What are the four phases of cellular respiration?
What are the four processes of respiration quizlet?
- Pulmonary ventilation/breathing. – inspiration (air in) & expiration (air out) in response to changes of O2 & CO2 in blood.
- External respiration. – exchange of O2, CO2 between alveoli/blood in the pulmonary capillaries.
- Transport of respiratory gases. …
- Internal respiration.
What would happen to a cell if cellular respiration suddenly ceased?
Without the process of cellular respiration, there is no gaseous exchange and the cells, tissue and other organs die due to the lack of oxygen and by the accumulation of carbon dioxide within the cells and tissues. Can we live without cellular respiration?
What are the major steps in cellular respiration?
Steps Of Cellular Respiration
- (1) Glycolysis. Glycolysis is the first step in the chain of catabolic reactions the comprise the process of cellular respiration.
- (2) Pyruvate Decarboxylation. Once pyruvate is formed from glycolysis, the body still needs to process the pyruvate to access the chemical energy stored in its bonds.
- (3) Citric Acid Cycle. ...
- (4) Oxidative Phosphorylation. ...
What is cellular respiration and where does it occur?
Cellular respiration occurs inside cells; specifically, cellular respiration happens inside the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell. Cellular respiration is a critical function by which cells release energy for various cellular activities like locomotion, biosynthesis, and even the transportation of molecules between membranes.

What happens to the 3 products of respiration?
The products of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide, ATP, and water. During the production of acetyl-CoA from pyruvate, two carbon dioxide are formed. An additional four carbon dioxide are formed during the Krebs cycle. This carbon dioxide is transferred to the blood and then taken to the lungs.
What happens during cellular respiration?
During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. Along the way, some ATP is produced directly in the reactions that transform glucose. Much more ATP, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
What happens to the energy released during cellular respiration?
Answer: Solution: The energy released during respiration is used for carrying out various life processes. Some of the energy liberated during the breakdown of the glucose molecule is in the form of heat, but a large part of it is converted into chemical energy released by these ATP molecules.
What happens to the oxygen that is used in cellular respiration?
The oxygen used during cellular respiration is converted to water during oxidative phosphorylation of the electron transport chain.
What are the 4 steps of cellular respiration?
In eukaryotes, the 4 stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, transition reaction (pyruvate oxidation), the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation through the electron transport chain.
What are the 3 steps of cellular respiration?
There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis; the citric acid (TCA) or the Krebs cycle; and the electron transport chain, where oxidative phosphorylation occurs.
What are the 7 steps of cellular respiration in order?
Terms in this set (6)Glycolysis. Stage 1 of cellular respiration. ... Citric Acid Cycle. Stage 2 of cellular respiration. ... Oxidative Phosphorylation. Stage 3 of cellular respiration. ... Pyruvate grooming. Between Glycolysis and Citric acid cycle. ... Electron Transport Chain. 1st part of stage 3 of cellular respiration. ... Chemiosomosis.
Where does cellular respiration happen?
While most aerobic respiration (with oxygen) takes place in the cell's mitochondria, and anaerobic respiration (without oxygen) takes place within the cell's cytoplasm.
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an organic compound the body can use for ene...
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is used to generate usable ATP energy in order to support many other reactions in the body. ATP is particularly important for...
What are the main steps of cellular respiration?
There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis; the citric acid (TCA) or the Krebs cycle; and the electron transport chain, where o...
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of each cell of the body. Glycolysis occurs inside the cytoplasm, while the TCA...
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
The reactants of cellular respiration vary at each stage, but initially, it requires an input of glucose, ATP, and NAD+. NAD+, a nicotinamide deriv...
What are the products of cellular respiration?
The final end products of cellular respiration are ATP and H2O. Glycolysis produces two pyruvate molecules, four ATPs (a net of two ATP), two NADH,...
What are the rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration?
There are three primary rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration. These enzymes catalyze the rate-limiting steps, which are the slowest rea...
What diseases can affect cellular respiration?
Several diseases can affect cellular respiration. Since cellular respiration is so vital to bodily functions, many of these diseases severely affec...
What are the most important facts to know about cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions...
What is the main product of cellular respiration?
The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This molecule stores the energy released during respiration and allows the cell to transfer this energy to various parts of the cell. ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy.
How does aerobic respiration work?
Instead of directly reducing intermediates of the Krebs cycle, aerobic respiration uses oxygen as the final electron receptor. But first, the electrons and protons bound to electron carriers (such as NADH), are processed through the electron transport chain. This chain of proteins within the mitochondrial membrane uses the energy from these electrons to pump protons to one side of the membrane. This creates an electromotive force, which is utilized by the protein complex ATP synthase phosphorylate a large number of ATD molecules, creating ATP.
How much ATP does aerobic respiration produce?
The process of aerobic respiration produces a huge amount of ATP from each molecule of sugar. In fact, each molecule of sugar digested by a plant or animal cell yields 36 molecules of ATP! By comparison, fermentation usually only produces 2-4 molecules of ATP.
Why is ATP not used for long term energy storage?
Because ATP is not stable over long periods of time, it is not used for long-term energy storage. Instead, sugars and fats are used as a long-term form of storage, and cells must constantly process those molecules to produce new ATP. This is the process of respiration. The process of aerobic respiration produces a huge amount ...
What is the process of converting sugars into energy?
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form.
Why is aerobic respiration so efficient?
Aerobic respiration is so efficient because oxygen is the most powerful electron acceptor found in nature. Oxygen “loves” electrons – and its love of electrons “pulls” them through the electron transport chain of the mitochondria.
Why is aerobic respiration important for eukaryotes?
Aerobic respiration is an extremely efficient process allows eukaryotes to have complicated life functions and active lifestyles. However, it also means that they require a constant supply of oxygen, or they will be unable to obtain energy to stay alive.
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
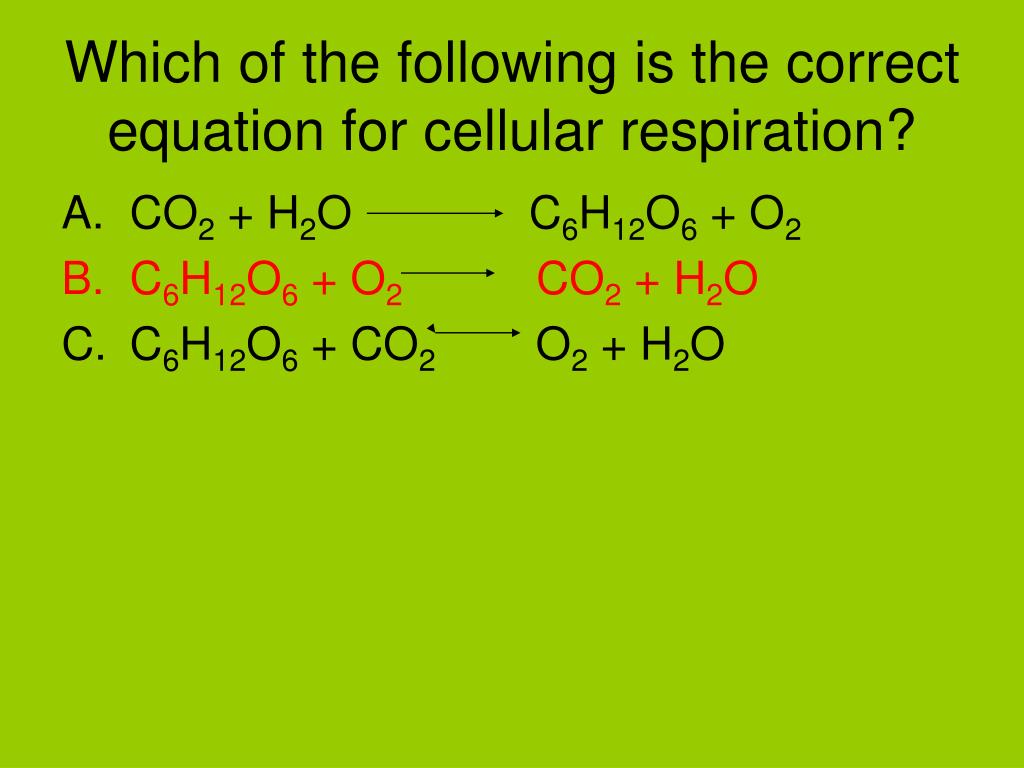
Cellular respiration is the process responsible for converting chemical energy, and the reactants/products involved in cellular respiration are oxygen, glucose (sugar), carbon dioxide, and water. While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration.
How do plants release carbon dioxide?
Carbon dioxide is released by many different microorganisms during not only the process of cellular respiration but also the process of fermentation. Plants use carbon dioxide to create their own energy, much as heterotrophic organisms use glucose and oxygen to create energy. The carbon dioxide will enter the cells of the plant through small holes in the leaves referred to as stomata. After the carbon dioxide has entered the cells of the plant, the chloroplasts within the cell will begin the process of photosynthesis and create carbohydrates as a result.
What is released during the citric acid cycle?
Carbon dioxide is released during the citric acid cycle, and ATP, FADH2, and NADH are produced here. The electrons within FADH2 and NADH are then sent to the next portion of the cellular respiration process, the electron transport chain.
How does glucose convert into pyruvate?
The cells of animals convert glucose into a substance known as pyruvate through a process called glycolysis. The glycolysis process takes glucose and generates two molecules of ATP, or energy, with it. Dioxygen, frequently just called oxygen, it made up of two oxygen atoms and it is what vertebrates used to breathe.
What is the relationship between oxygen and glucose?
In plain English, this can be read as: Glucose + oxygen –> carbon dioxide + water + energy. During the course of cellular respiration, oxygen and glucose are utilized to create carbon dioxide, water, and energy. The oxygen that an organism breathes in is used to break down the sugars found in food.
How does oxygen break down sugar?
The oxygen that an organism breathes in is used to break down the sugars found in food. This produces heat energy, similar to how burning a piece of wood releases heat. With cellular respiration, after oxygen breaks down the sugar and its energy is released, carbon dioxide is released as a byproduct.
What happens if there is no oxygen supply?
If there is not an adequate supply of oxygen, anaerobic respiration will take place instead. Anaerobic respiration can produce ATP without an oxygen supply, but it is much less efficient than aerobic respiration, producing around 1/18th the amount of energy that aerobic respiration does.
What is the process of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Where does cellular respiration happen?
Cellular Respiration happens in your cells and you entire body is made up of cells, it goes on all throughout your body including your lungs and brain. Comment on DonaShae's post “Cellular Respiration happ...”. Button opens signup modal.
How many carbons are in a pyruvate?
Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol.
What is the name of the molecule that is converted to a two carbon molecule?
Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to coenzyme A, called acetyl CoA. Carbon dioxide is released and NADH is made. Citric acid cycle. The acetyl CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule.
What is the cycle of carbon dioxide and NADH?
Carbon dioxide is released and NADH is made. Citric acid cycle. The acetyl CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule. ATP (or, in some cases, GTP), NADH, and FADH_2 are made, and carbon dioxide is released.
How do protons flow back into the matrix?
The protons flow back into the matrix through an enzyme called ATP synthase, making ATP. At the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water.
How is ATP produced?
Oxidative phosphorylation is powered by the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain , a series of proteins embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
What are the end products of cellular respiration?
Assuming that you refer to cellular respiration (i.e., not to breathing ( a.k.a. ventilation), the three “end products” are water, carbon dioxide, and energy (in the form of ATP molecules).
What is the process of respiration?
In biology, respiration (or cellular respiration) is a process in living organisms involving the production of energy, typically with the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide from the oxidation of complex organic substances
How many molecules of CO2 are produced by aerobic respiration?
Aerobic Respiration of 1 molecule of Glucose gives the by-products - 6 molecules of CO2 (Carbon Dioxide gas) and 6 molecules of H2O (Water).
Why is aerobic respiration the only type of respiration?
Because of the vast diversity of organisms on earth, talking about aerobic respiration as the only type of respiration is very limiting.
How does respiration affect the environment?
Respiration results in several effects, some desirable ones, some byproducts, and some that may be detrimental. Obviously, the major effect is the harnessed usable energy, stored in the bonds of ATP. CO2 is a byproduct that may be problematic, if it accumulates in excessive amount, but normally serves a useful role in buffering body fluids - and, of course, providing plants with the vital component for photosynthesis. Respiration also produces water as a result of transferring hydrogen with its electron to oxygen, and this is actually very important source of water for some desert animals, that do not encounter much, if any, of liquid water, or occasionally suffer a water shortage, like camels.
How does glucose make ATP?
Basically sugars such as glucose go through substrate level phosphorylation, and oxidative phosphorylation to create ATP, a high energy molecule that carries chemical energy throughout the body. Before I go into detail I just want to clarify that this is a cyclic process, and it all the steps rely one each other, but are happening constantly, in fact every time you take a breath each cell creates about 10 million ATP!!
What is the process by which an organism converts the complex organic substances in its body into energy?
First, I will start with the basics of respiration . In simple words, respiration is the process by which any living organism converts (or uses up) the complex organic substances in its body (mainly Glucose) into Energy (in the form of ATP) and its By-Products.
What happens during cellular respiration?
By Staff Writer Last Updated April 9, 2020. Follow Us: During cellular respiration, glucose breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. This process releases a store of energy, or ATP, that cells can use for their needs. Cellular respiration is a process by which glucose, or sugar, oxidizes intocarbon dioxide and water, ...
Where does cellular respiration occur?
The process occurs partially in the cytoplasm, which is the material within the living cell, and partially in the mitochondria, an organelle found in most cells.
What is the waste product of the acetyl CoA cycle?
All that remains of the glucose is carbon dioxide, which is a waste product, and water.
