
Two major forces move liquid water through the soil pores: gravity and adhesion. It causes a downward force on water. When a soil is near saturation, the large pores are filled and water moves rapidly through them.
What happens when water is added to a field?
When rain or irrigation water is supplied to a field, it seeps into the soil. This process is called infiltration. Infiltration can be visualized by pouring water into a glass filled with dry powdered soil, slightly tamped. The water seeps into the soil; the colour of the soil becomes darker as it is wetted (see Fig. 31).
What is the relationship between soil and groundwater?
They are constant for a given soil, but vary widely from one type of soil to another. Part of the water applied to the soil surface drains below the rootzone and feeds deeper soil layers which are permanently saturated; the top of the saturated layer is called groundwater table or sometimes just water table (see Fig. 40).
Can water move down in soil?
Soil with an impermeable layer not far below the rootzone should be irrigated with precaution, because in the case of over irrigation (too much irrigation), the perched water table may rise rapidly. So far, it has been explained that water can move downward, as well as horizontally (or laterally).
How does soil drain when building a house?
People building houses need to know how well the surrounding soil is able to drain water. In many areas, septic systems collect and drain household waste water away from the home and its water supply. For the systems to work properly, the soils must drain at a certain rate or the septic system backs up.
How to teach students about watering plants?
Complete this investigation by asking your students to reflect on the investigation question and how their answers may have changed as a result of what they have learned. Ask them why they think it’s important for water to move through soil. Remind the students that how well a soil holds onto water and how well it drains water helps plants to grow. Elementary students know the importance of watering plants with just the right amount of water—not too much and not too little.
What are the three types of particles in soil?
Soil is likely to have several kinds of rock and mineral particles. A few kinds are very common. The three most common kinds are quartz particles, feldspar particles , and small pieces of rock. A soil sample is very likely to have a lot of at least one of these three kinds of particles. Quartz parti cles have irregular shapes. They look gray and glassy. Their surfaces are often stained brown or orange, because they are coated with rust. Feldspar particles are usually white or cream-colored. Their surfaces are often flat, at least partly, rather than irregular. There are many kinds of rock particles. You can tell them apart from the mineral particles because rocks are made of many different particles of minerals, all stuck tightly together.
How to teach a plant to grow in a pot?
If you have a potted plant growing in the classroom, show it to the class. Pick up the pot, and have the students notice that there is a hole in the bottom of the pot. Ask why the hole is there, and why they think you put a saucer under the plant. (Students will probably know that the hole allows water to drain.) Ask the students what would happen if you watered the plant and there was no drainage hole in the pot. (They will say that the soil gets “soggy”, “too wet”, “full of water”. They may even say that this would not be good for the plant.)
What is the best soil sample?
The finest part of a soil sample is probably mostly very small flakes of clay. They are too small for you to see even with a hand lens. Sandy soils are loose and easy to dig. Soils with a lot of clay are harder to dig. Some plants like sandy soils and others like soils with more clay. Most soils have lots of organic matter. Some of the organic matter is in the form of living things, such as earthworms, insects, and microorganisms. Most soils are also rich in decaying plants. If the plant has decayed only slightly, you can usually recognize scraps of leaves, roots, and seeds. When the plant has decayed more, it turns into a soft, fine, dark material called humus. Humus is very important in soils. New plants can easily put their roots into humus. It is also good at holding water for later use by growing plants.
What happens when you crush dry soil?
When dry soil is crushed in the hand, it can be seen that it is composed of all kinds of particles of different sizes.
What determines the texture of soil?
The amount of sand, silt and clay present in the soil determines the soil texture.
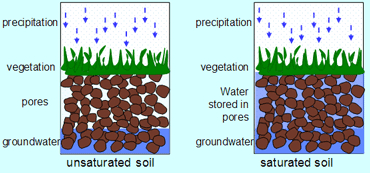
How to tell if soil is saturated?
During a rain shower or irrigation application, the soil pores will fill with water. If all soil pores are filled with water the soil is said to be saturated. There is no air left in the soil (see Fig. 37a). It is easy to determine in the field if a soil is saturated. If a handful of saturated soil is squeezed, some (muddy) water will run between the fingers.
Why does the depth of the groundwater table vary from place to place?
The depth of the groundwater table varies greatly from place to place, mainly due to changes in topography of the area (see Fig. 41).
How to visualize infiltration?
Infiltration can be visualized by pouring water into a glass filled with dry powdered soil, slightly tamped. The water seeps into the soil; the colour of the soil becomes darker as it is wetted (see Fig. 31).
What is the name of the succession of horizons in soil?
These layers are called horizons. This succession of horizons is called the profile of the soil (Fig. 27).
Where is the perched water layer?
A perched groundwater layer can be found on top of an impermeable layer rather close to the surface (20 to 100 cm). It covers usually a limited area. The top of the perched water layer is called the perched groundwater table.
What happens when water is added to soil?
Soil is an extremely general term. With different soils, there are different results when it has water added to it. Some soils are very permeable, like sandy soil, which will allow water to quickly percolate through it, while loamy soils will become saturated, and when the moisture content reaches 100% the water will begin to pond on it. Depending on how long water stands on saturated soil, other things may happen to a varying degree. Some soil constituents may actually dissolve and may then leach out, some may migrate with heavier materials segregating downward and lighter materials floating to the top. Expansive soils will increase in volume as they absorb water, and shrink after the water dries up.
How does water go into soil?
Water goes into the soil in many different ways, on different scales, from the tipping of a teaspoon into a tiny succulent in a dish, to a watering can, a rainfall, flooding of a river, melting of ice underground in the tundra.
What type of soil has large pores?
Soil particles with crumby or granular structure have large number of pores to accumulate water in them. Coming to texture, soils with clay content will accumulate much water in them.
How does soil hold water?
As you water the soil, the moisture content or the degree of water saturation will increase until the soil reaches its water holding capacity. Once the water holding capacity of a soil is reached, any extra water added will move downward, lost to gravity and when that happens the lost water will leach the soil from its nutrients. Therefore, excess watering is detrimental to the fertility of the soil!
What is the difference between clay soil and sandy soil?
The excess water will move downward into the subsoil and will be lost to crops. A clay soil will hold a lot more water, but again less than 10% is available for plant use because the clay will hold on tight to the water. A better soil (silty loam soil) will hold about 21% of the water that you apply but , contrary to sandy soils, this water is available for plant growth. Therefore, it is important to know the water holding capacity of your soil so that you don’t over water it.
How long to dry soil in oven?
1. Put the soil to dry in the oven at 200F for about 30 minutes.
What is the moisture content of clay soil?
Fat clay soils frequently have moisture contents between 50 and 100 , and some types of bentonite can have moisture contents as high as 600 percent. Highly organic soils also frequently have moisture contents higher than 100 percent also.
