Which rule states that neurons fire together?
How do neuronal cells communicate?
How many dendrites do neurons have?
What are the components of synaptic transmission?
How many neurotransmitters are there in the human body?
Which neuron receives the neurotransmitter/message?
What triggers an action potential?
See 2 more

What happens when neurons fire together?
This principle is known as the Hebbian learning rule (1): i.e., if interconnected neurons become active very close in time during a particular event, their connection strengthens and “a memory” of this event is formed (1). In other words, “neurons wire together, if they fire together” (2).
How do two neurons fire together?
In 1949, psychologist Donald Hebb laid out his compelling “assembly theory” of how the brain achieves this feat. It is best summarized by the mantra “neurons that fire together wire together.” The idea is that neurons responding to the same stimulus connect preferentially to form “neuronal ensembles.”
What phenomenon does this quote depict neurons that fire together wire together?
Hebb's axiom reminds us that every experience, thought, feeling, and physical sensation triggers thousands of neurons, which form a neural network. When you repeat an experience over and over, the brain learns to trigger the same neurons each time. It can be beneficial to have neurons wired together.
What is an example of Hebbian learning?
One example is Long-Term Potentiation (LTP), a theory that emerged in the late 1960s showing that synapses are strengthened by recent patterns of activity, therefore confirming the findings of Hebbian Learning.
How do you fire neurons?
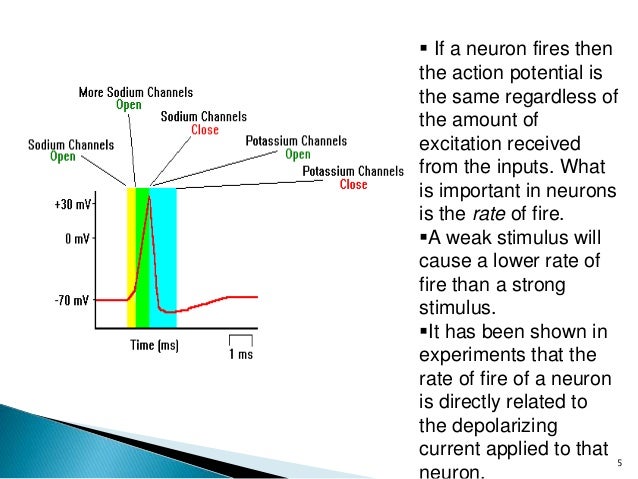
When a nerve impulse (which is how neurons communicate with one another) is sent out from a cell body, the sodium channels in the cell membrane open and the positive sodium cells surge into the cell. Once the cell reaches a certain threshold, an action potential will fire, sending the electrical signal down the axon.
Does everyone have mirror neurons?
They concluded that there was a significant asymmetry between the two processes that indicated that mirror neurons do not exist in humans.
What fires wires together?
“Neurons that fire together, wire together.” - Donald Hebb. This is why the practice of gratitude can be so powerful. Neuropsychologist Donald Hebb first used this phrase in 1949 to describe how pathways in the brain are formed and reinforced through repetition.
What is Hebbian synaptic plasticity?
Hebbian plasticity is a form of synaptic plasticity which is induced by and further amplifies correlations in neuronal activity. It has been observed in many brain areas and can be induced quickly on a timescale of seconds to minutes. Its effect, however, is often long-lasting.
How is Hebb's rule implemented in the brain?
Hebb's Rule describes how when a cell persistently activates another nearby cell, the connection between the two cells becomes stronger. Specifically, when Neuron A axon repeatedly activates neuron B's axon, a growth process occurs that increases how effective neuron A is in activating neuron B.
What is Hebb rule explain with example?
The Hebb learning rule assumes that – If two neighbor neurons activated and deactivated at the same time. Then the weight connecting these neurons should increase. For neurons operating in the opposite phase, the weight between them should decrease. If there is no signal correlation, the weight should not change.
Which type of memory is most impaired by damage to the hippocampus?
If the hippocampus is damaged by disease or injury, it can influence a person's memories as well as their ability to form new memories. Hippocampus damage can particularly affect spatial memory, or the ability to remember directions, locations, and orientations.
Which response is an example of a Hebbian synapse?
Most typical examples of Hebbian mechanisms are long-term potentiation (LTP), and long-term depression (LTD). LTP is an activity-dependent increase in synaptic transmission between two neurons. In contrast, LTD is an activity-dependent decrease in synaptic transmission between two neurons.
What is Hebb rule explain with example?
The Hebb learning rule assumes that – If two neighbor neurons activated and deactivated at the same time. Then the weight connecting these neurons should increase. For neurons operating in the opposite phase, the weight between them should decrease. If there is no signal correlation, the weight should not change.
What causes synaptic pruning?
Early synaptic pruning is mostly influenced by our genes. Later on, it's based on our experiences. In other words, whether or not a synapse is pruned is influenced by the experiences a developing child has with the world around them. Constant stimulation causes synapses to grow and become permanent.
Are neurons like wires?
The nervous system is made up of neurons, the specialized cells that can receive and transmit chemical or electrical signals, and glia, the cells that provide support functions for the neurons. A neuron can be compared to an electrical wire: it transmits a signal from one place to another.
How is Hebb's rule implemented in the brain?
Hebb's Rule describes how when a cell persistently activates another nearby cell, the connection between the two cells becomes stronger. Specifically, when Neuron A axon repeatedly activates neuron B's axon, a growth process occurs that increases how effective neuron A is in activating neuron B.
What happens when neurons fire together?
When neurons fire together, the synaptic strength between the two neurons increases . The most important changes occur in the postsynaptic (receiving) neuron.
Why do neurons like each other?
Also–while the neurons are not technically firing at precisely the exact same time, it’s the temporal proximity of the firing that is important, and causes the neurons to like each other.
How does synaptic transmission occur?
Synaptic transmission is initiated when a neuron is stimulated. Stimulation causes the neuron to want to send information—a message—to neighboring neurons. Neuronal stimulation triggers an “action potential.” An action potential begins at the juncture between the soma and axon and involves rapid depolarization followed by hyperpolarization, which sets in motion a wave of electrical energy down the axon, which triggers the terminal buttons to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
How do neurotransmitters release into the synaptic cleft?
Even though neurotransmitters don’t linger in the synaptic cleft, increasing amounts of neurotransmitter can be released into the synaptic cleft by rapid firing of the presynaptic neuron. The faster the presynaptic neuron fires (via action potential—see below), the more neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft, and consequently, the stronger the message received by the postsynaptic neuron.
What is the effect of the received neurotransmitter on the dendrites of the postsynaptic?
The received neurotransmitter causes excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP’s) in the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron. The EPSP’s travel up the dendrites to the soma, then to the juncture of the soma and axon. If the EPSP is strong enough, then an action potential occurs in the postsynaptic (receiving) neuron—and that neuron fires. Thus, the neurons “fire together.”
How do neuronal cells communicate?
Neurons communicate via “synaptic transmission.” Communication takes place between a “presynaptic neuron” (the neuron sending information from the soma down its axon to the terminal button) and the “postsynaptic neuron” (the neuron that receives the information at its membrane—usually the information is received at one of the postsynaptic neuron’s many dendritic spines).
How many neurotransmitters are there in the human body?
(A compelling reason to eat a healthy and varied diet!) There are over 100 known neurotransmitters, and most neurons create and transmit more than one type. Neurons can also “be receptive” to many different neurotransmitters. Some of the neurotransmitters you may be familiar with are serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
Which rule states that neurons fire together?
Hebb’ s Rule—“ Neurons that Fire Together Wire Together ”. “When an axon of cell A is near enough to excite cell B and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that A’s efficiency, as one of the cells firing B, is increased.”.
How do neuronal cells communicate?
Neurons communicate via “synaptic transmission.” Communication takes place between a “presynaptic neuron” (the neuron sending information from the soma down its axon to the terminal button) and the “postsynaptic neuron” (the neuron that receives the information at its membrane—usually the information is received at one of the postsynaptic neuron’s many dendritic spines).
How many dendrites do neurons have?
Neurons can have many dendrites, and the dendrites perform an important role: they receive information. One Axon: An axon is a tube extending from the soma that transports information from the soma down to the terminal button (see below). A neuron has only one axon protruding from the soma, but the axon may branch and divide.
What are the components of synaptic transmission?
In order to understand synaptic transmission, it’s important to first understand the component parts: neurons, neurotransmitters and synapses. The Structure of Neurons: Cells in the brain are called “neurons.”. Neurons are made up of: One Soma—the cell body.
How many neurotransmitters are there in the human body?
(A compelling reason to eat a healthy and varied diet!) There are over 100 known neurotransmitters, and most neurons create and transmit more than one type. Neurons can also “be receptive” to many different neurotransmitters.
Which neuron receives the neurotransmitter/message?
Neurotransmitters are the chemical messengers. The presynaptic neuron releases neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft and the postsynaptic neuron receives the neurotransmitter/message.
What triggers an action potential?
Stimulation causes the neuron to want to send information—a message—to neighboring neurons. Neuronal stimulation triggers an “action potential.”.