In normal economic circumstances, a fall in the oil price can help the economy. Lower oil prices reduce the cost of transport and lead to lower costs for business, which can increase profitability. Consumers see a reduction in cost of transport and heating, leading to higher discretionary incomes
Will oil stocks increase?
These oil stocks could produce a gusher of profits as crude prices continue rallying. Bank of America recently made a bold prediction. The banking giant believes that supply and demand imbalances in the oil market will push crude prices up to $100 a barrel by next year.
When will oil stocks rise?
The stock trades at roughly 11 times 2022 earnings expectations and if oil continues higher, those growth estimates will likely tiptoe higher.
When will oil prices improve?
The EIA forecast that Brent crude oil prices will average $103.37/b in 2022. WTI is forecast to average $97.96/b in 2022. Oil prices are rising due to an increase in demand and a decrease in supply. OPEC is gradually increasing oil production after limiting it due to a decreased demand for oil during the pandemic.
Why are crude oil prices rising?
Why are oil prices rising? As the world economy recovers from COVID-19, global demand for crude oil has increased in 2021 resulting in a sharp rise in prices. Another reason for a sharp increase in international oil prices is the supply restrictions maintained by the OPEC+ grouping nations.
What happens if oil price decrease?
Lower oil prices tend to push equity markets higher. The recent fall in oil is already addressing the depreciating rupee problem but we'll come to that later. Rising oil prices lead to higher inflation as prices of majority of products increase. Petrol and diesel prices rise and food prices follow.
How does the price of oil impact the economy?
Oil price increases are generally thought to increase inflation and reduce economic growth. In terms of inflation, oil prices directly affect the prices of goods made with petroleum products. As mentioned above, oil prices indirectly affect costs such as transportation, manufacturing, and heating.
Who benefits from a drop in oil prices?
Synthetic textile manufacturers are also one of the key beneficiaries of falling crude oil prices, since crude oil is an important component of industrial inputs like fibre, yarn, fabric and other textile products.
How does lower gas prices affect the economy?
Inversely, when gas prices fall, it is cheaper to fill up the tank for both households and businesses, and really eases costs on transportation-focused industries like airlines and trucking—but it also puts a damper on the domestic oil industry. In general, higher oil prices are a drag on the economy.
Does oil prices cause inflation?
Crude oil is a major economic input, so a rise in oil prices contributes to inflation, which measures the overall rate of price increases across the economy. Inflation as measured by the annual gain in the U.S. Consumer Price Index (CPI) set a 40-year high in March 2022 amid COVID-19 supply disruptions.
Is the US economy based on oil?
America's oil and natural gas industry supports 10.3 million jobs in the United States and nearly 8 percent of our nation's Gross Domestic Product. We spur economic growth through hundreds of billions of dollars investing right here at home every year.
Who owns the oil in Russia?
RosneftRosneft Headquarters, Sofiyskaya Embankment, Moscow, September 2005Total equity$88.1 billion (2021)OwnerRosneftegaz + subsidiaries (70%) Moscow Exchange (10.70%) QIA (18.46%) (2021)Number of employees334,600 (2019)Websiterosneft.com15 more rows
What industries are affected by oil prices?
High oil costs have hurt airlines and other transportation companies. Bigger energy bills also are pinching profits in a host of other industries — from semiconductor equipment makers who use fuel to make plastic components to energy-intensive industrial concerns such as DuPont and Alcoa.
What stocks to buy when oil is high?
Here are the seven Bank of America buy-rated stocks with the highest correlation to WTI crude oil prices:Schlumberger Ltd. (ticker: SLB)Hess Corp. (HES)Halliburton Co. (HAL)Baker Hughes Co. (BKR)Marathon Petroleum Corp. (MPC)Chevron Corp. (CVX)APA Corp. (APA)
Are higher gas prices good for the economy?
But higher fuel prices are a headwind for the wider economy too, beyond just consumers having less spending money. The rising cost of fuel, especially diesel, means that anything transported on a truck, train or ship is affected.
Are we in a recession 2022?
According to the general definition—two consecutive quarters of negative gross domestic product (GDP)—the U.S. entered a recession in the summer of 2022. The organization that defines U.S. business cycles, the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER), takes a different view.
Why is inflation so high right now?
The current high inflation rate can be attributed to many different factors, many of which are a result of the Covid-19 pandemic. Gapen pins rising prices on three general causes — increases in household demand and supply-chain shortages due to the pandemic, the war in Ukraine and the presence of a strong labor market.
What happens if oil price increase?
An increase in oil prices usually lowers the expected rate of economic growth and increases inflation expectations over shorter horizons. Decreasing economic growth prospects, in turn, lower companies' earnings expectations, resulting in a dampening effect on stock prices.
Why do oil prices matter to the global economy?
Oil accounts for approximately 3% of GDP and is one of the most important commodities in the world – petroleum products can be found in everything from personal protective equipment, plastics, chemicals and fertilisers through to aspirin, clothing, fuel for transportation and even solar panels.
Why is oil important to the economy?
The oil and gas industry supports millions of American jobs, provides lower energy costs for consumers, and ensures our energy security.
How is gas prices affecting the economy?
Average price for regular unleaded gallon of gas. These higher energy prices seep into almost every major part of the economy. They drive up the costs for electricity, transportation, shipping, logistics, air travel, agriculture, fertilizer and the production of other commodities.
How does oil affect the economy?
economy, but it goes two ways because of the diversity of industries. High oil prices can drive job creation and investment as it becomes economically viable for oil companies to exploit higher-cost shale oil deposits. However, high oil prices also hit business and consumers with higher transportation and manufacturing costs. Lower oil prices hurt the unconventional oil activity, but benefits manufacturing and other sectors where fuel costs are a primary concern.
Why was oil price drop positive?
oil production, drops in the price of oil were largely viewed as positive because it lowered the price of importing oil and reduced costs for the manufacturing and transport sectors. This reduction of costs could be passed on to the consumer.
Why did companies draw oil and gas from shale deposits that were once considered depleted?
In the latter half of the 2000s, however, new technology allowed companies to economically draw oil and gas from shale deposits that were once considered depleted because the cost of extraction would be impractical.
What are the groups that suffer when oil prices drop?
The other groups that tend to suffer when U.S. oil prices drop are the banking and investment sectors. There are a lot of different companies drilling and servicing wells on the shale deposits, and many of these companies finance their operations by raising capital and taking on debt.
What does lower oil prices mean?
Lower oil prices mean less drilling and exploration activity because most of the new oil driving the economic activity is unconventional and has a higher cost per barrel than a conventional source of oil. Less activity can lead to layoffs which can hurt the local businesses that catered to these workers.
How does less activity affect shale oil?
Less activity can lead to layoffs which can hurt the local businesses that catered to these workers. Therefore, the negative impact will be felt keenly in the shale regions even as some of the positive impacts of lower oil prices start to show in other regions of the United States.
How does oil affect the cost of doing business?
Oil and the Cost of Doing Business. The price of oil influences the costs of other production and manufacturing across the United States. For example, there is the direct correlation between the cost of gasoline or airplane fuel to the price of transporting goods and people.
How does falling oil prices affect the economy?
In normal economic circumstances, a fall in the oil price can help the economy. Lower oil prices reduce the cost of transport and lead to lower costs for business, which can increase profitability. Consumers see a reduction in cost of transport and heating, leading to higher discretionary incomes.
What are the consequences of oil prices falling?
However, the fall in oil prices is forcing the economies to diversify and invest in industries, such as manufacturing and agriculture. In the long term, this could lead to benefits as it is always dangerous to have an economy reliant on one commodity, such as oil. Countries which rely on oil exports, can suffer from a phenomena known as the “ Dutch Disease ” So the painful re-adjustment may be worth it in the long-run.
What happens if oil prices fall 10%?
If petrol prices fall 10%, then consumers will spend less on petrol / getting to work and have the ability to spend this extra discretionary income on other goods. Therefore, the fall in oil prices can lead to higher consumer spending in other areas of the economy.
Why are oil prices lower?
With lower oil prices, Central Banks have a better trade-off between inflation and unemployment. With falling prices helping to reduce inflation, Central Banks can keep interest rates lower without the risk of headline inflation.
What are the micro effects of falling oil prices?
But, evidence suggests that consumers are responding to a fall in petrol prices by driving more. A 10% increase in traffic levels on UK’s crowded roads could cause very significant problems of congestion.
What are the problems caused by deflation?
If we get deflation, then it can cause many problems in the economy, such as debt deflation, rising real interest rates and rising real wages. Falling oil prices could help embed deflationary pressures in the economy. The point is that falling oil prices can be beneficial in normal economic circumstances. However, because the global economy is ...
What will happen if oil companies go bankrupt?
With oil firms going bankrupt and investment being curtailed, there will be a negative impact on the global finance system. Banks which had lent money for oil investment are at risk of losing money, leading to a possible tightening of global credit. (with parallels to previous credit crunch)
What will happen to oil prices if the economy slows down?
If the world economy slows—and it certainly looks as if it has slowed, or will, due to the COVID-19 virus and people’s reaction to it—the demand for oil will fall. With a given supply, that will cause the price of oil to fall. The fall in the price of oil is not bad per se; rather, it’s a consequence of something bad, namely, the slowing of the world economy. And it certainly appears that a fall in demand due to a slowing economy caused prices to fall before last weekend. But it’s unlikely that there was a sudden fall in demand last weekend. We have to look elsewhere.
Why did oil prices drop?
There are three (and only three) reasons that oil prices drop: (1) demand decreases, (2) supply increases, or (3) the monopoly power of oil producers falls.
How does OPEC work?
First, recall that OPEC is a cartel. Government officials of the member countries get together and try to agree on a price. They want a price above what the competitive, non-colluding price would be. To achieve that cartel price, the members must produce an output below the output they would ideally like to produce. Each firm or, more accurately, government (since we’re talking about OPEC) would like to produce more and have every other country produce less. The members of OPEC meet regularly in Vienna to hash out their differences and try to reach an agreement. This time, though, there was real tension between Saudi Arabia’s desires and those of Russia. OPEC lists its members on its website, and although the Russians attended the latest meeting, and typically attend OPEC meetings, Russia is not, and never has been, an OPEC member.
How about an increase in supply?
How about an increase in supply? If supply increases, then, with a given demand, prices will fall. Notice that I'm using the word "supply" to mean not the quantity supplied, but the whole supply curve. When an economist says that supply increased, he means that at any given price, the quantity supplied has increased. The whole supply curve has shifted to the right. This sounds wonky and may remind you of an old economics class in which the professor insisted on the distinction between a shift in supply and a movement along a stable supply curve. But here we need a little wonkiness to help us analyze.
Why has the stock market fallen?
So why has the stock market fallen so much? Part of the reason is, no doubt, the increased panic, possibly justified, about the loss in output due to the Covid-19 virus. You might expect that if the only event affecting the stock market was OPEC’s temporary loss in monopoly power, the losses to industries that produce energy would be only slightly larger than the gain to industries that use energy as an input. But that ignores the fact that a large percentage of the gain from the drop in price is to final consumers, and most of us consumers don’t sell stock in our wealth. There’s no stock called David Henderson, Inc., for example. So a large part of the gain is not visible on the stock market.
When did OPEC raise the price of oil?
Ever since the fall of 1973, when OPEC raised the world price of oil from $3 per barrel to $11, OPEC has had some monopoly power in the world oil market. This causes the price to be higher than the competitive price would be and we oil users respond by using less oil than we would use at that lower competitive price.
What causes the price of oil to fall?
The other possible cause of a fall in the demand for oil is an increase in the supply of a substitute for oil. If, for example, solar or nuclear energy became more competitive, the demand for oil would fall. In that case, the fall in oil’s price would be a sign of something good happening in the economy.
How does declining oil prices affect the economy?
First, declining oil prices leads to declining revenue for oil and gas companies. Given that drilling for oil is a very capital intensive process requiring a lot of manufactured goods, equipment, supplies, transportation, and support, the decrease in prices leads to a reduction in activity as represented by Capital Expenditures (CapEx.) The chart below shows the 6-month average of the 6-month rate of change in oil prices as compared to CapEx spending in the economy.
What would happen if oil prices were depressed?
If oil prices, a reflection of global economic demand, remains depressed for a considerable period of time, the negative impacts of loss of employment, reductions in capital expenditures and declines in corporate profitability could outstrip any small economic benefit gained from lower oil prices.
What are the ramifications of the oil price plunge?
The obvious ramification of the plunge in oil prices is that eventually the loss of revenue will lead to cuts in production, declines in capital expenditure plans (which comprises almost 1/4th of all capex expenditures in the S&P 500), freezes and/or reductions in employment, and declines in revenue and profitability.
How can we view the impact of oil prices on inflation?
We can also view the impact of oil prices on inflation by looking at breakeven inflation rates as well. As I noted in “Oil Sends A Crude Warning:”
Why is lower oil price good?
The argument is that lower oil prices gives consumers more money to spend certainly seems entirely logical. Since we know that roughly 80% of households in America effectively live paycheck-to-paycheck, they will spend, rather than save, any extra disposable income.
What will increase consumer spending?
The only thing that will increase consumer spending are increases in INCOME, not SAVINGS. Consumers only have a finite amount of money to spend. They can choose to “save more” which is a drag on economic growth in the short-term (called the “paradox of thrift” ) or they can spend what they have. But they can’t spend more.
Is falling oil prices a drag on economic growth?
Another important issue to this analysis is that falling oil prices are a bigger drag on economic growth than the incremental “savings” received by the consumer.
What happened to oil prices in the 1980s?
During the oil price decline of the 1980s, most oil-dependent countries suffered the consequences of the resulting collapse in investment and consumption. A few, such as Oman and Malaysia, were able to compensate for the price collapse by increasing production, but many oil exporters suffered, also due to the production cuts agreed by Opec. Some recovered better than others, but in general between 1982 and 2002 they fared much more poorly than the rest of the developing world.
Is oil abundance a curse?
Oil abundance is not necessarily a curse. Most producers are better prepared this time around, but for the few that learned nothing from the past, the reality will be as harsh as the grasshoppers’ winter.
Is oil a curse?
Poverty and unemployment rose sharply. In fact, such underperformance led to the widespread idea that having oil is a curse, which has generated extensive literature. The reality is more complex, as shown by economic overperformance during the past decade’s boom. In fact, taking out those two “bust” decades, oil countries have outperformed their peers over the past 70 years. So the real “curse” is in fact an oil price collapse.
Will net importers benefit from the oil price decline?
Net importers, like most European countries, will benefit from the oil price decline. In the US, citizens will pay significantly less for gasoline than they have over the past five years, leading them to spend more on other goods. A vast transfer of wealth from exporters to importers is occurring.
The State of the War
Nord Stream Pipeline: Explosions under the Baltic Sea and the rupture of major natural gas pipelines from Russia to Germany appeared to be a deliberate attack, European officials said, exposing the vulnerability of the continent’s energy infrastructure.
Live Updates: Russia-Ukraine War
Moscow releases final results of discredited referendums in occupied territories.
What caused the oil price to collapse?
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered an unprecedented demand shock in the oil industry, leading to a historic market collapse in oil prices. Demand for oil cratered as governments around the world shuttered businesses, issued stay-at-home mandates, and restricted travel.
What happened to oil prices in 2020?
oil prices to go negative for the first time on record. In a matter of hours on April 20, the May 2020 contract futures price for West Texas Intermediate (WTI) plummetted from $18 a barrel to around -$37 a barrel. 1
How much did Brent oil cost in June?
For the month of June, Brent crude oil spot prices averaged $40 per barrel, an increase of $11 per barrel from May's average. 6 Production cuts by OPEC and their partner countries (OPEC+) contributed to the decrease in global oil supply and a stabilization of oil prices.
How much did Brent oil increase in November?
In November, Brent crude oil spot prices increased to an average of $43 per barrel, an increase of $3 a barrel from October's per barrel average. 9 .
How much oil will be produced in 2021?
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) forecasts total U.S. crude oil production will fall from 12.2 million barrels a day in 2019 to 11.1 million barrels a day in 2021. 10 .
How long did the price war last?
The month-long price war ended in April when the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies agreed to cut overall crude oil production by 9.7 million barrels per day for an initial period of two months starting on May 1. This represented the single largest output cut in history.
Why did the demand for oil fall in 2020?
In 2020, worldwide demand for oil fell rapidly as governments closed businesses and restricted travel due to the COVID-19 pandemic. An oil price war between Russia and Saudi Arabia erupted in March when the two nations failed to reach a consensus on oil production levels. In April, an oversupply of oil led to an unprecedented collapse in oil ...
When the price of oil signals a recession and how close we are to it
As an analyst covering the auto sector earlier in his career, Colas remembers the presentation decks used by economists employed by the “Big Three” automakers three decades ago, which they had been using since the 1970s oil shocks.
Consumer demand, gas usage and the economy
Still, underneath it all, oil prices drive gas prices and the consumer is 70% of the U.S. economy. “When you take that much money out of their pocket, it has to come from somewhere else,” Colas said.
Stock picks and investing trends from CNBC Pro
Is it time to buy Treasurys? Here’s how to allocate your portfolio, according to the pros
The S&P 500 history of oil companies
The past decade has not been kind to the energy sector of the S&P 500 and most investors are underweight energy stocks. As of now, the energy sector is 3.8% of the U.S. stock market. Even as energy stocks have bounced since the pandemic low of March 2020, their overall market profile has not risen.
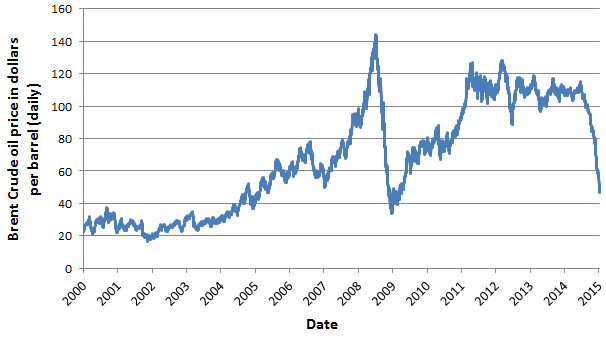
When did oil prices drop?
Between mid-2014 and early 2016, the global economy faced one of the largest oil price declines in modern history. The 70 percent price drop during that period was one of the three biggest declines since World War II, and the longest lasting since the supply-driven collapse of 1986.
Why did oil prices fall in 2014?
In the event, the benefits of substantially lower oil prices were muted by the low responsiveness of economic activity in key oil-importing emerging markets, the effects on U.S. activity of a sharp contraction in energy investment and an abrupt slowdown in key oil exporters.
What happened to the oil price in 2015?
Rather than lifting global growth, the oil price plunge was accompanied by a slowdown in 2015 and 2016. A sharp deceleration in oil-exporting economies dragged global economic activity down, but disappointing growth in oil-importing economies, including the United States, China and non-oil commodity exporting emerging markets, explained most of the negative surprise around that period.
Is oil price downgraded?
Long-term oil price forecasts have been considerably downgraded over the last few years, and numerous factors limit upside risks to the outlook. These include: the potential for further gains in shale oil production, an accelerated uptake of more fuel-efficient technologies, and policies supporting renewable energies.