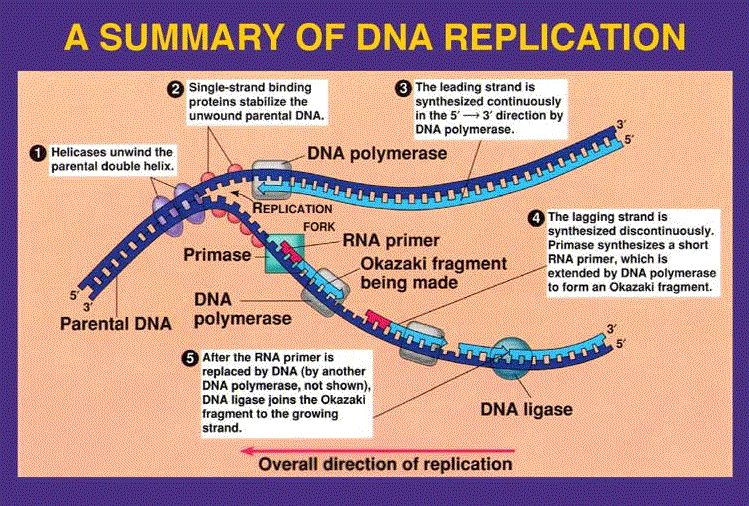
What helps DNA unwind during transcription?
- RNA polymerase moves along the DNA unwinding the strand.
- Hydrogen bonds between base pairs break which allows the unzipping of the double helix.
- As RNA polymerase breaks the bonds, it synthesises a primary transcript of mRNA using RNA nucleotides. ...
- The primary transcript of mRNA is processed to produce a mature transcript of mRNA.
What must happen to DNA before making RNA?
mRNA Processing
- 5′ Capping. While the pre-mRNA is still being synthesized, a 7-methylguanosine cap is added to the 5′ end of the growing transcript by a phosphate linkage.
- 3′ Poly-A Tail. ...
- Pre-mRNA Splicing. ...
What part of DNA is recognized during transcription?
During transcription of DNA a special sequence of nucleotides known as “Promoter” is recognized by RNA polymerase in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes it is recognized by RNA polymerase second. Promoter is a site on DNA where RNA polymerase recognizes...
What happens during the initiation step of DNA transcription?
Transcription initiation is the phase during which the first nucleotides in the RNA chain are synthesized. It is a multistep process that starts when the RNAP holoenzyme binds to the DNA template and ends when the core polymerase escapes from the promoter after the synthesis of approximately the first nine nucleotides.

How does DNA transcription occur in eukaryotes?
In prokaryotes, such as bacteria, the DNA is transcribed by one RNA polymerase molecule without the assistance of transcription factors. In eukaryotic cells, transcription factors are needed for transcription to occur and there are different types of RNA polymerase molecules that transcribe the DNA depending on the type of genes. Genes that code for proteins are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, genes coding for ribosomal RNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase I, and genes that code for transfer RNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase III. In addition, organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own RNA polymerases which transcribe the DNA within these cell structures.
What is the purpose of DNA transcription?
DNA transcription is a process that involves transcribing genetic information from DNA to RNA. The transcribed DNA message, or RNA transcript, is used to produce proteins. DNA is housed within the nucleus of our cells. It controls cellular activity by coding for the production of proteins. The information in DNA is not directly converted into proteins, but must first be copied into RNA. This ensures that the information contained within the DNA does not become tainted.
What enzymes unwind the DNA strand and allow RNA polymerase to transcribe only a single?
Elongation. Certain enzymes called transcription factors unwind the DNA strand and allow RNA polymerase to transcribe only a single strand of DNA into a single stranded RNA polymer called messenger RNA (mRNA). The strand that serves as the template is called the antisense strand.
How does reverse transcription work?
DNA is transcribed and translated to produce proteins. Reverse transcription converts RNA to DNA. In reverse transcription, RNA is used as a template to produce DNA. The enzyme reverse transcriptase transcribes RNA to generate a single strand of complementary DNA (cDNA).
How do ribosomes and RNA work together?
Once in the cytoplasm, ribosomes and another RNA molecule called transfer RNA work together to translate mRNA into a protein. This process is called translation. Proteins can be manufactured in large quantities because a single DNA sequence can be transcribed by many RNA polymerase molecules at once.
What enzyme transcribes DNA?
DNA is transcribed by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. Specific nucleotide sequences tell RNA polymerase where to begin and where to end. RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA at a specific area called the promoter region.
How does mRNA translate into protein?
Once in the cytoplasm, ribosomes and another RNA molecule called transfer RNA work together to translate mRNA into a protein. This process is called translation. Proteins can be manufactured in large quantities because a single DNA sequence can be transcribed by many RNA polymerase molecules at once.
What happens to the RNA Transcription?
In the process of RNA transcription, in which a DNA sequence of the gene is copied out or transcribed to create an RNA molecule. The main enzyme involved in RNA transcription is known as RNA polymerase. The process of transcription starts when RNA polymerase binds a promoter sequence near the start location of the gene. The process of RNA transcription ends in the process known as �termination�. The termination depends on the sequence in RNA that gives the signal that transcription is finished.
What is the process of transcription termination?
Transcription Termination: Various processes of regulator transcription termination had discovered in eukaryotes and bacteria. RNA polymerase works for the two principal mechanisms of the termination of transcription occurs in E. coli. In the additional protein, the transcription termination factor known as Rho, which is a need in one mechanism but not in another mechanism. These two mechanisms are referred to as Rho-independent and Rho-dependent termination. The process of the ending of transcription is known as �transcription termination� and occurs once the polymerase transcribes in a DNA sequence called �terminator�.
What is the beginning step of transcription?
Transcription Initiation: Initiation is the beginning step or transcription. It lies when the RNA polymerase named enzyme binds to an area or region of a gene, known as �promoter�. The signals to the DNA for unwinding, so the enzymes can be read as the bases in one of the DNA strands. Then, the enzyme s ready to create a strand ...
What is the second stage of RNA polymerase?
Elongation: Elongation is the second stage, in which one strand of DNA or the template strand works as a template for RNA polymerase. This template one base at a time, the polymerase creates an RNA molecule out of complementary nucleotides, by making a chain, which grows from 5� to 3�.
What is the first step in the expression of a gene?
DNA Transcription Introduction: In DNA transcription, the DNA sequence of a gene is copied out (transcribed) in order to make a molecule of RNA. It is the first step in the expression of the gene. The process of DNA Transcription is done by the enzymes known as RNA polymerases.
What is the function of a promoter in bacteria?
Promoter in bacteria is the common feature of DNA transcription regulators in their ability to recognizes the particular DNA pattern to modulate gene expression. The upstream regulation of the region of bacterial coding consists of a promoter, which is the DNA sequence that determines the particular recognition by the RNAP holoenzyme.
Which factor binds the sequence and begins climbing up the transcription toward the RNA polymerase?
The Rho factor binds the sequence and begins �climbing up� the transcription toward the RNA polymerase. Rho-independent termination: In the mechanism of Rho-independent termination, it depends on the particular sequence in the DNA template strand. RNA polymerase approach at the end of the gene being transcribed, ...
How does transcription work?
Through transcription, the sequence of bases of the DNA is transcribed into the reciprocal sequence of bases in a strand of RNA. Through transcription, the information of the DNA molecule is passed onto the new strand of RNA which can then carry the information to where proteins are produced.
What is the purpose of transcription and translation?
Transcription and translation take the information in DNA and use it to produce proteins. Transcription uses a strand of DNA as a template to build a molecule called RNA.
What is the sequence of nitrogenous bases?
Sequence of nitrogenous bases and the template strand. Each nitrogenous base of a DNA molecule provides a piece of information for protein production. A strand of DNA has a specific sequence of bases. The specific sequence provides the information for the production of a specific protein. Through transcription, ...
What is the section of DNA that is transcribed?
The section of DNA or the gene that is transcribed is known as the ‘transcription unit’ . Rather than RNA polymerase moving along the DNA strand, the DNA moves through the RNA polymerase enzyme. As the template strand moves through the enzyme, it is unravelled and RNA nucleotides are added to the growing mRNA molecule.
What are the two processes that convert a sequence of nucleotides from DNA into a sequence of amino?
Proteins are made from a sequence of amino acids rather than nucleotides. Transcription and translation are the two processes that convert a sequence of nucleotides from DNA into a sequence of amino acids to build the desired protein.
What is the process of producing a strand of RNA from a strand of DNA?
Transcription. Transcription is the process of producing a strand of RNA from a strand of DNA. Similar to the way DNA is used as a template in DNA replication, it is again used as a template during transcription. The information that is stored in DNA molecules is rewritten or ‘transcribed’ into a new RNA molecule.
What are the two bases that bond DNA?
Two strands of DNA are bonded together by their nitrogenous bases. The bases form what are called ‘base pairs’ where adenine and thymine bond together and guanine and cytosine bond together. Adenine and thymine are complementary bases and do not bond with the guanine and cytosine.