Full Answer
Will ultrasound show gallstones in the duct?
Mar 27, 2020 · What happens when a gallstone obstructs the cystic duct? Gallstones can enter and obstruct the cystic duct, preventing the flow of bile. The increased pressure in the gallbladder leads to swelling and pain. This pain, known as biliary colic, is sometimes referred to as a gallbladder "attack" because of its sudden onset. Click to see full answer.
What are the problems after gallbladder removal?
When the cystic duct is blocked by a gallstone, the gallbladder becomes inflamed, a condition called cholecystitis. A sudden attack of cholecystitis causes severe abdominal pain, …
What will happen if your gallbladder is removed?
May 05, 2020 · What happens when a gallstone obstructs the cystic duct? Gallstones can enter and obstruct the cystic duct, preventing the flow of bile. The increased pressure in the gallbladder leads to swelling and pain. This pain, known as biliary colic, is sometimes referred to as a gallbladder "attack" because of its sudden onset.
What are the symptoms and signs of bile duct cancer?
An inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) can occur if the flow of bile in the cystic duct is severely impeded or blocked by any gallstones. A less common but more serious problem occurs if the gallstones become lodged in the bile ducts between the liver and the small intestine.
What can happen when a gall stone is dislodged within the cystic duct?
Acute cholecystitis occurs when persistent stone dislodged the cystic duct causes the gallbladder to become distended and inflamed. The patient may also present with fever, pain in the right upper quadrant and tenderness over the gallbladder (this is known as Murphy's sign).
What happens if the cystic duct is blocked?
Bile passes out of the liver through the bile ducts and is stored in the gallbladder. After a meal, it is released into the small intestine. When the bile ducts become blocked, bile builds up in the liver, and jaundice (yellow color of the skin) develops due to the increasing level of bilirubin in the blood.
What happens when gallstones block the bile duct?
If a bile duct becomes permanently blocked, it can lead to a build-up of bile inside the gallbladder. This can cause the gallbladder to become infected and inflamed. The medical term for inflammation of the gallbladder is acute cholecystitis.
What happens to the cystic duct after cholecystectomy?
It is more common after laparoscopic cholecystectomy than open because in open surgery the cystic duct is ligated and cut as close to the common bile duct as possible, whereas in laparoscopic cholecystectomy, it is cut closer to the gallbladder to avoid iatrogenic injury to the common bile duct, leaving a longer ...Feb 1, 2013
How long can you survive with a blocked bile duct?
Death from obstructive jaundice in the first few weeks of its course is quite rare and is only occasionally observed. After a period varying from four to six months, however, patients suffering from occlusion of the common bile duct usually deteriorate rapidly and die.
Is a blocked bile duct an emergency?
If the blockage is not corrected, it can lead to life-threatening infection and a dangerous buildup of bilirubin. If the blockage lasts a long time, chronic liver disease can result. Most obstructions can be treated with endoscopy or surgery. Obstructions caused by cancer often have a worse outcome.Apr 30, 2020
Is an enlarged bile duct serious?
When the bile ducts become swollen or inflamed, this blocks the flow of bile. These changes can lead to scarring of the liver called cirrhosis. This is called biliary cirrhosis. Advanced cirrhosis can lead to liver failure.Apr 30, 2020
What does a blocked bile duct feel like?
People with bile duct obstruction also often experience: itching. abdominal pain, usually in the upper right side. fever or night sweats.Jun 11, 2018
How do you treat a blocked bile duct?
If your bile duct is blocked due to choledochal cysts, your doctor will perform surgery to treat your enlarged bile ducts. Biliary obstruction due to pancreatitis can be treated with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Your doctor may also prescribe medications to relieve pain.Jun 22, 2021
Is cystic duct removed in cholecystectomy?
A small incision is made just below the rib cage on the right side of the abdomen. The liver is moved to expose the gallbladder. The vessels and tubes (cystic duct and artery) to and from the gallbladder are cut and the gallbladder is removed.Sep 19, 2021
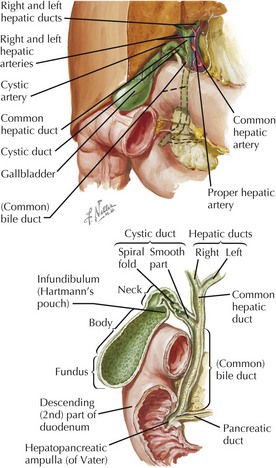
Is a patent cystic duct normal?
In most cases, the normal cystic duct is not seen at US. However, with optimal technique, the normal cystic duct can be visualized in up to 50% of cases as an anechoic tubular structure connecting the gallbladder and bile duct (Fig 3).
What is cystic duct stump leak?
DISCUSSION. The majority of cystic duct stump leaks heal spontaneously when bile is shunted past the defect. This is most commonly accomplished with endoscopic stenting and sphincterotomy or percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage.
What causes gallstones in the body?
Aside from a high concentration of cholesterol, there are two other factors that seem to be of importance in causing gallstones. Movement of the gallbladder is referred to as gallbladder motility. This small but muscular organ squeezes to force bile into the bile duct.
What is a bile duct stone?
What are bile duct stones? Gallstones that move out of the gallbladder can pass into your stomach. However, a stone may become lodged in your bile duct due to the size of the stone or the anatomy of the biliary tree. Thus, bile duct stones are gallbladder stones that have become lodged in the bile duct.
What are the risk factors for gallstones?
Risk factors for pigment stones include: cirrhosis of the liver. biliary tract infections. hereditary blood cell disorders (such as sickle cell anemia) Gallstones can be as small as a grain of salt or as large as a golf ball.
What are gallstones made of?
What are gallstones? Gallstones, which are created in the gallbladder, form when substances in the bile create hard, crystal-like particles. Cholesterol stones, as the name implies, are made of cholesterol and appear light in color. Eighty percent of gallstones are formed this way. Pigment stones are small, dark stones made ...
How many people have gallstones?
Gallstones affect approximately one million people every year, with women being twice as likely to become afflicted than men. They will join the estimated 20 million Americans —roughly 10 percent of the population— who already have gallstones. Those who are most likely to develop gallstones are: Women, ages 20 – 60.
How many people have gallbladder surgery?
Each year more than 500,000 Americans have gallbladder surgery. This surgery, called cholecystectomy, is the most common method for treating gallstones despite the development of some nonsurgical techniques. There are two types of cholecystectomy: the standard “open” cholecystectomy; and, a less invasive procedure called laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Can gallbladder cancer spread to liver?
Gallbladder cancer. Cancer, which can develop in the gallbladder wall, appears to be more common in patients with gallstones. Unfortunately, it often does not cause symptoms until the cancer has spread to the liver or adjacent bile duct. If technically possible, surgical removal is the recommended course of action.
What is gallstone disease?
Vote. Saved My Life. Gallstone disease affects the body's biliary system, which creates, transports, stores and releases bile. Bile is a thick fluid, stored in the gallbladder, which digests fat in the small intestine.
How much does gallstone disease cost?
Most people have gallstones without even knowing it and without symptoms. Gallstone disease has an estimated $5 billion yearly medical cost, a million new cases diagnosed each year and about 800,000 performed operations.
Can gallstones be removed?
A second gallstone attack shows a greater chance for future attacks, which may lead to the removal of the gallbladder. Without a gallbladder, bile will move from the liver to the intestine.
What are the two types of gallstones?
There are two types of gallstones: cholesterol and pigment stones. Cholesterol stones are associated with bile that contains an overabundance of cholesterol, or is "supersaturated" with cholesterol. Pigment stones, made of bilirubin (a product of blood cells), are rarely seen in the United States. They vary in color, either black ...
Can gallstones cause stomach pain?
Many of those with gallstones have no symptoms and don’t need treatment, says Johns Hopkins. Gallstones can cause problems by lodging in bile ducts, stopping the flow of bile or digestive enzymes, and causing symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, vomiting, inflammation and infection.
Can you have bile without a gallbladder?
Without a gallbladder, bile will move from the liver to the intestine. There may be slight changes in how you digest food, but the changes are not noticeable, says WebMD.com. See a doctor if you have pain that starts mid-stomach and migrates to your upper back and you have trouble taking deep breathes. Gallstones may be trapped in your bile ducts.
Does gallstone pain go away?
Moving around does not make the pain go away. About 1 to 5 hours of continuous pain is common, according to WebMD.com. When gallstones continue blocking a bile duct, you may have pain with fever and chills. Also your skin or the whites of your eyes may turn yellow, which could be a sign of an infected gallbladder.
What causes gallstones in the liver?
inflammation of the bile ducts. trauma. a biliary stricture, which is an abnormal narrowing of the duct. cysts. enlarged lymph nodes. pancreatitis . an injury related to gallbladder or liver surgery. tumors that have reached the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, or bile ducts.
What is the treatment for gallstones?
Some of the treatment options include a cholecystectomy and an ERCP. A cholecystectomy is the removal of the gallbladder if there are gallstones. An ERCP may be sufficient to remove small stones from the common bile duct or to place a stent inside the duct to restore bile flow.
What is a biliary obstruction?
A biliary obstruction is a blockage of the bile ducts. The bile ducts carry bile from the liver and gallbladder through the pancreas to the duodenum, which is a part of the small intestine. Bile is a dark-green or yellowish-brown fluid secreted by the liver to digest fats. After you eat, the gallbladder releases bile to help in digestion ...
What happens to the gallbladder after eating?
After you eat, the gallbladder releases bile to help in digestion and fat absorption. Bile also helps clear the liver of waste products. Obstruction of any of these bile ducts is referred to as a biliary obstruction. Many of the conditions related to biliary obstructions can be treated successfully.
What are the two types of bile ducts?
The two types of bile ducts in the liver are intrahepatic and extrahepatic ducts. Intrahepatic ducts: Intrahepatic ducts are a system of smaller tubes within the liver that collect and transport bile to the extrahepatic ducts.
What are the conditions that can be diagnosed with blood tests?
Blood tests can usually rule out certain conditions, such as: cholecystitis, which is an inflammation of the gallbladder. cholangitis, which is an inflammation of the common bile duct. an increased level of conjugated bilirubin, which is a waste product of the liver. an increased level of liver enzymes.
What is a biliary radionuclide scan?
Biliary radionuclide scan (HIDA scan) A hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scan, or HIDA scan, is also referred to as a biliary radionuclide scan. It uses radioactive material to provide valuable information about the gallbladder and any possible obstructions.