What happens when the intercostal muscles relax?
The innermost intercostal muscles relax, while the external intercostal muscles contract, causing the chest cavity to expand. This expansion allows the lungs to fill with air, due to the negative pressure created by the extra space.
What happens to the diaphragm and intercostal muscles during inhalation?
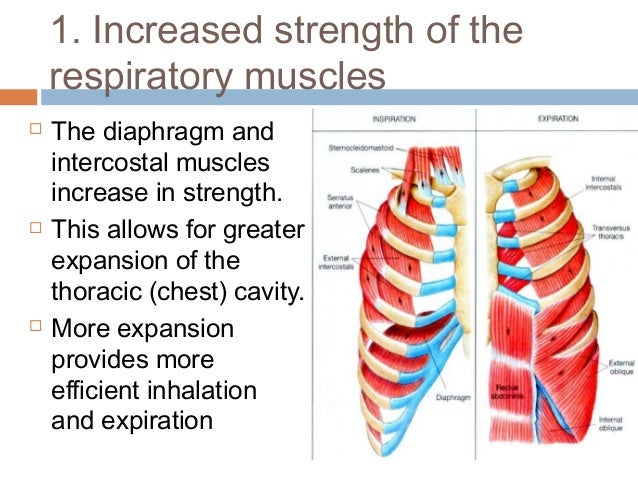
At rest, the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles (muscles between the ribs) contract and expand with each breath. Every breath expands and contracts the thoracic cavity, which is the space between the ribs and the spinal column. During inhalation, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases as air flows into the lungs.
What is the difference between internal and external intercostal?
The innermost intercostal lies inside the ribs. The internal intercostal muscle sits between two ribs. The external intercostal muscles sit on the outside of the ribs. Between each of the 12 ribs, each of these three intercostal muscles is present.
What causes intercostal muscle pain when exercising?
Oftentimes, people will experience pain in their intercostal muscles when exercising heavily. This pain is often caused by lactic acid build-up in the intercostal muscles. The muscles must work at a feverish pace when breathing hard, constantly contracting and releasing as a person breathes harder.
What do the intercostal muscles do during exercise?
Whilst the diaphragm acts as the primary flow generator during exercise, the role of the intercostal muscles is also important as they develop the necessary pressure to move the rib cage (Aliverti et al. 1997).
What happens to the intercostal muscles when?
When you inhale: the internal intercostal muscles relax and the external intercostal muscles contract, pulling the ribcage upwards and outwards. the diaphragm contracts, pulling downwards. lung volume increases and the air pressure inside decreases.
What happens to intercostal muscles during breathing?
The intercostal muscles are the muscles between the ribs. During breathing, these muscles normally tighten and pull the rib cage up. Your chest expands and the lungs fill with air. Intercostal retractions are due to reduced air pressure inside your chest.
What happens to the external intercostal muscles during inspiration?
In addition, the external intercostal muscles participate in inspiration by pulling the ribs abaxially to increase the width of the thoracic cavity. The net effect is an increase in the size of the thoracic cavity, producing subatmospheric intrathoracic pressure, to drive inspiration and pulmonary inflation.
How do intercostal muscles release?
3:054:22HOW TO DEAL WITH AN INTERCOSTAL STRAIN! - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOut you curl the fingers underneath the rib cage. So you're looking at about just the tip of theMoreOut you curl the fingers underneath the rib cage. So you're looking at about just the tip of the finger. And you're holding that for a couple of seconds. And then relaxing.
What is the role of the intercostal muscles and diaphragm?
The diaphragm is attached to the base of the sternum, the lower parts of the rib cage, and the spine. As the diaphragm contracts, it increases the length and diameter of the chest cavity and thus expands the lungs. The intercostal muscles help move the rib cage and thus assist in breathing.
What change occurs to the pressure and volume of the lungs when the external intercostal muscles contract?
What change occurs to the pressure and volume of the lungs when the external intercostal muscles contract? Pressure decreases and volume increases.
What muscle raises ribs and helps with breathing?
The external intercostal muscles are most important in respiration. These have fibres that are angled obliquely downward and forward from rib to rib. The contraction of these fibres raises each rib toward the rib above, with the overall effect of raising the rib cage, assisting in inhalation.
Do the internal intercostal muscles contract during expiration?
During expiration, the contraction of the internal intercostal muscles brings the rib cage back to its normal position and the abdominal muscles contract to assist the internal intercostal muscles and force the diaphragm upward. The respiratory system can adapt rapidly to the oxygen demands of the body.
What causes intercostal muscle spasms?
Common causes include: a direct blow to the rib cage, such as from a fall or car accident. an impact blow from contact sports, such as hockey or football. twisting the torso beyond its normal range of motion.
What happens during exhalation?
When the lungs exhale, the diaphragm relaxes, and the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases, while the pressure within it increases. As a result, the lungs contract and air is forced out.
Can intercostal muscle strain cause shortness of breath?
Difficulty breathing. Taking a full breath may be too painful with an intercostal muscle strain, causing breathing to become shallow. Breathing in shorter, shallower breaths to avoid pain can ultimately lead to less oxygen traveling through the body, undermining the healing process.
What muscles contract and expand with each breath?
At rest, the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles (muscles between the ribs) contract and expand with each breath. Every breath expands and contracts the thoracic cavity, which is the space between the ribs and the spinal column. During inhalation, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases as air flows into the lungs.
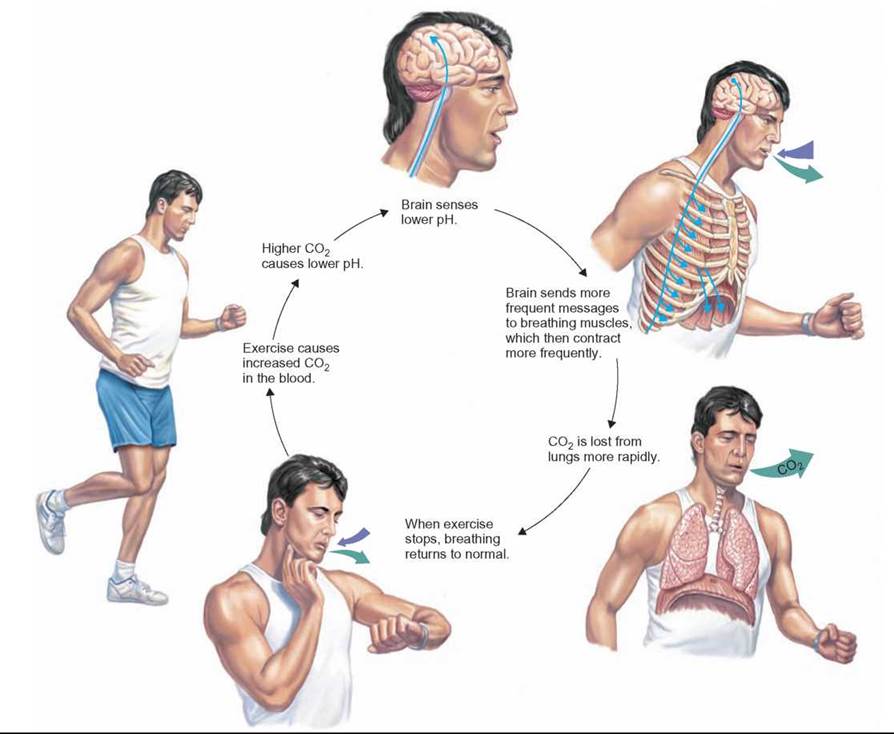
Why does respiration increase with exercise?
The rate of respiration also increases to facilitate the delivery of oxygen to the blood stream, where it is then transported to the working muscles.
What happens to the volume of the thoracic cavity when you breathe?
When the air is expelled, the volume decreases as air is forced out of the lungs. With every breath, air is moved into the lungs and oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
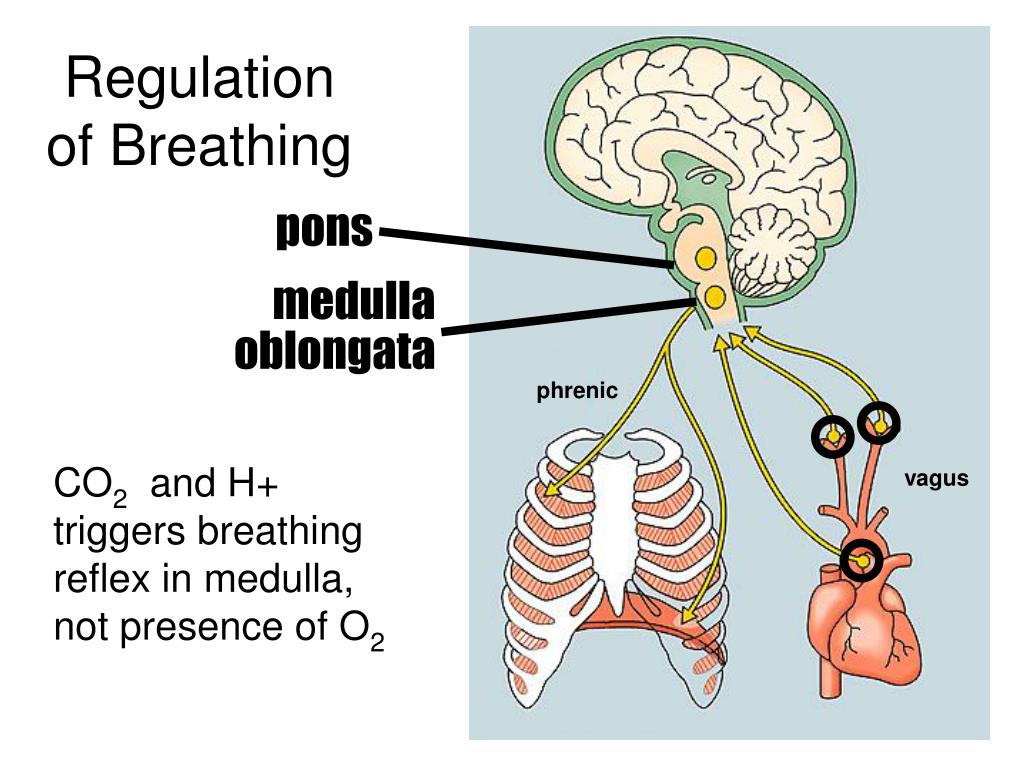
How does the body respond to CO2?
As the concentration of CO2 increases, the body responds by breathing deeper, and more frequently to dispel the CO2. Working muscles also require fresh oxygen. The rate of respiration also increases to facilitate the delivery of oxygen to the blood stream, where it is then transported to the working muscles.
How does endurance training help the body?
With continued endurance training, the body becomes more efficient at using oxygen, as well as ridding the body of metabolic byproducts. Working muscles become more proficient at extracting fresh oxygen from blood. The pulmonary system also adapts and improves its ability to transfer oxygen from the air to the blood stream ...
Does exercise increase ventilation?
As exercise intensifies and the body’s need for fresh oxygen increases, the ventilation rate responds accordingly. The metabolic byproducts of exercise build up as a result of cellular respiration, and the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the system also increases to act as a buffer against these acidic byproducts.
What are the intercostal muscles?
The intercostal muscles are a group of muscles found between the ribs which are responsible for helping form and maintain the cavity produced by the ribs. The muscles assist with expansion and contraction during breathing. The intercostal muscles consist of 11 muscle trios in humans.
How many types of intercostal muscles are there?
There are 3 types of intercostal muscle. The innermost intercostal lies inside the ribs. The internal intercostal muscle sits between two ribs. The external intercostal muscles sit on the outside of the ribs. Between each of the 12 ribs, each of these three intercostal muscles is present. The first and last ribs only have intercostal muscles on one ...
What muscles do snakes use?
While they have layers of muscles on top of their ribs that control their motion, the intercostal muscles have a much larger role to play in maintaining the shape and size of the body cavity. For instance, when a constricting a prey item, a large snake creates an enormous amount of pressure with their muscles.
What muscles help keep the ribs from separating?
This causes the chest cavity to contract as a whole, forcing the air out of your lungs. The internal intercostal muscles, or middle layer of muscle, helps keep the ribs from separating and holds the shape of the chest cavity.
How does the chest cavity contract?
To do this, the opposite process of inhalation happens. The diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract, applying force to the bottom and sides of the lungs. The innermost intercostal muscles now contract, while the external intercostal muscles relax. This causes the chest cavity to contract as a whole, forcing the air out of your lungs. The internal intercostal muscles, or middle layer of muscle, helps keep the ribs from separating and holds the shape of the chest cavity.
What muscles are involved in breathing?
In humans, the intercostal muscles play a large part in breathing. During inhalation, the diaphragm is relaxed, allowing the lungs to expand. The innermost intercostal muscles relax, while the external intercostal muscles contract, causing the chest cavity to expand.
Which muscle is used to expand and contract the lung?
By a similar process, the innermost and external intercostal muscles alternate their contracting and relaxing to expand and contract the lung. Snake skeleton. Snakes, having no limbs, must also use their intercostal muscles when making a variety of other movements.
Intercostal Muscles Definition
Intercostal Muscles Overview
Intercostal Muscles Function
- As exercise intensifies and the body’s need for fresh oxygen increases, the ventilation rate responds accordingly. The metabolic byproducts of exercise build up as a result of cellular respiration, and the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the system also increases to act as a buffer against these acidic byproducts. As the concentration of CO2 incr...
Examples of Intercostal Muscles