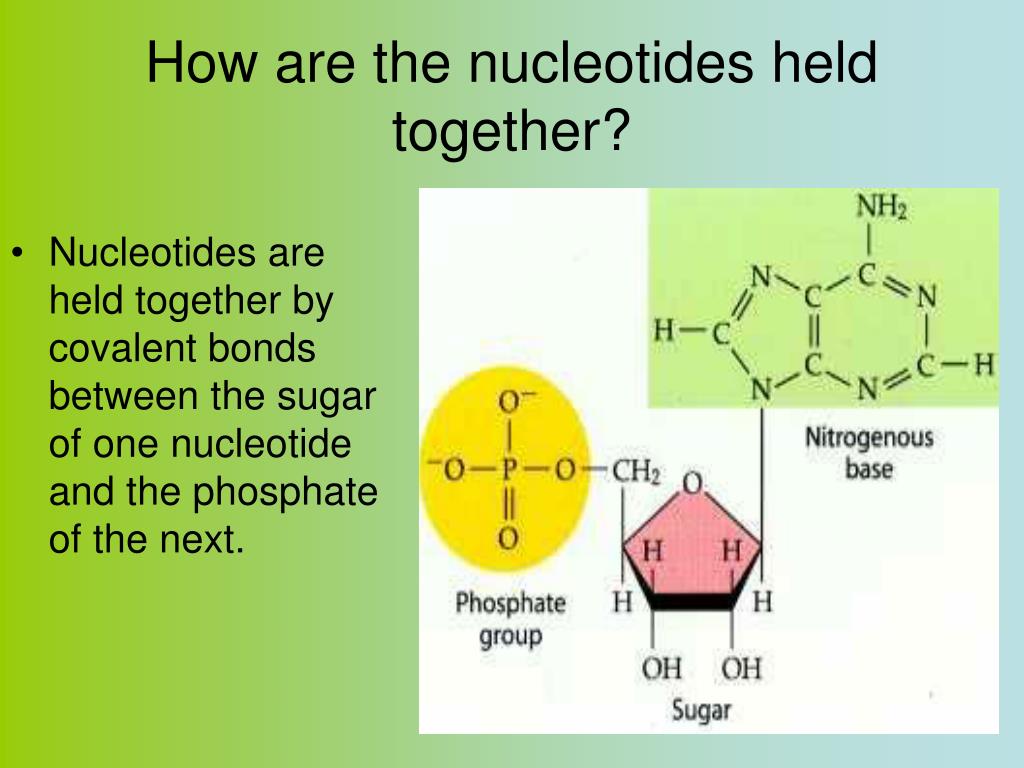
What is it called when sugar units are linked together?
However, sugar units can be bonded or linked together to form polysaccharides , which consist of many sugars linked together to form extensive chains of sugars. What happens when simple sugars combine? The simple sugars form the foundation of more complex carbohydrates.
Is glucose a monosaccharide or a polysaccharide?
Glucose and fructose are examples of monosaccharides, meaning they consist of a single sugar unit, while sucrose is an example of a disaccharide. However, sugar units can be bonded or linked together to form polysaccharides , which consist of many sugars linked together to form extensive chains of sugars.
What is a double sugar called?
A carbohydrate with two units of sugar is called a double sugar or a disaccharide (di = two). Sucrose (table sugar), which is made of one unit of fructose and one unit of glucose, is a disaccharide.
Is sugar a disaccharide or complex carbohydrate?
Sucrose (table sugar), which is made of one unit of fructose and one unit of glucose, is a disaccharide. Complex carbohydrates: Also known as polysaccharides (poly = many), these carbs have more than two units of sugar linked together. Carbs with three to ten units of sugar are sometimes called oligosaccharides (oligo = few).
How many sugar molecules are in a simple sugar?
What is simple sugar?
How much sugar is more likely to cause heart disease?
How many monosaccharides are in sugar?
What are the health effects of sugar?
Can sugar increase inflammation?
Do you have to list sugar in grams?
See 4 more
About this website

What happens when simple sugars combine?
The simple sugars form the foundation of more complex carbohydrates. The cyclic forms of two sugars can be linked together by means of a condensation reaction. The figure below shows how a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule combine to form a sucrose molecule.
What is a single sugar unit called?
Monosaccharides are single sugar molecules that are the building blocks for all other sugars and carbohydrates. Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of these.
What do you call bond between sugar units?
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
What is it called when a few simple sugars are linked together?
disaccharide, also called double sugar, any substance that is composed of two molecules of simple sugars (monosaccharides) linked to each other. Disaccharides are crystalline water-soluble compounds.
What substance is released when two monosaccharides are linked together?
In this process, the hydroxyl group of one monosaccharide combines with the hydrogen of another, releasing a molecule of water and forming a covalent bond known as a glycosidic linkage.
What is complex sugar?
Complex carbohydrates are made up of sugar molecules that are strung together in long, complex chains. Complex carbohydrates are found in foods such as peas, beans, whole grains, and vegetables. Both simple and complex carbohydrates are turned to glucose (blood sugar) in the body and are used as energy.
What type of bond is formed between two sugars in a disaccharide?
glycosidic bondDisaccharides. Disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharide units linked together by a glycosidic bond. The most common glycosidic bonds connecting monosaccharide units are O-glycosidic bonds in which the oxygen from a hydroxyl group becomes linked to the carbonyl carbon.
Will the sucrose molecule stay together?
When sugar dissolves, these whole sucrose molecules separate from one another. The molecule itself doesn't come apart: The atoms that make up each molecule stay together as a sucrose molecule.
What type of bonds are the bonds between simple sugar molecules in a carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates are made up of monosaccharides linked together into polysaccharide chains by a type of covalent bond known as a glycosidic bond. These glycosidic bonds are formed in a dehydration synthesis reaction.
How are sugar units combined together?
A disaccharide is two sugar units linked together. For example, sucrose is a bond between glucose and fructose. Sucrose is also commonly known as table sugar. It's found in a variety of products and naturally occurring in some fruits and vegetables.
How are complex sugar molecules broken apart?
Glucose and other food molecules are broken down by controlled stepwise oxidation to provide chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADH.
How many sugar units make up polysaccharides?
As a rule of thumb, polysaccharides contain more than ten monosaccharide units, whereas oligosaccharides contain three to ten monosaccharide units; but the precise cutoff varies somewhat according to convention. Polysaccharides are an important class of biological polymers.
What is the unit of sugar?
mmol/L or Millimoles Per Litre: – International standard unit for measuring the concentration of glucose in the blood – also known as millimolar (mM). This unit is used in the UK. mg/dL: Milligrams per 100 millilitres: Unit for measuring concentration of glucose in the blood in the USA – milligrams per decilitre.
What is meant by sugar unit?
Sugars are classified based on the number of monomeric units present. The term simple sugars denote the monosaccharides. The term table sugar or granulated sugar actually refers to sucrose, which is a disaccharide made of two monosaccharides: glucose and fructose.
What are the 3 main types of sugar?
Types of SugarWhite Sugars.Brown Sugars.Liquid Sugars.
How are sugars classified?
Chemically, sugar consists of carbon (C), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H) atoms, and is classified as a carbohydrate .
Listing of Foods Which Contain Simple Sugars - Proper Nutrition ...
There are many foods high in simple sugars, but some of the most common are: Table sugar Maple syrup Honey Dates Watermelon Pineapple Apples Sodas Ice cream Milk Sugary cereals Sport drinks Candy Condiments like ketchup Some peanut butters.Names for added sugars include: Anhydrous dextrose Brown sugar Confectioners powdered sugar Corn syrup High-fructose corn syrup (HCFS).Although they have a ...
A Purely Fabulous List of Simple Carbohydrate Foods - Nutrineat
A Purely Fabulous List of Simple Carbohydrate Foods. Carbohydrates are often dreaded by many, but that shouldn't be the case. These are energy-rich nutrients that provide the body with the required energy to function.
The 15 Types of Sugar and How to Use Them — Eat This Not That
When you think of sugar, a couple types probably come to mind immediately: white sugar and brown sugar.But while those are the most likely options to be found in your sugar canister or pantry, there are actually a wide variety of sugars used in cooking and baking.
How many sugar molecules are in a simple sugar?
Simple sugars contain one or two sugar molecules. A carbohydrate with one sugar molecule is called a monosaccharide, whereas one with two sugar molecules bonded together is a disaccharide.
What is simple sugar?
Simple sugars are a type of carbohydrate. Carbohydrates are one of the three basic macronutrients — the other two being protein and fat. Simple sugars are found naturally in fruits and milk, or they can be produced commercially and added to foods to sweeten, prevent spoilage, or improve structure and texture. ...
How much sugar is more likely to cause heart disease?
One study found that people who got 10–25% of their calories from added sugars were 30% more likely to die from heart disease compared to those who got less than 10% of their calories from added sugar ( 18 ).
How many monosaccharides are in sugar?
Simple sugars are carbs with one (monosaccharide) or two (disaccharide) sugar molecules.
What are the health effects of sugar?
Added sugars have been associated with rising levels of obesity, heart disease, and increased cancer risk.
Can sugar increase inflammation?
Excess calories from added sugars can increase inflammation and oxidative stress.
Do you have to list sugar in grams?
By 2020, however, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has mandated that manufacturers must list added sugars in grams and as a percentage of the Daily Value (DV) on food labels ( 29. Trusted Source. ). Many large food companies have already complied, making it easier to assess the added sugar content of products.
What are the two types of sugars that are disaccharides?
Disaccharides are crystalline water-soluble compounds . The monosac charides within them are linked by a glycosidic bond (or glycosidic linkage), the position of which may be designated - or - or a combination of the two (-,-). Glycosidic bonds are cleaved by enzymes known as glycosidases. The three major disaccharides are sucrose , lactose , and maltose . In the bacterium Escherichia coli, energy is derived from the metabolism of disaccharide and oligosaccharide sugars and other small molecules. Sucrose , which is formed following photosynthesis in green plants, consists of one molecule of glucose and one of fructose bonded via an -,-linkage. Lactose (milk sugar), found in the milk of all mammals , consists of glucose and galactose connected by a -linkage . Maltose , a product of the breakdown of starches during digestion, consists of two molecules of glucose connected via an -linkage. Another important disaccharide, trehalose , which is found in single-celled organisms and in many insects , also consists of two molecules of glucose and an -linkage, but the linkage is distinct from the one found in maltose. Continue reading >>
How do glycosidic bonds work?
Because sugars contain many hydroxyl groups, glycosidic bonds can join one monosaccharide to another. Oligosaccharides are built by the linkage of two or more monosaccharides by O-glycosidic bonds (Figure 11.10). In maltose, for example, two d-glucose residues are joined by a glycosidic linkage between the α-anomeric form of C-1 on one sugar and the hydroxyl oxygen atom on C-4 of the adjacent sugar. Such a linkage is called an α-1,4-glycosidic bond. The fact that monosaccharides have multiple hydroxyl groups means that various glycosidic linkages are possible. Indeed, the wide array of these linkages in concert with the wide variety of monosaccharides and their many isomeric forms makes complex carbohydrates information-rich molecules. Go to: 11.2.1. Sucrose, Lactose, and Maltose Are the Common Disaccharides A disaccharide consists of two sugars joined by an O-glycosidic bond. Three abundant disaccharides are sucrose, lactose, and maltose (Figure 11.11). Sucrose (common table sugar) is obtained commercially from cane or beet. The anomeric carbon atoms of a glucose unit and a fructose unit are joined in this disaccharide; the configuration of this glycosidic linkage is α for glucose and β for fructose. Sucrose can be cleaved into its component monosaccharides by the enzyme sucrase. Lactose, the disaccharide of milk, consists of galactose joined to glucose by a β-1,4-glycosidic linkage. Lactose is hydrolyzed to these monosaccharides by lactase in human beings (Section 16.1.12) and by β-galactosidase in bacteria. In maltose, two glucose units are joined by an α-1,4 glycosidic linkage, as stated earlier. Maltose comes from the hydrolysis of starch and is in turn hydrolyzed to glucose by maltase. Sucrase, lactase, and maltase are located on the outer surfaces of epith Continue reading >>
What are carbohydrates made of?
Most carbohydrates are sugars or composed mainly of sugars. By far, the most common carbohydrate found in nature is glucose, which plays a major role in cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Some carbohydrates are for structural purposes, such as cellulose (which composes plants' cell walls) and chitin (a major component of insect exoskeletons). However, the majority of carbohydrates are used for energy purposes, especially in animals. Carbohydrates are made up of a 1:2:1 ratio of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen (CH2O)n These are used only for energy in living organisms. Simple carbohydrates are also known as "Monosaccharides".The chemical formula for all the monosaccharides is CnH2nOn. They are all structural isomers of each other. There are two main types of monosaccharides. The first type are aldoses, containing an aldehyde on the first carbon, and the second type are ketoses, which have a ketone on the second carbon (This carbonyl group is always located on the second carbon). Name Formula Aldoses Ketoses Trioses C3 H6 O3 Glycerose Dihydroxyacetone Tetroses C4 H8 O4 Erythrose Erythrulose Pentoses C5 H10 O5 Ribose Ribulose Hexoses C6 H12 O6 Glucose Fructose Heptose C7 H14 O7 Glucoheptose Sodoheptulose The suffix -oses is kept for the aldoses & the suffix -uloses is kept for the ketoses. Except fructose ketoses are as common as aldoses.The most abundant m Continue reading >>
What are the three elements that make up carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates (also called saccharides) are molecular compounds made from just three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose) and disaccharides (e.g. sucrose) are relatively small molecules. They are often called sugars. Other carbohydrate molecules are very large (polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose). Carbohydrates are: a source of energy for the body e.g. glucose and a store of energy, e.g. starch in plants building blocks for polysaccharides (giant carbohydrates), e.g. cellulose in plants and glycogen in the human body components of other molecules eg DNA, RNA, glycolipids, glycoproteins, ATP Monosaccharides Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and are often called single sugars. They are the building blocks from which all bigger carbohydrates are made. Monosaccharides have the general molecular formula (CH2O)n, where n can be 3, 5 or 6. They can be classified according to the number of carbon atoms in a molecule: n = 3 trioses, e.g. glyceraldehyde n = 5 pentoses, e.g. ribose and deoxyribose ('pent' indicates 5) n = 6 hexoses, e.g. fructose, glucose and galactose ('hex' indicates 6) There is more than one molecule with the molecular formula C5H10O5 and more than one with the molecular formula C6H12O6. Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae are called structural isomers. Glyceraldehyde's molecular formula is C3H6O3. Its structural formula shows it contains an aldehyde group (-CHO) and two hydroxyl groups (-OH). The presence of an aldehyde group means that glyceraldehyde can also be classified as an aldose. It is a reducing sugar and gives a positive test with Benedict's reagent. CH2OHCH (OH)CHO is oxidised by Benedict's reagent to CH2OHCH (OH)COOH; the aldehyde group is oxidised to Continue reading >>
What is the formula for lactose?
It consists of a molecule of D-galactose and a molecule of D-glucose bonded by beta-1-4 glycosidic linkage. It has a formula of C12H22O11. A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water); in other words, with the empirical formula Cm (H2O)n (where m could be different from n). [1] This formula holds true for monosaccharides. Some exceptions exist; for example, deoxyribose, a sugar component of DNA, [2] has the empirical formula C5H10O4. [3] Carbohydrates are technically hydrates of carbon; [4] structurally it is more accurate to view them as polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. [5] The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of 'saccharide', a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecular weight) carbohydrates, are commonly referred to as sugars. [6] The word saccharide comes from the Greek word σάκχαρον (sákkharon), meaning "sugar". [7] While the scientific nomenclature of carbohydrates is complex, the names of the monosaccharides and disaccharides very often end in the suffix -ose. For example, grape sugar is the monosaccharide glucose, cane sugar is the disaccharide sucrose, and milk sugar is the disaccharide lactose. Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. Polysaccharides serve for the storage of energy (e.g. starch and glycogen) and as structural components (e.g. cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). The 5-carbon monosaccharide ribose is an important component of co Continue reading >>
How are polysaccharides made?
They are constructed by animals and plants from simpler, monosaccharide molecules, by joining together large numbers of the simpler molecules using glycosidic bonds (-O-). In some of the largest polysaccarhide structures there can be 10,000 individual units joined together. There is a large diversity of polysaccharide form; they can differ in the type of sugar, the connections between the sugars and the complexity of the overall molecule. Sometimes known as glycans, there are three common and principal types of polysaccharide, cellulose, starch and glycogen, all made by joining together molecules of glucose in different ways. It has been estimated that 50% of the world's organic carbon is found in one molecule; cellulose. This molecule is synthesized, stored, modified and used as a building material by plants. It is certainly the most abundant of all the polysaccharides. In the cellulose molecule the individual glucose monosaccharides are all linked to one another in the form of a long, long, linear chain. The carbon atom number 1 (C1) in one sugar is linked to the fourth carbon atom (C4) of the next sugar in an extended array. All the glucose molecules in cellulose have the beta-configuration at the C1 atom, so all the glycosidic bonds that join the glucose molecules together are also of the beta type. This means that the cellulose molecule is straight, and many such molecules can lay side by side in a parallel series of rows. Tiny forces called hydrogen bonds hold the glucose molecules together, and the chains in close proximity. Although each hydrogen bond is very, very weak, when thousands or millions of them form between two cellulose molecules the result i Continue reading >>
What are simple carbohydrates?
This preview shows page 1 - 6 out of 16 pages. Term:simple carbohydratesDefinition:Monosaccharides and disaccharides. Sugars composed of a single sugarmolecule (a monosaccharide) or twojoined sugar molecules (adisaccharide).Term:monosaccharidesDefinition:Single sugar units. The common onesare glucose, fructose, and galactose.Term:disaccharidesDefinition:Carbohydrates composed of twomonosaccharide units chemicallylinked. They include sucrose (commontable sugar), lactose (milk sugar), andmaltose.Term:glucoseDefinition:A common monosaccharide that is acomponent of disaccharides (sucrose,lactose, and maltose) and variouscomplex carbohydrates; present in theblood. Also known as DEXTROSE. Term:fructoseDefinition:A common monosaccharide naturallypresent in honey and many fruits. Also called LEVULOSE or FRUITSUGAR.Term:galactoseDefinition:A monosaccharide that has a structuresimilar to glucose; usually joined withother monosaccharides.Term:sucroseDefinition:A disaccharide composed of onemolecule of glucose and one moleculeof fructose joined together. Alsoknown as TABLE SUGAR.Term:lactoseDefinition:A disaccharide composed of glucoseand galactose; also called MILKSUGAR because it is the major sugarin milk and dairy products. Term:maltoseDefinition:A disaccharide composed of twoglucose molecules; sometimes calledMALT SUGAR. Seldom occursnaturally in foods but is formedwhenever long molecules of starchbreak down.Term:complex carbohydratesDefinition:Chains of more than twomonosaccharides. May beoligosaccharides or polysaccharides.Term:oligosaccharidesDefinition:Short carbohydrate chains composedof 3 to 10 sugar molecules.Term:polysaccharidesDefinition:Long carbohydrate chains composedof more than 10 sugar molecules. Canbe straight or branched. Term:starchDefinition:The major storag Continue reading >>
What is the term for the process in which molecules are joined together through condensation reactions?
Polymerization in which molecules are joined together through condensation reactions.
What is a large molecule made up of subunits called?
a large molecule made up of subunits called amino acids.
Why are amino acids considered monomers?
amino acids are considered monomers due to their GENERAL 'identical' structure (carbon backbone).
What happens when hydrogen molecules break off and release water?
condensation polymerisation. hydrogen molecules from amino acids break off and release water and the amino acids become known as amino acid residue (since their hydrogen molecule has gone).
Do many different combinations produce the same amino acid?
20. However, many different combinations produce the same amino acid. This reduces significance of mutations.
Which base has a double ring structure?
Bases with a double-ring structure. adenine and guanine.
Do peptides go through the quaternary structure?
no, some are made up of only ONE peptide chain and therefore do not go through the quaternary structure stage .
How many sugar molecules are in a simple sugar?
Simple sugars contain one or two sugar molecules. A carbohydrate with one sugar molecule is called a monosaccharide, whereas one with two sugar molecules bonded together is a disaccharide.
What is simple sugar?
Simple sugars are a type of carbohydrate. Carbohydrates are one of the three basic macronutrients — the other two being protein and fat. Simple sugars are found naturally in fruits and milk, or they can be produced commercially and added to foods to sweeten, prevent spoilage, or improve structure and texture. ...
How much sugar is more likely to cause heart disease?
One study found that people who got 10–25% of their calories from added sugars were 30% more likely to die from heart disease compared to those who got less than 10% of their calories from added sugar ( 18 ).
How many monosaccharides are in sugar?
Simple sugars are carbs with one (monosaccharide) or two (disaccharide) sugar molecules.
What are the health effects of sugar?
Added sugars have been associated with rising levels of obesity, heart disease, and increased cancer risk.
Can sugar increase inflammation?
Excess calories from added sugars can increase inflammation and oxidative stress.
Do you have to list sugar in grams?
By 2020, however, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has mandated that manufacturers must list added sugars in grams and as a percentage of the Daily Value (DV) on food labels ( 29. Trusted Source. ). Many large food companies have already complied, making it easier to assess the added sugar content of products.