How is energy absorbed and released during photosynthesis?
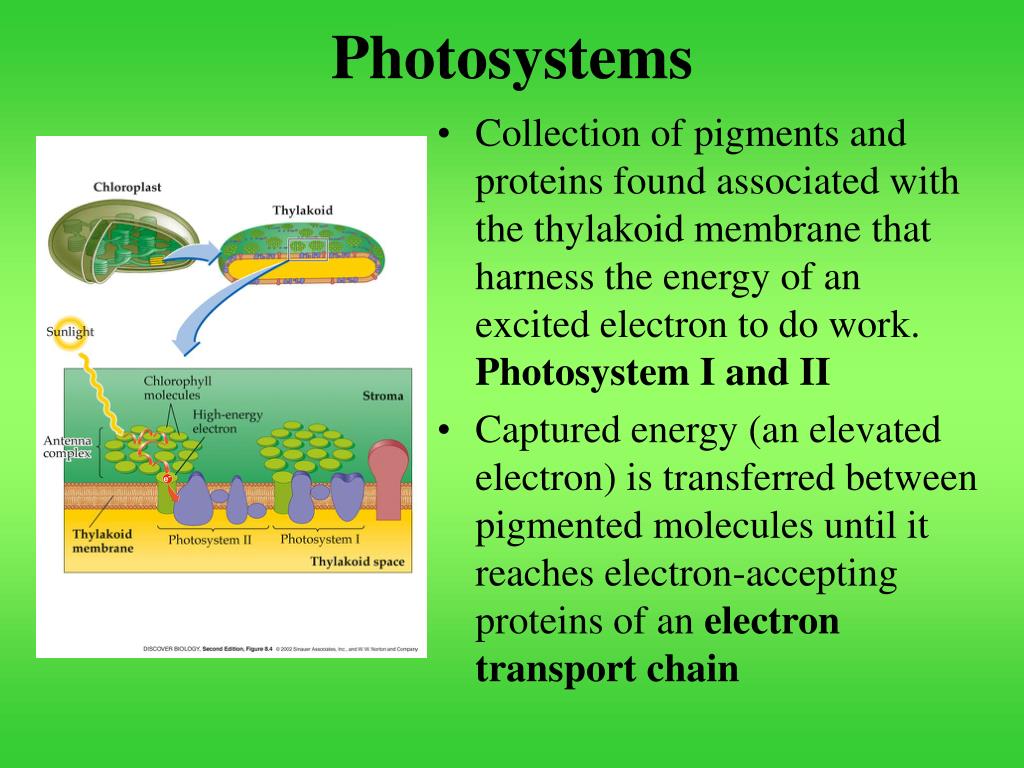
In the first part of photosynthesis, the light-dependent reaction, pigment molecules absorb energy from sunlight. The most common and abundant pigment is chlorophyll a. A photon strikes photosystem II to initiate photosynthesis. Energy travels through the electron transport chain, which pumps hydrogen ions into the thylakoid space.
What happens when light is absorbed in photosystem 2?
When light is absorbed by one of the pigment molecules in photosystem II, the energy is transferred from pigment molecule to pigment molecule before reaching the reaction centre. Once in the reaction centre, the energised electron is transferred to a specialised pair of chlorophyll molecules called P680.
What happens in the light phase of photosynthesis?
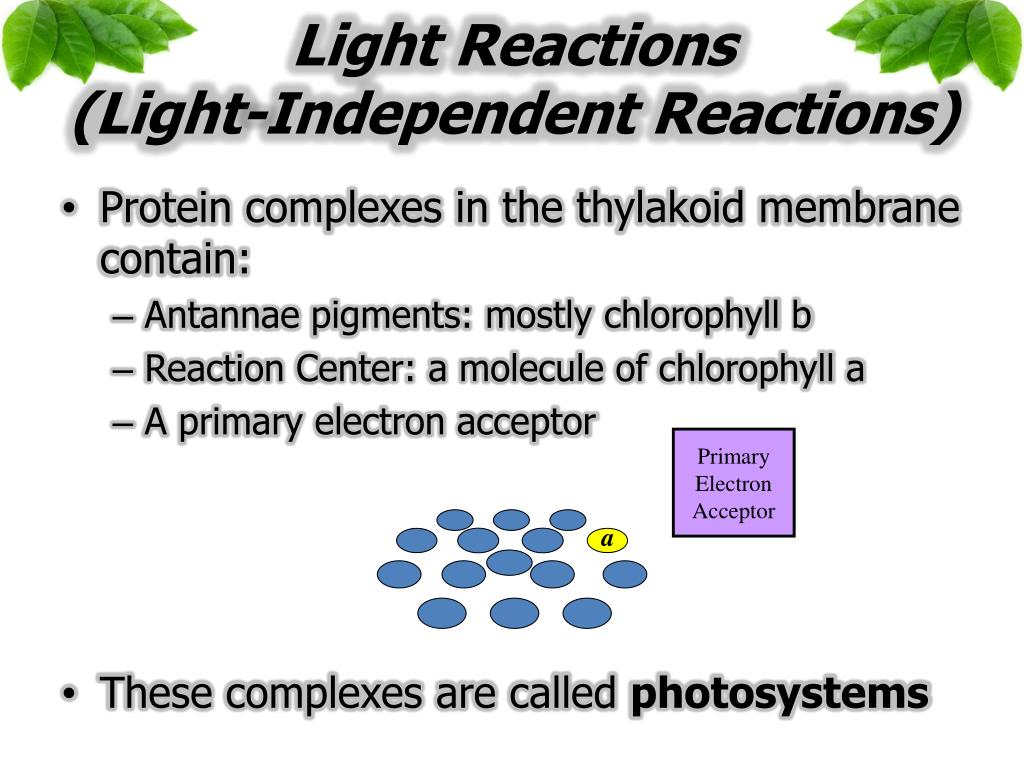
The light phase is the first phase of photosynthesis. It refers to the conversion of solar energy into chemical energy. Light is absorbed by complexes made up of chlorophylls and proteins called photosystems, which are located in the chloroplasts.
What happens to light energy absorbed by chlorophyll molecules?
Light energy is absorbed by a chlorophyll molecule and the photon is passed along a pathway to other chlorophyll molecules. The energy culminates in a molecule of chlorophyll found in the reaction center. The energy “excites” one of its electrons enough to leave the molecule and be transferred to a nearby primary electron acceptor.

What happens to the light absorbed by a plant during photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll is what absorbs the sun's energy and turns it into chemical energy.
What happens after light energy is absorbed by plants?
Photosynthesis is the process in which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of sugars. In a process driven by light energy, glucose molecules (or other sugars) are constructed from water and carbon dioxide, and oxygen is released as a byproduct.
What happens to the electrons after absorbing energy from light photosynthesis?
The electron arrives at photosystem I and joins the P700 special pair of chlorophylls in the reaction center. When light energy is absorbed by pigments and passed inward to the reaction center, the electron in P700 is boosted to a very high energy level and transferred to an acceptor molecule.
Which is the product of photosynthesis after a plant absorbs light?
Key Takeaways. In photosynthesis, energy from light is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. For 6 carbon dioxide and 6 water molecules, 1 glucose molecule and 6 oxygen molecules are produced.
What happens to light energy when absorbed?
When light hits an object, it either bounces off, and stays as light energy, or it is absorbed by the object. When it is absorbed, it is converted into heat energy, and the object heats up.
What happens to light after it is absorbed?
If the photon energy is absorbed, the energy from the photon typically manifests itself as heating the matter up. The absorption of light makes an object dark or opaque to the wavelengths or colors of the incoming wave: Wood is opaque to visible light.
What happens when light is absorbed by a body?
The light energy is absorbed by the molecules of a body and is then transformed into kinetic energy. The rise in movement of the molecules produces heat which is radiated to the surroundings.
What do plants do with the energy from the sun?
Plants are autotrophs, which means they produce their own food. They use the process of photosynthesis to transform water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide into oxygen, and simple sugars that the plant uses as fuel. These primary producers form the base of an ecosystem and fuel the next trophic levels.
Where does light energy come from in a chlorophyll molecule?
The energy culminates in a molecule of chlorophyll found in the reaction center. The energy “excites” one of its electrons enough to leave the molecule and be transferred to a nearby primary electron acceptor.
How does light energy travel?
The photon causes an electron in the chlorophyll to become “excited.” The energy given to the electron then travels from one pigment molecule to another until it reaches a pair of chlorophyll a molecules called the reaction center. This energy then excites an electron in the reaction center causing it to break free and be passed to the primary electron acceptor. The reaction center is therefore said to “donate” an electron to the primary electron acceptor (Figure 1).
How does energy travel through the electron transport chain?
The energy is present initially as light. A photon of light hits chlorophyll, causing an electron to be energized. The free electron travels through the electron transport chain, and the energy of the electron is used to pump hydrogen ions into the thylakoid space, transferring the energy into the electrochemical gradient. The energy of the electrochemical gradient is used to power ATP synthase, and the energy is transferred into a bond in the ATP molecule. In addition, energy from another photon can be used to create a high-energy bond in the molecule NADPH.
How do hydrogen ions pass through the thylakoid membrane?
The hydrogen ions are allowed to pass through the thylakoid membrane through an embedded protein complex called ATP synthase. This same protein generated ATP from ADP in the mitochondrion. The energy generated by the hydrogen ion stream allows ATP synthase to attach a third phosphate to ADP, which forms a molecule of ATP in a process called photophosphorylation. The flow of hydrogen ions through ATP synthase is called chemiosmosis, because the ions move from an area of high to low concentration through a semi-permeable structure.
What is the name of the photosystem in eukaryotes?
In eukaryotes, two photosystems exist, the first is called photosystem II, which is named for the order of its discovery rather than for the order of function. After the photon hits, photosystem II transfers the free electron to the first in a series of proteins inside the thylakoid membrane called the electron transport chain.
What is the most common pigment in the first part of photosynthesis?
The most common and abundant pigment is chlorophyll a . A photon strikes photosystem II to initiate photosynthesis.
Which photosystem uses the electron to transport hydrogen ions into the interior of the thylakoid?
Figure 2. From photosystem II , the excited electron travels along a series of proteins. This electron transport system uses the energy from the electron to pump hydrogen ions into the interior of the thylakoid. A pigment molecule in photosystem I accepts the electron.
How does photosystem II split water to produce oxygen?
These electrons are subsequently passed from photosystem II to photosystem I by the electron transport chain. The electrons from water are needed to ÒÞll the holeÓ that is left when the absorption of one photon of light leads to donation of an electron from photosystem II to the electron transport chain.
How is water converted to oxygen in photosynthesis?
In the light reactions of photosynthesis, water is converted to oxygen by oxidation and NADP+ is reduced to NADPH. The series of redox reactions is coupled to the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP in a process called photophosphorylation.
What is the primary electron acceptor in photosynthesis?
The excited chlorophyll passes an electron to a pri-mary acceptor. In photosystem II, the primary electron acceptor is a molecule of pheophytin (Pheo), one of the accessory pigments of the photosynthetic apparatus. The structure of pheophytin differs from that of chlorophyll only in the substitution of two hydrogens for the magnesium. The transfer of electrons is mediated by events that take place at the reaction center. The next electron acceptor is plastoquinone (PQ). The structure of plastoquinone (Figure 22.8) is similar to that of coenzyme Q (ubiquinone), a part of the respiratory electron transport chain, and plastoquinone serves a very similar purpose in the transfer of electrons and hydrogen ions.
What is the reaction center of photosystem II?
Similarly, the reaction-center chlo-rophyll of photosystem II is designated P680 because the longest wavelength of absorbed light that initiates the reaction is 680 nm. Note particularly that the path of electrons starts with the reactions in photosystem II rather than in pho-tosystem I.
What is the energy of an endergonic reaction?
This is an endergonic reaction with a positive ∆G° = +220 kJ mol-1 = +52.6 kcal mol-1. The light energy absorbed by the chlorophylls in both photosystems provides the energy that allows this endergonic reaction to take place. A series of electron carriers embedded in the thylakoid membrane link these reactions. The electron carriers have an organization very similar to the carriers in the electron transport chain.
How many nm is the photosystem I?
Photosystem I can be excited by light of wavelengths shorter than 700 nm, but photosystem II requires light of wavelengths shorter than 680 nm for excitation. Both photosystems must operate for the chloroplast to produce NADPH, ATP, and O2, because the two photosystems are connected by the electron transport chain.
What is the second part of the photosynthesis?
The second part of the reaction is the oxidation of water to produce oxygen, carried out by photosystem II (PSII). Both photosystems carry out redox (electron transfer) reactions. The two photosystems interact with each other indirectly through an electron transport chain that links the two photosystems. The production of ATP is linked ...
What happens during photosynthesis?
What Happens During Photosystem II? Photosystem II is the first step of photosynthesis, where the chlorophyll molecule uses light energy to take an electron from a water molecule. This splits the water molecule, generating oxygen and hydrogen ions.
What are the electrons and hydrogen ions used for in photosynthesis?
The electrons and hydrogen ions are used to power the creation of ATP, and ultimately carbohydrates, in later stages of photosynthesis. During photosystem II, the energy from light excites one of the electrons in chlorophyll, causing it to be lost to other receptor molecules that pass it along away from the chlorophyll.
Is chlorophyll a reaction center?
The chlorophyll is actually just one part of a large complex of molecules known as a reaction center, and each major step is actually accompanied by many minor steps, passing electrons from one functional group to the next.
Does chlorophyll have to wait to be in photosystem II?
Chlorophyll molecules don't have to wait until a photon strikes them directly to initiate photosystem II. They are capable of using the energy from light even if the initial encounter is in another nearby molecule. Indeed, the photosystem uses a molecular array of light-harvesting antennae that capture and transfer the energy from light to ...
What is the energy that is absorbed by chlorophyll?
In light-dependent reactions, the energy from sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll and converted into chemical energy in the form of electron carrier molecules like ATP and NADPH. Light energy is harnessed in Photosystems I and II, both of which are present in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
Where is light energy stored?
Light energy is harvested and stored in chemical bonds of ATP and carbohydrates, made from CO2 and H2O
What is the movement of hydrogen ions across a membrane during cellular respiration?
Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a selectively permeable membrane, down their electrochemical gradient. More specifically, it relates to the generation of ATP by the movement of hydrogen ions across a membrane during cellular respiration or photosynthesis.
Which molecule is involved in photosynthesis?
The synthesis of ATP during photosynthesis, coupled to the cyclic passage of electrons to and from P700, the specialized form of chlorophyll a which is involved in photosystem I, using a series of carrier molecules.
What enzymes are used to capture CO2?
In this type of photosynthesis, an enzyme called RuBP carboxylase grabs CO2 in one of the first steps of photosynthesis. This works fine as long as there is plenty of carbon dioxide and relatively little oxygen. If there is too much oxygen, RuBP carboxylase will grab that instead of the CO2, and a process called photorespiration will occur.
What happens to light energy once it is absorbed?
When pigments absorb a photon, an electron reaches an excited state, which is a highly unstable and transient state. When the electrons return to a ground state, they release this energy, giving off heat and fluorescence. In the chloroplasts, the electron is transferred to another pigment molecule, beginning a chain of electron flow from pigment molecule to pigment molecule.
How do pigments absorb photons?
These pigment molecules absorb the photon and use the energy to energise electrons, which are passed in a chain from pigment molecule to pigment molecule in the light-harvesting complex. This happens until the electron gets to the reaction centre, eventually transferring it to the “ primary electron acceptor ”.
How is light energy harvested?
Light energy is not only harvested by photosystem II, it is also harvested by photosystem I, where it is carried through a similar chain to the reaction centre, and joins the specialised pair of chlorophyll molecules here – P700. The primary electron acceptor in photosystem I then accept an electron from P700. This transfer of electrons to the primary electron acceptor means there is a space for new electrons in P700, and the electron from photosystem II is transferred here. Another electron transport chain occurs, and the electron is passed to NADP+, forming NADPH with another electron from the same process, and NADPH is formed. The ATP and NADPH are used to power reactions in the next stage of photosynthesis.
How are chlorophyll molecules organized?
Chlorophyll molecules are organised in photosystems. These photosystems are in the thylakoid membrane and consist of reaction-centre complexes surrounded by light-harvesting complexe s. The light harvest complex consists of pigments. These pigment molecules absorb the photon and use the energy to energise electrons, which are passed in a chain from pigment molecule to pigment molecule in the light-harvesting complex. This happens until the electron gets to the reaction centre, eventually transferring it to the “ primary electron acceptor ”. This is the first step in the light reactions and is a type of redox reaction.
Why is photosystem II named after photosystem I?
Photosystem II is named as such because it was discovered after photosystem I. When light is absorbed by one of the pigment molecules in photosystem II, the energy is transferred from pigment molecule to pigment molecule before reaching the reaction centre.
Why do leaves turn green?
The reason we see leaves as green is because chlorophyll absorbs red and blue light, and transmits and reflects green light.
What is the electron transport chain in photosynthesis?
Another electron transport chain occurs, and the electron is passed to NADP+, forming NADPH with another electron from the same process, and NADPH is formed. The ATP and NADPH are used to power reactions in the next stage of photosynthesis. An alternative route that electrons can take is cyclic electron flow.