What are the 7 stages of mitosis in order?
What are the 7 stages of mitosis in order?
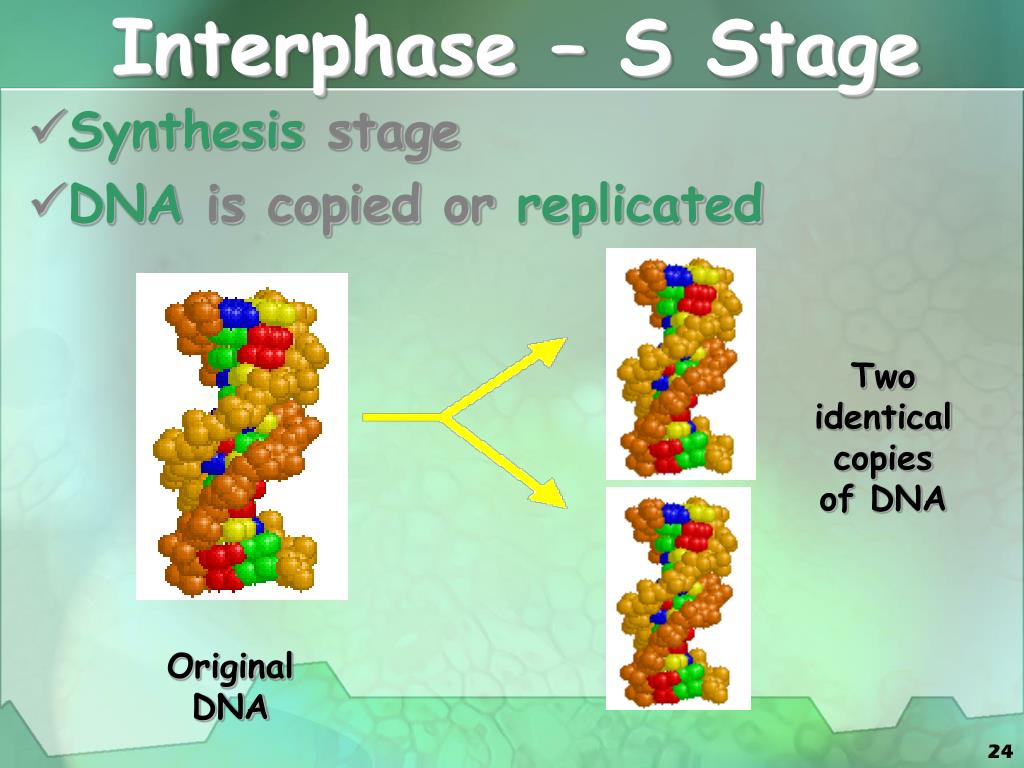
- Interphase. Cell performs normal functions, Cell growth (G1 and g2), Synthesizes new molecules and organelles.
- Prophase.
- Prometaphase.
- Metaphase.
- Anaphase.
- Telophase.
- Cytokinesis.
What happens in Stage 2 of mitosis?
When prophase is complete, the cell enters prometaphase — the second stage of mitosis. During prometaphase, phosphorylation of nuclear lamins by M-CDK causes the nuclear membrane to break down into numerous small vesicles. As a result, the spindle microtubules now have direct access to the genetic material of the cell.
What are the stages of the cell cycle in order?
Twitter. The stages of the cell cycle in order are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. This process is known as mitosis and is used to generate new cells. The cell cycle contains six main stages: Interphase is the resting stage of a cell. The replication of DNA occurs during the S phase of this stage.
What are facts about mitosis?
What is mitosis?
- During mitosis one cell? divides once to form two identical cells.
- The major purpose of mitosis is for growth and to replace worn out cells.
- If not corrected in time, mistakes made during mitosis can result in changes in the DNA? that can potentially lead to genetic disorders?.

Does the original cell exist after mitosis?
Mitosis is the process in which one cell replicates itself into two new identical cells. The original cell is referred to as a parent cell, and the two new cells are called daughter cells.
What happens to cells after cell division?
When cells divide, they make new cells. A single cell divides to make two cells and these two cells then divide to make four cells, and so on. We call this process "cell division" and "cell reproduction," because new cells are formed when old cells divide. The ability of cells to divide is unique for living organisms.
What happens to the daughter cells after mitosis?
At the end of mitosis, the two daughter cells will be exact copies of the original cell. Each daughter cell will have 30 chromosomes. At the end of meiosis II, each cell (i.e., gamete) would have half the original number of chromosomes, that is, 15 chromosomes. 2.
How do the final cells produced in mitosis compared to the original cell?
Mitosis creates two identical daughter cells that each contain the same number of chromosomes as their parent cell. In contrast, meiosis gives rise to four unique daughter cells, each of which has half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
What happens to a cell after M phase of cell cycle?
M phase or mitotic phase is the process of cell division which includes the division of nucleus (karyokinesis) followed by the division of cytoplasm (cytokinesis) to form two daughter cells.
What happens to the structure of the chromosomes after entering mitosis?
During mitosis, chromosomes reorganise into compact cylindrical bodies so that the spindle can distribute one copy of the genome to each daughter cell.
Do daughter cells become parent cells?
The mature cell which is undergoing cell division is the parent cell or the mother cell while the new cells originating at the end of the cell division are daughter cells. Likewise, mitosis produces two daughter cells from a single parent cell while the meiosis produces four daughter cells from a single mother cell.
What is final product of meiosis?
Cytokinesis splits the chromosome sets into new cells, forming the final products of meiosis: four haploid cells in which each chromosome has just one chromatid. In humans, the products of meiosis are sperm or egg cells.
What will happen to the offspring after the replication in cell division?
This process involves replication of the cell's chromosomes, segregation of the copied DNA, and splitting of the parent cell's cytoplasm. The outcome of binary fission is two new cells that are identical to the original cell.
What kind of cells are produced at the end of mitosis?
The result of mitosis is two identical daughter cells, genetically identical to the original cell, all having 2N chromosomes.
What is produced by mitosis?
During mitosis, a cell duplicates all of its contents, including its chromosomes, and splits to form two identical daughter cells.
How many chromosomes are there after mitosis?
When the cell divides, the copies are pulled apart, and each new cell gets one identical copy of each chromosome. This type of cell division is called mitosis, and it produces cells with a total of 46 chromosomes.
How does cell division affect cell organelles?
An important aspect of cell division is the distribution of these organelles into the daughter cells to ensure proper functioning of these progeny cells (Warren 1993). This concept is immediately obvious for organelles that originate from fission of preexisting organelles, such as mito- chondria and plastids.
What will happen to the offspring after the replication in cell division?
This process involves replication of the cell's chromosomes, segregation of the copied DNA, and splitting of the parent cell's cytoplasm. The outcome of binary fission is two new cells that are identical to the original cell.
Why do cells undergo cell division?
Cells must divide repeatedly for an embryo to develop or for you to grow. Cells also divide in order to replace damaged or worn-out cells. Most cell division produces genetically identical cells, meaning they have the same DNA.
What is cell division Short answer?
Cell division is the process by which a cell, called the parent cell, divides into two cells, called daughter cells. When the cell divides, everything inside it divides also. The nucleus and the chromosomes divide, and the mitochondria divide also.