What happens if you damage your primary motor cortex?
When an injury damages the primary motor cortex, the person will typically present with poor coordination of movements and poor dexterity. For example, the person usually loses the ability to perform fine motor movements. Fine motor movements involve the muscles of the hands, fingers, and wrists.
What causes motor nerve damage?
What is an Explainable Nerve Damage?
- Conditions of the spine, which compresses a spinal nerve. Tip: Most spinal conditions like bulging discs can heal by its own, others can’t especially if they are due to a ...
- Cancers. ...
- Poor nutrition. ...
- Chemotherapy side-effect. ...
- Illegal substances and alcohol abuse. ...
- Depression. ...
- Diabetes. ...
- As a side effect of your treatments. ...
What are the symptoms of frontal cortex damage?
What are the signs of frontal lobe damage?
- Difficulty temporarily keeping information available for processing.
- Reduction in fluency of speech
- Apathy.
- Lack of attention.
What are the symptoms of frontal lobe injury?
Frontal Lobe Damage Symptoms. Weakness on one side of the body or one side of the face. Falling. Inability to problem solve or organize tasks. Reduced creativity. Impaired judgment. Reduced sense of taste or smell. Depression. Changes in. After an injury to the frontal lobe, your personality and social behavior may change drastically.

How does motor cortex affect body movement?
Primary motor cortex encodes the direction of movement. Many neurons in the primary motor cortex are selective for a particular direction of movement. For example, one cell may fire strongly when the hand is moved to the left, whereas it will be inhibited when the hand is moved to the right (Figure 3.8).
What functions does the motor cortex control?
The primary function of the motor cortex is to generate signals to direct the movement of the body. It is part of the frontal lobe and is anterior to the central sulcus. It consists of the primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, and the supplementary motor area.
What happens to the body when motor neurons are injured?
When the lower motor neurons cannot receive signals from the upper motor neurons, it can cause muscle stiffness (spasticity) and overactive reflexes. This can make voluntary movements slow and difficult. Over time, individuals with MNDs may lose the ability to walk or control other movements.
What does damage to the sensory cortex cause?
Damage to the somatosensory cortex can produce numbness or sometimes paraesthesia, which is a tingling sensation in certain parts of the body. Numbness can result due to damage in the cortex which then affects the receptors on the body for certain areas.
What part of the brain is the motor cortex in?
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements. Classically, the motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately anterior to the central sulcus.
Why is the primary motor cortex important?
The primary motor cortex, located just in front of the central sulcus, is the area that provides the most important signal for the production of skilled movements. Electrical stimulation of this area results in focal movements of muscle groups on the opposite side of the body, depending on the area stimulated.
What happens to the body when motor neurons are injured quizlet?
What happens to the body when motor neurons are injured? It releases more neurotransmitters.
What is the function of the motor nerves?
Motor nerves carry signals to your muscles or glands to help you move and function.
What are motor neurons responsible for?
Motor neurons of the spinal cord are part of the central nervous system (CNS) and connect to muscles, glands and organs throughout the body. These neurons transmit impulses from the spinal cord to skeletal and smooth muscles (such as those in your stomach), and so directly control all of our muscle movements.
What part of the brain controls emotions and personality?
The frontal lobes are the largest of the four lobes and are responsible for many different functions. The frontal lobes are considered our emotional control center and home to our personality.
What part of the brain controls memory and concentration?
The prefrontal cortex plays an important part in memory, intelligence, concentration, temper and personality.
What does the sensory cortex control?
The primary somatosensory cortex is responsible for processing somatic sensations. These sensations arise from receptors positioned throughout the body that are responsible for detecting touch, proprioception (i.e. the position of the body in space), nociception (i.e. pain), and temperature.
What does the sensory cortex control?
The primary somatosensory cortex is responsible for processing somatic sensations. These sensations arise from receptors positioned throughout the body that are responsible for detecting touch, proprioception (i.e. the position of the body in space), nociception (i.e. pain), and temperature.
Which part of the brain controls motor skills?
One of the brain areas most involved in controlling these voluntary movements is the motor cortex. The motor cortex is located in the rear portion of the frontal lobe, just before the central sulcus (furrow) that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe.
What is the visual cortex responsible for?
The primary purpose of the visual cortex is to receive, segment, and integrate visual information. The processed information from the visual cortex is subsequently sent to other regions of the brain to be analyzed and utilized.
What happens if you have a motor cortex?
If you mean the cerebellum, then a number of consequences are possible, including spasmodic paralysis and/or death. If you mean the medulla and pons (involuntary autonomic motor function), then death is imminent.
What happens when the brain is damaged?
When it is damaged, control of the body's muscles and attitude is modified, sometimes in bizarre ways. Loss of balance, ability to write and manipulate everyday things like dressing oneself or feeding oneself are a few of the results. Damage from strokes sometimes can be learned around like regaining the damaged usage of one side of the body. Speech is also affected by stroke and sometimes can be learned around, but not as often as lost gross motor skills.
Which part of the brain controls the body?
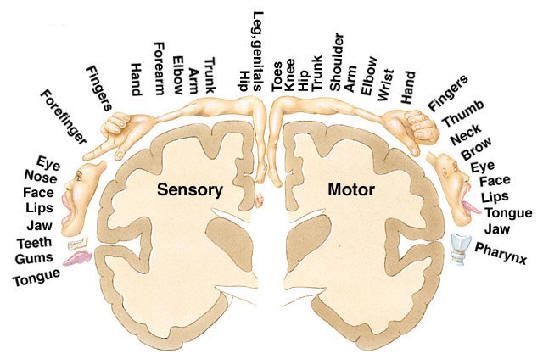
Some regions of the body require more neurons to control them than other ones do. The primary motor cortex isn’t divided up equally in proportion to body size; it’s divided according to the complexity of movement and number of muscles involved. To control your hands, for example, requires more brain tissue (cortex) than to control all your body from your neck to your hips. Even your tongue is controlled by more cortex than the entire torso. Below is a diagram of the primary motor cortex marked off by regional control. The portion to the left of the figure, with facial control centers, is on the lateral aspect of the brain near one’s ear, and the portion on the right, controlling the leg and foot, is down in the groove between the two cerebral hemispheres.
Why is the hand disproportionately large?
Notice that the hand, face (especially the lips), and tongue engage disproportionately large amounts of cortex. This is because of the importance of manual dexterity, fine manual control, and speech to what it means to be human.
Which cortex will have some problems in refining processes?
1.) The motor cortex will have some problems in refining processes
Where do motor neurons terminate?
Nerve fibers from the primary motor cortex descend through the white matter and terminate on lower motor neurons in gray matter of the brainstem and spinal cord. Those motor neurons and neural pools (logic circuits) further process the signal and relay commands to the muscles themselves by way of cranial nerves (for muscles of the head and neck) and spinal nerves (for other muscles of the neck and all muscles below it).
What side of the lesion can you end up paralyzed on?
You can end up paralyzed on the opposite side of the lesion (so damage the left side means paralysis on the right side), fully paralyzed, or difficulty to learn and select the right movement for the action you want.
What Happens If The Motor Cortex Is Damaged?
The motor cortex takes up a large portion of the brain and there are numerous blood vessels that feed the brain. So, damage to these blood vessels can cause various symptoms.
What is the function of motor cortex?
As your body moves, your brain grooves. Motor cortex facilitates optimal functioning on a daily basis. It enables us to walk, run, and use our hands to navigate the world. It allows us to use facial expressions to communicate emotions.
What part of the brain is responsible for all voluntary muscle movements?
The motor cortex is a part of the cerebrum. It sends electrical impulses to your muscles in order to move them. It’s in charge of all voluntary muscle movements, from walking down the street to eating a cupcake.
What are the two areas of the motor cortex?
The motor cortex is made up of 2 basic areas: the primary motor cortex and the association cortex. The primary motor cortex is in charge of the basic motor functions, including walking, running, kicking, throwing, etc.
Which part of the brain is responsible for higher level motor functions?
The association cortex is responsible for higher level motor functions. It consists of the premotor cortex and supplementary motor area.
What is the ability to make a movement with precision?
A motor skill is the ability to make a movement with precision.
Which part of the brain is responsible for thinking?
The brain’s motor cortex is pretty large and takes up the back part of the frontal lobe. There are actually four lobes of the brain in total, but the frontal lobe is what’s responsible for much of our higher thinking and processing.
What are the problems caused by cerebral cortex damage?
Because the cerebral cortex includes almost every lobe within the brain, damage to the cerebral cortex can lead to multiple issues, including problems with: Cognition. Sensation. Movement.
How to recover from cerebral cortex damage?
To regain function after cerebral cortex damage, you will need to take part in rigorous therapy. The therapy you use will depend on which part of the cortex was damaged. Here are a few types of therapy that can help you promote a successful recovery: Speech therapy.
What is the Cerebral Cortex?
The cerebral cortex acts as the outer layer of tissue that covers the cerebrum (the uppermost part of the brain, above the cerebellum).
How many lobes are there in the cerebral cortex?
The brain is divided into the left and right hemispheres, and it is also composed of four lobes: The frontal lobe. The parietal lobe. The temporal lobe. The occipital lobe. Each lobe is responsible for different functions. Thus, damage to the cerebral cortex can ...
How to recover muscle strength after cerebral cortex damage?
To recover muscle strength and coordination after cerebral cortex damage, participate in PT. Exercising your affected limbs will stimulate your brain and rekindle the neural networks that help you move. Cognitive training. This training can help improve memory, attention, problem-solving, and learning skills.
What is the most common sign of occipital lobe damage?
The most common sign of occipital lobe damage is different types of blindness and visual distortions, including: Partial blindness (hemianopsia) Word blindness (alexia) Difficulty perceiving more than one object at once (Balint’s syndrome) Finally, damage to the visual cortex can cause total blindness.
Why is neuroplasticity important?
This process, known as neuroplasticity, is what allows patients to regain abilities after damage to the cerebral cortex.