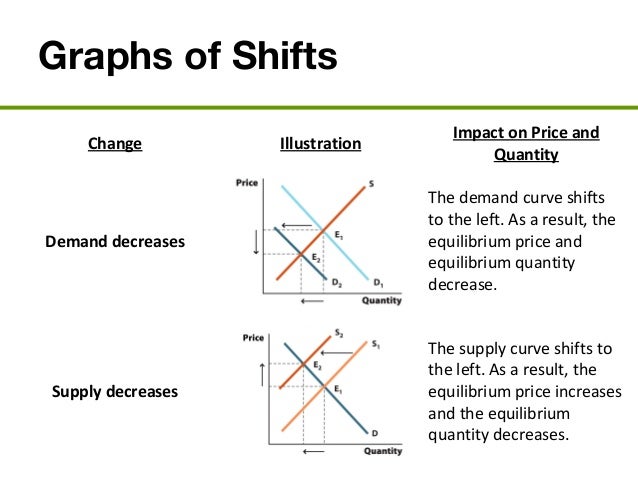
Upward shifts in the supply and demand curves affect the equilibrium price and quantity. If the supply curve shifts upward, meaning supply decreases but demand holds steady, the equilibrium price increases but the quantity falls. For example, if gasoline supplies fall, pump prices are likely to rise.
How to calculate equilibrium price?
Calculating the equilibrium price becomes simple when you know the supply function, demand function, and equilibrium price formula. The linear supply function is-Qs = x + yP, where Qs= supplied quantity, x= quantity, P= price. The demand function is-Qd = x + yP, where Qd= demanded quantity, x= quantity, P= price. Finally, the equilibrium price formula is-Qs = Qd
How do I find the new equilibrium price?
- Graphical method: find the intersection of the demand and supply curves on a graph.
- Table method: find the price at which quantity supplied and quantity demanded are equal.
- Algebraic method: set the supply and demand functions equal to one another and solve for price.
When prices are above the equilibrium price?
When the price of a commodity goes above the equilibrium price it means there is shortage in supply and high a demand for the goods. Most producers try to take advantage of this period, when they eventually produce more it will lead to surplus goods and a fall in price.
How do prices affect the market equilibrium?
With increase in Price, Suppliers will provide a higher Quantity. If the Price is set above the Equilibrium Price, then the Quantity Supplied will be higher than the Quantity Demanded and there will be a surplus which will drive the Price back to the Equilibrium Price. What happens if demand increases and supply decreases?

What would happen to equilibrium price and quantity if there is an increase in the price of sugar?
As a result, the equilibrium price increases and equilibrium quantity decreases.
What happens to price and quantity when price increases?
As we can see on the demand graph, there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. Economists call this the Law of Demand. If the price goes up, the quantity demanded goes down (but demand itself stays the same). If the price decreases, quantity demanded increases.
What happens to market equilibrium when price increases?
Once you raise the price of your product, your product's quantity demanded will drop until equilibrium is reached. Therefore, shortage drives price up. If a surplus exist, price must fall in order to entice additional quantity demanded and reduce quantity supplied until the surplus is eliminated.
What happens when prices increase?
In an inflationary environment, unevenly rising prices inevitably reduce the purchasing power of some consumers, and this erosion of real income is the single biggest cost of inflation. Inflation can also distort purchasing power over time for recipients and payers of fixed interest rates.
Does an increase in price increase quantity?
An increase in price almost always leads to an increase in the quantity supplied of that good or service, while a decrease in price will decrease the quantity supplied.
Why would equilibrium price increase?
An increase in demand, all other things unchanged, will cause the equilibrium price to rise; quantity supplied will increase. A decrease in demand will cause the equilibrium price to fall; quantity supplied will decrease.
Why does quantity increase when price increases?
The higher the price, the higher the quantity supplied. Lower prices mean reduced supply, all else held equal. Higher prices give suppliers an incentive to supply more of the product or commodity, assuming their costs aren't increasing as much. Lower prices result in a cost squeeze that curbs supply.
What causes price and quantity to increase?
An increase in demand, all other things unchanged, will cause the equilibrium price to rise; quantity supplied will increase. A decrease in demand will cause the equilibrium price to fall; quantity supplied will decrease.
What happens to price and quantity?
If demand increases, equilibrium price and quantity both increase. If demand decreases, equilibrium price and quantity both decrease. If supply increases, equilibrium price decreases, and quantity increases. If supply decreases, equilibrium price increases and equilibrium quantity decreases.
What happens to quantity when price falls?
If the price of a good falls, the quantity demanded of that good increases. The relationship between the quantity demanded and the price of a good when all other influences on buying plans remain the same. Demand is a list of quantities at different prices and is illustrated by the demand curve.
What happens when a price is above equilibrium?
Just as a price above the equilibrium price will cause a surplus, a price below equilibrium will cause a shortage. A shortage is the amount by which the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied at the current price.
How to find equilibrium price?
Draw a downward-sloping line for demand and an upward-sloping line for supply. The initial equilibrium price is determined by the intersection of the two curves. Label the equilibrium solution. You may find it helpful to use a number for the equilibrium price instead of the letter “P.” Pick a price that seems plausible, say, 79¢ per pound. Do not worry about the precise positions of the demand and supply curves; you cannot be expected to know what they are.
How does equilibrium affect supply and demand?
The equilibrium of supply and demand in each market determines the price and quantity of that item. Moreover, a change in equilibrium in one market will affect equilibrium in related markets. For example, an increase in the demand for haircuts would lead to an increase in demand for barbers.
How does the demand and supply of coffee affect the equilibrium price?
Both the demand and the supply of coffee decrease. Since decreases in demand and supply, considered separately, each cause equilibrium quantity to fall, the impact of both decreasing simultaneously means that a new equilibrium quantity of coffee must be less than the old equilibrium quantity. In Panel (a), the demand curve shifts farther to the left than does the supply curve, so equilibrium price falls. In Panel (b), the supply curve shifts farther to the left than does the demand curve, so the equilibrium price rises. In Panel (c), both curves shift to the left by the same amount, so equilibrium price stays the same.
What happens when the supply curve and demand curve intersect?
With an upward-sloping supply curve and a downward-sloping demand curve, there is only a single price at which the two curves intersect. This means there is only one price at which equilibrium is achieved. It follows that at any price other than the equilibrium price, the market will not be in equilibrium. We next examine what happens at prices other than the equilibrium price.
How does an increase in demand for coffee affect the demand curve?
An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right, as shown in Panel (a) of Figure 3.17 “Changes in Demand and Supply”. The equilibrium price rises to $7 per pound. As the price rises to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied increases to 30 million pounds of coffee per month. Notice that the supply curve does not shift; rather, there is a movement along the supply curve.
What is the equilibrium price of coffee?
The equilibrium price in any market is the price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The equilibrium price in the market for coffee is thus $6 per pound. The equilibrium quantity is the quantity demanded ...
What happens to equilibrium price if supply and demand increase?
4.27 (a). If increase in supply is greater than the increase in demand as in Fig. 4.27 (b), new equilibrium price will be lower than the initial price.
What is the initial equilibrium price and quantity?
Initial equilibrium price and quantity are OP* and OQ*, respectively. Increase in supply means shifting of the supply curve to S 1 S 1. However, new equilibrium price declines to OP 1, while equilibrium quantity remains stationary at OQ*.
What happens to demand curve when demand increases?
If demand increases, demand curve will shift to D 1 D 1 and the new equilibrium price will rise to OP 1 and quantity demanded and supplied will increase to OQ 1. Similarly, when demand curve shifts downward to D 2 D 2, price and quantity decline to OP 2 and OQ 2, respectively.
What happens if the supply curve is drawn perfectly inelastic?
4.25 (c)] an increase in demand will cause price to rise to OP 1. Equilibrium quantity will remain the same (OQ).
What does change in supply mean?
By change in supply, we mean shifting of the supply curve. If supply increases (or decreases) supply curve will shift rightward (or leftward). In Fig. 4.26 (a), OP* is the initial equilibrium price and OQ* the equilibrium quantity.
What is change in demand?
Change in Demand: Change in demand refers to an increase (or decreases) in demand following a rise (or fall) in consumer’s money income, tastes and preferences, etc. Under the circumstances, own price of the commodity remains fixed.
Does equilibrium quantity increase or decrease?
Increase in demand and decrease in supply will lead to an increase in price [Fig. 4.27 (d)], but equilibrium quantity may increase or decrease. However, equilibrium quantity may remain unchanged at OQ* if increase in demand is offset by a decrease in supply by the same amount.
Why is the new equilibrium price lower than the equilibrium price in #2 above?
The new equilibrium price will be lower than the equilibrium price in # 2 above because more B is available at every price than was the case in # 2. It might be lower than it was even in #1, but that is not certain. It would depend upon how much the B industry expanded.
What happens when the price of substitute good demand falls?
With the fall in the price of substitute good demand for it also rises which brings excess demand into the market ,keeping that there is no change in the supply for the commodity.
What happens when the quantity demanded of bread decreases?
This leads to an downward (left) shift of the demand curve along the supply curve, which also causes a decrease in price.
How does the demand curve travel?
If we want to look at the long run, to get back to our original equilibrium, the demand curve has to travel downward (to the left) along the supply curve. Once we have been forced back into equilibrium (both curves have shifted), we see that we have arrived back at our original price, but our overall quantity demanded is lower.
What happens if B is more expensive than it used to be?
If this happens, the amount of B supplied at every price will be higher than it was, making B even less expensive (relatively) than it used to be. This is a change in supply, which is the result of non-price factors. If they believe that the higher price of A is temporary, then they are unlikely to expand production.
Is there a direct relationship between the price of one substitute good and quantity of the other?
Thus, there is direct relationship between the price of one substitute good and quantity of the other.
Do shifts in the demand curve shift the supply curve?
In micro analysis, shifts in the demand curve do not shift the supply curve.
