
The atmosphere, in turn, filters the Sun 's rays to a certain extent, as does everybody, causing:
- A reflection and a back-scattering of the rays, due to their albedo, to the clouds and atmospheric gases themselves.
- An absorption that causes an increase in temperature due to emitting radiation in any direction according to Wien's law. However, this absorption is modest in the visible light band, making it transparent to direct solar radiation.
How does solar radiation travel through the atmosphere?
The incoming solar radiation from the sun is scattered through the atmosphere and depending how saturated or dry the atmosphere is determines if the solar radiation will be reflected back out to space or absorbed and used modify the air mass it enters.
What is incoming solar radiation?
Incoming Solar Radiation This is energy from the sun. It is also called short-wave radiation because the sun is hotter than the earth and emits shorter wavelengths of radiation. These fall mainly in the ultraviolet and visible portions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
How does the Earth’s atmosphere affect the Sun’s radiation?
The most popular event that takes place from incoming solar radiation and the effect the earth’s atmosphere has on it is the greenhouse effect. Although this is the most noticeable effect, there are many other interactions between the earth and the sun’s radiation. The sun is approximately 20 times warmer than the earth (using Kelvin scale).
How much solar radiation reaches any one spot on the Earth?
The amount of solar radiation that reaches any one spot on the Earth's surface varies according to: Local weather. Because the Earth is round, the sun strikes the surface at different angles, ranging from 0° (just above the horizon) to 90° (directly overhead). When the sun's rays are vertical, the Earth's surface gets all the energy possible.
What is the sum of diffuse and direct solar radiation?
How do scientists measure solar energy?
Why is the Earth closer to the Sun?
How is solar energy measured?
What is solar radiation?
Why is solar energy important?
What is the tilt of the Earth's axis?
See 4 more
About this website
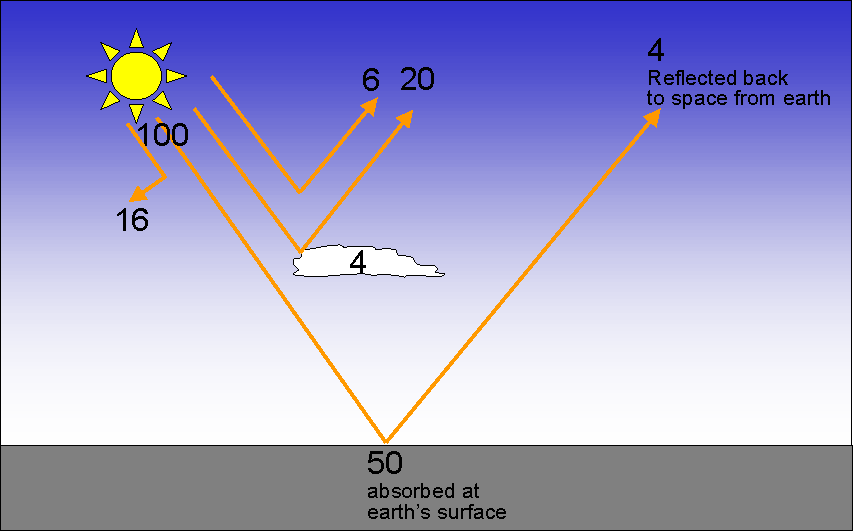
How does scattering affect incoming solar radiation?
Scattering of solar radiation occurs when the radiation strikes very small objects in Earth's atmosphere, such as air molecules, tiny water droplets, ice crystals, or aerosols (tiny airborne particles), which disperse the solar radiation in all directions.
What happens to the incoming solar radiation?
The Earth absorbs most of the energy reaching its surface, a small fraction is reflected. In total approximately 70% of incoming radiation is absorbed by the atmosphere and the Earth's surface while around 30% is reflected back to space and does not heat the surface.
How does incoming solar radiation affect climate?
Some of these ways include: Increasing or decreasing amount of sunlight that is absorbed by the surface of the Earth. This can affect Earth's average temperature. Increasing or decreasing temperatures, which can alter the distribution of snow and ice cover.
What happens to the scattered insolation as it reaches Earth?
APPROXIMATELY HALF OF INSOLATION is transmitted to Earth's surface, and this energy is variably reflected, absorbed, and re-emitted. Earth absorbs energy of short wavelengths, including insolation, but re-emits it at longer wavelengths.
What is incoming solar radiation called?
The energy received by the earth is known as incoming solar radiation which in short is termed as insolation.
What absorbs incoming solar radiation?
About 23 percent of incoming solar energy is absorbed in the atmosphere by water vapor, dust, and ozone, and 48 percent passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by the surface. Thus, about 71 percent of the total incoming solar energy is absorbed by the Earth system.
What are the 4 main effects of solar radiation on Earth?
As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, some of it is absorbed, scattered, and reflected by:Air molecules.Water vapor.Clouds.Dust.Pollutants.Forest fires.Volcanoes.
Why is solar radiation harmful?
Sunburn, immunodepression, photoaging, and photocarcinogenesis, are some of the most significant adverse effects of solar radiation in humans. Children are population group of special vulnerability, due to the fact that exposure to the sun has more pronounced biological effects compared to adults.
What is solar radiation and how does it impact the Earth?
Solar radiation is the energy emitted by the Sun through electromagnetic waves and life on Earth depends on it. In addition to determining atmospheric and climatological dynamics and trends, it makes plant photosynthesis possible, among other processes.
Which type of land surface would probably reflect the most incoming solar radiation?
For example, land located over tropical regions can reflect more sunlight than tropical oceans. Clouds, especially, low, thick clouds, reflect incoming sunlight (shortwave radiation) back to space. High clouds reflect less solar radiation and trap longwave, infrared radiation (heat) re-radiated from Earth's surface.
How does incoming solar radiation change with latitude?
At higher latitudes, the angle of solar radiation is smaller, causing energy to be spread over a larger area of the surface and cooler temperatures.
What happens to the solar energy that is not absorbed by Earth's surface?
About 30% of the solar energy that reaches Earth is reflected back into space. The rest is absorbed into Earth's atmosphere. The radiation warms the Earth's surface, and the surface radiates some of the energy back out in the form of infrared waves.
What happens to most of the incoming solar energy on Earth quizlet?
Most incoming solar energy is absorbed by Earth's land and water surfaces.
What three things can happen to solar radiation once through the Earth's atmosphere?
This is an energy balance diagram which shows you what happens to solar radiation when it enters the atmosphere. You see some high energy radiation (from the sun) is reflected by clouds, absorbed by the oceans and land and then some is re-emitted by the land as infrared radiation, which is much lower energy.
What happens to Earth when incoming energy is greater than the outgoing energy?
Explanation: When the incoming energy is greater than the outgoing energy, the earth's temperature rises. This results in global heating and the entire planet feels the “heat”. 7.
Do solar panels give off radiation?
Electricity from solar panels and transmission to the power grid emits extremely weak electromagnetic fields. Exposure to low-level electromagnetic fields has been studied extensively, and there is no evidence that it is harmful to human health, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
What Is Solar Radiation? Definition and Types
Solar radiation definition: it is the energy emitted by the Sun in interplanetary space.. When we speak about the amount of solar energy reaching the surface of our planet, we use irradiance and irradiation concepts.
What is Solar Radiation? - Definition & Effects - Study.com
Solar radiation is simply the light and energy that is transmitted from the sun, which is very useful on Earth. Learn more about solar radiation,...
National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) Home Page | NREL
National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) Home Page | NREL
What is the sum of diffuse and direct solar radiation?
The sum of the diffuse and direct solar radiation is called global solar radiation. Atmospheric conditions can reduce direct beam radiation by 10% on clear, dry days and by 100% during thick, cloudy days.
How do scientists measure solar energy?
Scientists measure the amount of sunlight falling on specific locations at different times of the year. They then estimate the amount of sunlight falling on regions at the same latitude with similar climates. Measurements of solar energy are typically expressed as total radiation on a horizontal surface,or as total radiation on a surface tracking ...
Why is the Earth closer to the Sun?
When the sun is nearer the Earth, the Earth's surface receives a little more solar energy. The Earth is nearer the sun when it is summer in the southern hemisphere and winter in the northern hemisphere. However, the presence of vast oceans moderates the hotter summers and colder winters one would expect to see in the southern hemisphere as a result of this difference.
How is solar energy measured?
Measurements of solar energy are typically expressed as total radiation on a horizontal surface,or as total radiation on a surface tracking the sun. Radiation data for solar electric (photovoltaic) systems are often represented as kilowatt-hours per square meter (kWh/m 2 ). Direct estimates of solar energy may also be expressed as watts per square ...
What is solar radiation?
Solar Radiation Basics. Solar radiation, often called the solar resource or just sunlight, is a general term for the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. Solar radiation can be captured and turned into useful forms of energy, such as heat and electricity, using a variety of technologies.
Why is solar energy important?
The solar resource across the United States is ample for photovoltaic (PV) systems because they use both direct and scattered sunlight. Other technologies may be more limited. However, the amount of power generated by any solar technology at a particular site depends on how much of the sun's energy reaches it.
What is the tilt of the Earth's axis?
The 23.5° tilt in the Earth's axis of rotation is a more significant factor in determining the amount of sunlight striking the Earth at a particular location. Tilting results in longer days in the northern hemisphere from the spring (vernal) equinox to the fall (autumnal) equinox and longer days in the southern hemisphere during the other 6 months. Days and nights are both exactly 12 hours long on the equinoxes, which occur each year on or around March 23 and September 22.
What gases absorb light?
Not all of the gases in Earth's atmosphere are good at absorbing incoming radiation. Many of them are responsible for scattering incoming radiation, particularly light waves, causing them to bounce off the molecules in multiple directions. The size of the gas molecule can influence the size of the wavelengths those gases can scatter. For example, oxygen and nitrogen are two of the most abundant gases in the atmosphere and are relatively small in size, compared to some of the larger compounds in the atmosphere, like water and carbon dioxide. Oxygen and nitrogen tend to scatter shorter wavelengths of light: blue and violet light. Our eyes don't see violet light as easily as they do blue, so this is why the sky is blue on a sunny day!
Why do sunsets turn red?
But what about the spectacular oranges and reds of sunset? When the sun's relative position lowers on the horizon, the radiation it emits hits the atmosphere at a lower angle, causing the incoming light to have to pass through more of the atmosphere before it reaches your eyes. This causes more light to scatter, particularly on the yellow and orange range of the light wavelengths. Interestingly, the more aerosols, or atmospheric particles are present in the atmosphere, the more reddish the sunsets will appear.
Why do gases provide insulation?
The gases of Earth's atmosphere provide that insulation because some of them are greenhouse gases, gases that absorb and trap infrared radiation, which include water vapor and carbon dioxide. The more greenhouse gases are present in the atmosphere, the more heat is trapped, and the warmer the atmosphere tends to be.
How does solar radiation transfer occur?
Solar radiation transfer occurs when the Earth absorbs, reflects, and scatters radiation in order to maintain a livable climate. Explore incoming radiation and Earth's methods for transferring radiation. Updated: 11/08/2021
Why is solar radiation important?
Not only does solar radiation keep our planet's climate livable for its inhabitants, it also is the driving force behind photosynthesis, the water cycle, and many other processes that make Earth habitable to the living things that call it home.
What percentage of radiation is absorbed?
The other 70% of the radiation is absorbed. The reflected radiation simply bounces off of Earth's atmosphere and is re-emitted into space. All objects have some degree of albedo, except for theoretical blackbody objects, which absorb 100% of the radiation it receives and reflect none, hence appearing to be black.
Why does the Earth glow?
Reflective Earth. Any object that can absorb radiation will also reflect some of that radiation. This is the reason why, from space, Earth appears bright and glowing, reflecting away some of the Sun's light. Earth's albedo, the amount of radiation reflected, is about 30% of the total incoming radiation from the Sun.
What Is the Greenhouse Effect?
The greenhouse effect is a natural and beneficial phenomenon for the Earth system.
What Is Diffuse Solar Radiation?
Diffuse radiation is also called indirect radiation. It depends on the atmospheric conditions.
What causes the sky to be blue?
Increases relative to total in cloudy skies. In particular, the Rayleigh scattering of the blue component of solar radiation is responsible for the blue color of the sky. Some of the diffuse radiation is back into space.
What is the amount of radiation that hits the unit area proportional to?
According to Lambert's law, the amount of radiation that hits the unit area is proportional to the incidence angle cosine.
How much energy does the Sun produce?
The average intensity of solar energy reaching the top of the atmosphere facing the Sun is about 1,366 watts per square meter (solar constant). This amount of solar irradiance is related to the thresholds of the atmosphere and the plane perpendicular to the incoming solar rays.
What is the albedo of the Earth?
The albedo is the reflection coefficient c. Values of c are generally between 0 and 1 or are expressed as a percentage. It is given by the relationship between the radiant energy reflected from a surface concerning the incident energy. The Earth has an average value of 40% (c = 0.4). At the albedo altitude of the Earth, we add the radiations reflected by atmospheric particles into space.
Which layer of the atmosphere absorbs ultraviolet radiation?
Thanks to the ozone layer, the stratosphere absorbs ultraviolet rays included in the 200-300 nm band. The troposphere absorbs infrared radiation thanks to water vapor and CO2. The filtering action of the bands in the ultraviolet wavelengths, mostly lethal, is essential for the development of life.
Why is the sun called short wave radiation?
This is energy from the sun. It is also called short-wave radiation because the sun is hotter than the earth and emits shorter wavelengths of radiation. These fall mainly in the ultraviolet and visible portions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Why is the sky blue?
Rayleigh/molecular scattering – This occurs when the size parameter (x) is much less than 1μm and caused by air molecules scattering out a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. This is why the sky is blue. The blue wavelengths are scattered out of the visible spectrum during the day. Rayleigh scattering is the least amount of atmospheric scattering expected.
How much more radiation does the Sun emit than the Earth?
The sun is approximately 20 times warmer than the earth (using Kelvin scale). How much more solar radiation will the sun emit? Answer: The amount of radiation emitted is proportional to the fourth power of the temperature. If the sun in 20 times warmer than the earth, it will emit 20⁴ times more radiation. (20)⁴ = 1.6 x 10⁵ more radiation emitted by the sun.
How does the atmosphere absorb energy?
For energy leaving the surface of the earth: terrestrial radiation is emitted by the surface of the earth. Some is absorbed by the atmosphere and reemitted in all directions and the atmosphere radiates some.
Why is scattering and absorption important?
Scattering and absorption are beneficial when an aircraft does not want to be detected by radar. A radar emits a beam and looks for the return. If the object scatters or absorbs the beam, little to no signal will get back to the radar receiver and the aircraft can go undetected.
What is the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves?
Radiation is the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves (have electrical and magnetic properties).
What is the most common event that takes place from incoming solar radiation and the effect the Earth’s atmosphere has on?
The most popular event that takes place from incoming solar radiation and the effect the earth’s atmosphere has on it is the greenhouse effect. Although this is the most noticeable effect, there are many other interactions between the earth and the sun’s radiation.
What is the sum of diffuse and direct solar radiation?
The sum of the diffuse and direct solar radiation is called global solar radiation. Atmospheric conditions can reduce direct beam radiation by 10% on clear, dry days and by 100% during thick, cloudy days.
How do scientists measure solar energy?
Scientists measure the amount of sunlight falling on specific locations at different times of the year. They then estimate the amount of sunlight falling on regions at the same latitude with similar climates. Measurements of solar energy are typically expressed as total radiation on a horizontal surface,or as total radiation on a surface tracking ...
Why is the Earth closer to the Sun?
When the sun is nearer the Earth, the Earth's surface receives a little more solar energy. The Earth is nearer the sun when it is summer in the southern hemisphere and winter in the northern hemisphere. However, the presence of vast oceans moderates the hotter summers and colder winters one would expect to see in the southern hemisphere as a result of this difference.
How is solar energy measured?
Measurements of solar energy are typically expressed as total radiation on a horizontal surface,or as total radiation on a surface tracking the sun. Radiation data for solar electric (photovoltaic) systems are often represented as kilowatt-hours per square meter (kWh/m 2 ). Direct estimates of solar energy may also be expressed as watts per square ...
What is solar radiation?
Solar Radiation Basics. Solar radiation, often called the solar resource or just sunlight, is a general term for the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. Solar radiation can be captured and turned into useful forms of energy, such as heat and electricity, using a variety of technologies.
Why is solar energy important?
The solar resource across the United States is ample for photovoltaic (PV) systems because they use both direct and scattered sunlight. Other technologies may be more limited. However, the amount of power generated by any solar technology at a particular site depends on how much of the sun's energy reaches it.
What is the tilt of the Earth's axis?
The 23.5° tilt in the Earth's axis of rotation is a more significant factor in determining the amount of sunlight striking the Earth at a particular location. Tilting results in longer days in the northern hemisphere from the spring (vernal) equinox to the fall (autumnal) equinox and longer days in the southern hemisphere during the other 6 months. Days and nights are both exactly 12 hours long on the equinoxes, which occur each year on or around March 23 and September 22.
