays four levels. Below the energy pyramid, an arrow labeled light energy points to producers. Producers correspond to one hundred percent of available energy. Above this, primary consumers correspond to ten percent available energy. Secondary consumers are the next level up and correspond to one percent of available energy. At the top are tertiary consumers, which correspond to zero point one percent available energy.
How does matter pass through an ecosystem?
Matter can pass between ecosystems as well. Water falls from the sky as rain to enter an ecosystem, and water drains away through rivers to the sea. Chemicals and seeds from elsewhere are even carried to an area on the bodies of animals or by the wind.
How does an ecosystem receive water?
An ecosystem will receive water through rain, lose water in rivers, gain and lose nutrients, and gain energy from the sun. This energy from the sun is the biggest flow into an ecosystem, and is responsible for almost all life on earth. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.
What is an Ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a group of living organisms interacting with one another and with their environment. That environment can include soil, air, water, and weather systems. Ecosystems can be simple and sparsely populated or complex and full of life. Some of the most densely packed and varied ecosystems in the world are places like rainforests and underwater coral reefs.
What is the process of converting light energy into glucose?
Matter Changes & Flow. We've already talked about photosynthesis, where plants turn light energy into glucose. But that glucose is made of more than pure energy -- it contains matter. Photosynthesis requires light energy, carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide is absorbed on the underside of leaves.
What is the flow of matter and energy from one place to another?
Ecosystems are a constant flow of matter and energy from one place to another. In this lesson, we will discuss some of the important energy and matter cycles that take place within and between ecosystems.
How does glucose pass down the food chain?
The matter that forms this glucose passes down the food chain in the same way that energy does -- from animal to animal as they eat one another. These are the building blocks from which humans and other animals are made.
Why are rainforests considered the lungs of the world?
That's why rainforests are often described as the lungs of the world. Plants also pass on material when they drop their leaves in the autumn, or die and fall to the forest floor. Ecosystems even have movements of matter and energy inside the ecosystem too. An example of this is something called the nitrogen cycle.
