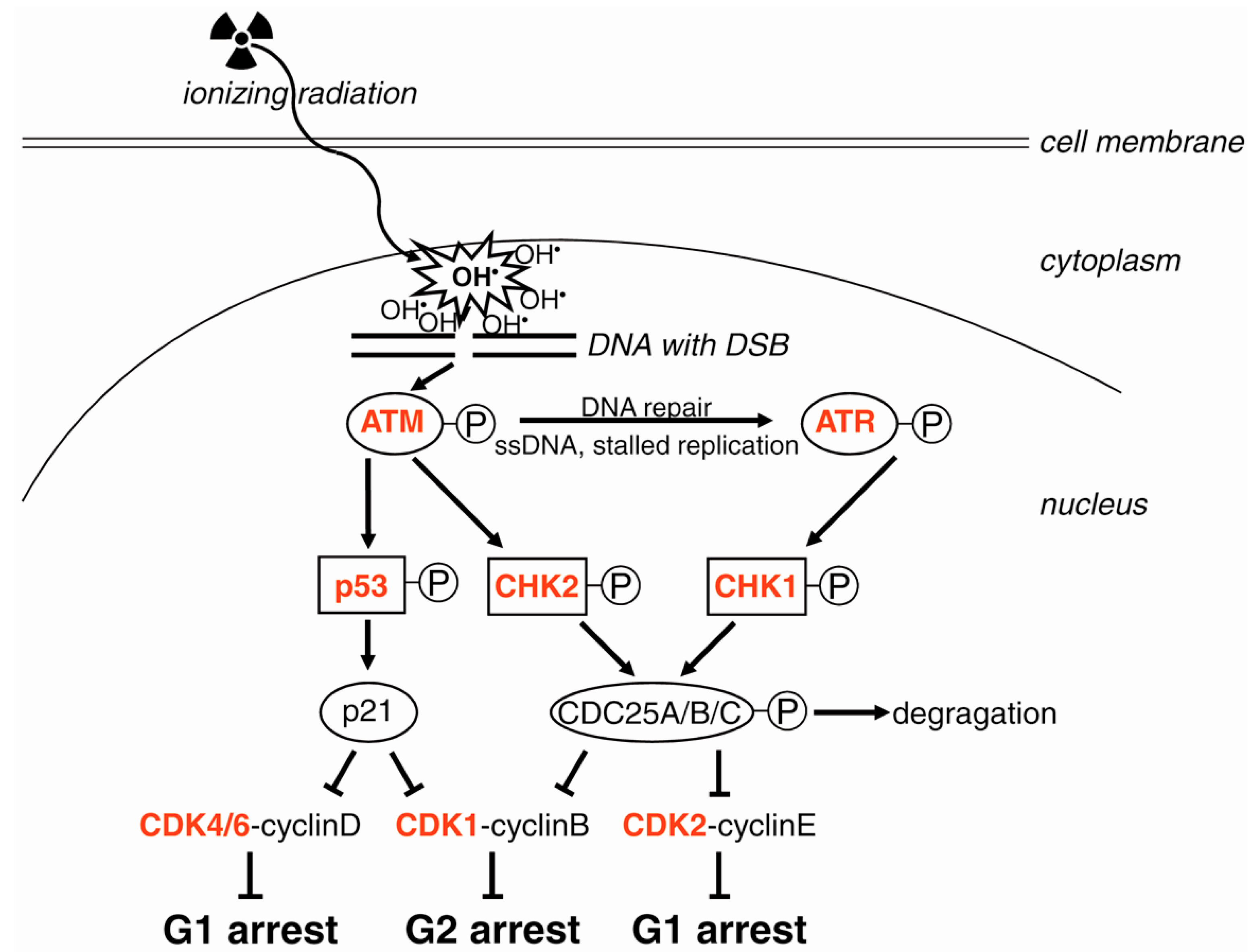
- Abstract. The helical structure of double-stranded DNA is destabilized by increasing temperature. ...
- Experimental Procedures. SSO10610) from S. ...
- Results. ...
- Discussion. ...
- Acknowledgments. ...
- Supporting Information Available. ...
- Notes. ...
- Notes. ...
- References. ...
What happens if you heat up DNA?
5. Heating. In aqueous solution, DNA is subject to oxidation and acid hydrolysis damage. Like most chemical reactions, these speed up as the temperature increases, which is why we store DNA at low temperatures and you should avoid excessively heating your DNA samples.
What is the melting temperature of DNA?
The melting temperature of the DNA is the temperature at which half of the DNA molecules are denatured. That means at this temperature half of the DNA molecules present in the solution will be single-stranded and other half will be double-stranded. melting temperature is found at the midpoint of the melting curve besides denaturation.
Can DNA break covalent bonds at high temperature?
However, the degradation of DNA at high temperature, that is, breaking the covalent bonds within each DNA strand, has not been thoroughly investigated before. Here we measure, for the first time, the thermal degradation of the DNA molecule.
What is the thermal degradation temperature of deoxyribonucleic acid?
In this article, we investigate the thermal degradation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). We find that under dry conditions, complete DNA degradation occurs at above 190°C. In addition, as the boiling temperature of water is pressure dependent, we have investigated the thermal degradation of the DNA in water for different applied partial pressures.
Does DNA break down with heat?
We find that under dry conditions, complete DNA degradation occurs at above 190°C. In addition, as the boiling temperature of water is pressure dependent, we have investigated the thermal degradation of the DNA in water for different applied partial pressures.
At what temperature does DNA melt?
The melting temperature depends on a variety of factors, such as the length of DNA [11], [12] (shorter pieces tend to melt more easily, [13]), the nucleotide sequence composition [14]–[16], salt concentration (ionic strength of the added salt) [14]–[15], [17] and generally lies between 50°C and 100°C.
Why does DNA need to be heated?
All Answers (4) Heating helps to denature proteins, extract DNA from spots, increase speed of chemical reactions, inactivate enzymatical reactions inhibitors etc. Heating is not an alternative method of DNA precipitation. Heating will always eliminate nucleases and increase DNA yield .
Why does DNA denature at high temperature?
DNA melting temperature Specifically, adenine bases pair with thymine bases and guanine bases pair with cytosine bases. Heating a DNA sample disrupts these hydrogen bonds, thus “unwinding” the double helix and denaturing the DNA.
What happens when DNA melts?
DNA melting, also called DNA denaturation, is the process by which double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid unwinds and separates into single-stranded strands through the breaking of hydrogen bonding between the bases.
What does hot water do to DNA?
The warm water (between 55 and 60 degrees Celsius) will deactivate an enzyme in the cell that can break down DNA. After the cell wall is broken down, our next barriers are the cell membrane and nuclear membrane. The warm water will melt the membranes and soap can be added to dissolve the lipid layers.
How do you melt DNA?
Dissociation of the double stranded DNA helix into single coils is referred to as DNA melting. It can be accomplished by simply heating double stranded DNA. The temperature at which the DNA strands dissociates into single coils depends on the number of hydrogen bonds holding the complementary strands.
What happens to DNA at high temperatures?
The helical structure of double-stranded DNA is destabilized by increasing temperature. Above a critical temperature (the melting temperature), the two strands in duplex DNA become fully separated. Below this temperature, the structural effects are localized.
What is melting temperature in PCR?
The recommended melting temperature of PCR primers is usually in the range of 55°C to 70°C and within 5°C of each other. Because of the differences in sequence, length, and composition of the primers, it is often difficult to have similar melting temperatures (Tms) between the two.
Guest Emperor
Hey guys, I was wondering if DNA can survive through intense heat, more specifically a fire, thanks!
chatlack
Some different forms of DNA can live , I think... But it would be very different living , cause it cant change in time for this condition. It must have become living in this condition...
What is the melting temperature of DNA?
The melting temperature of the DNA is the temperature at which half of the DNA molecules are denatured. That means at this temperature half of the DNA molecules present in the solution will be single-stranded and other half will be double-stranded. melting temperature is found at the midpoint of the melting curve besides denaturation.
What are the factors that affect the melting temperature of DNA?
The melting temperature of DNA is affected by three main factors these are. - Nucleotide content of the DNA molecule. - Length of the DNA molecule and. - Ionic strength of the DNA solution.
Why does DNA require more energy to dissociate?
This is because longer the molecule greater the stabilizing forces between the two DNA strands more heat energy is required to dissociate the strands and hence higher will be the melting temperature.
How does DNA become stable?
In the laboratory the DNA molecules present in a solution are stabilized by adding positively charged ions, such as sodium (Na+). Being positively charged these ions bind to the sugar phosphate backbone and neutralize the negative charges on the phosphate groups. Thus DNA in a solution becomes stable ionic strength.
Why is DNA less stable in the first solution?
But in the first solution since ionic strength is low DNA molecules will be less stable as compared to the first this is because negative charges, which are not mute relized by sodium ions will repel each other. This will contribute in the disruption of forces between the two strands.
Why does DNA melt?
This is because more heat energy is required to disrupt the stable base stacking interaction in this molecule. Thus the melting temperature of DNA is influenced by it's GC content. This can also be shown graphically (figure).
What is the backbone of DNA?
The backbone of a DNA helix is made up of sugar and Phosphate. Each phosphate group in a DNA strand carries a negative charge. Thus overall each strand of DNA molecule carries a negative charge. The negative charges on both DNA strands will repel each other.
Why is DNA stored at low temperatures?
In aqueous solution, DNA is subject to oxidation and acid hydrolysis damage. Like most chemical reactions, these speed up as the temperature increases, which is why we store DNA at low temperatures and you should avoid excessively heating your DNA samples. Now you know.
What are the causes of DNA nicks?
2. Mechanical shearing. Excessive rough handling (e.g. pipetting or vortexing) of DNA can cause breaks and nicks. The longer the DNA, the more sensitive it is to shearing so treat things like gDNA especially carefully if you require intact DNA. 3. Phenol extraction. Phenol can oxidise bases, especially guanine.
Can DNA be damaged?
DNA can be damaged in a number of ways. Although the level or type of damage may not affect your experiments, sometimes enough damage can be sustained to ruin them. Forearmed is fore-warned so here are 5 ways that your DNA can be damaged.
Does phenol oxidize bases?
Phenol can oxidise bases, especially guanine. The oxo-guanine which can mis-pair with adenine, resulting in faulty replication and mutagenesis. Good job there’s hardly any need to do any phenol extraction any more!. 4. Dessication. Breaks and nicks, as well as base oxidation, can also be caused by harsh drying of DNA.
What happens when DNA is heated?
Answer: When the DNA solution is heated above 90 o C, the increase in kinetic energy is enough to disturb the non covalent hydrogen bonds present between the two strands of DNA. These non-covalent interactions are responsible for stabilizing DNA. Disturbance of these forces leads to the denaturation of DNA. Generally the melting temperature of DNA of every organism is above 90 o C.
Why does DNA denaturate?
Answer: Denaturation of DNA happens because of the breakage of non covalent interactions thus it is only denatured not destroyed. Polynucleotide strands are made up of sugar phosphate backbone is made up of covalent linkages (bonds) which do not break during the denaturation process.
What is the final product of DNA denaturation?
However there are numerous procedures related with DNA denaturation, the final product is something similar: the connections between the strands are broken and single stranded DNA is produced, which can be determined by several methods. The best method of DNA denaturation relies upon what the DNA should be utilized for, how exact and explicit the correlations should be, and the volume of material that must be processed.
How is DNA held together?
Answer: DNA strands are held together by non covalent interactions like hydrogen bonding. Breaking of these hydrogen bonds causes separation of the strands of DNA which is known as denaturation of DNA. The hydrogen bonds present between the nucleotides of DNA can be broken by several ways.
What is the best way to denaturate DNA?
Besides heating the DNA sample, Chemicals like NaOH can also be used to achieve denaturation of DNA. A specific concentration of NaOH can be utilized to denature DNA. As the amount of NaOH utilized is lowered, the denaturation will take longer time than expected – yet the DNA can in any case be completely denatured. NaOH has been demonstrated to be perhaps the best and efficient strategies for complete denaturation of DNA.
Why does DNA absorb less UV light?
Double helical DNA absorbs less UV light as compared to the single strand of DNA because of the base pair stacking. When DNA melts, percentage of single stranded DNA increases which results into a increase in the UV absorption profile. This phenomenon is known as hyperchromicity. Thus, the extent of denaturation or melting can be monitored by measuring absorbance at 260 nm.
Why is DNA important for life?
Answer: As we know the stability of DNA is important for every living cell to function properly. But, there are certain occasions in which denaturation of DNA in beneficial for the cell to carry out normal life processes. DNA denatures to produce two polynucleotide strands, it is carried out by the help of specific enzymes like gyrase, topoisomerase and helicase and the denaturation is often localized.