The thyroid gland produces thyroxine, which is a relatively inactive prohormone and lower amounts of the active hormone, triiodothyronine. Collectively, thyroxine and triiodothyronine are referred to as the thyroid hormones.
What is necessary for the production of thyroid hormone?
- Dairy products
- Seafood especially shellfish
- Meat
- Breads
- Eggs
- Multivitamin containing iodine
- Yogurt/Frozen yogurt/Ice cream
- Seaweed
- Soy milk/Soy sauce
How can you naturally increase thyroid hormones?
What Works For Increasing Thyroid Hormone Naturally?
- The Thyroid Reset Diet. This is by far the most prominent way to increase your thyroid hormone. ...
- Weight Loss. We know that thyroid disease can cause weight gain, but it’s a two-way street. We also know that weight gain can cause thyroid disease!
- Deprescribing. Basically, this means going off thyroid medication! ...
What is the primary function of thyroid hormones?
The thyroid hormone is well known for controlling metabolism, growth, and many other bodily functions. The thyroid gland, anterior pituitary gland, and hypothalamus comprise a self-regulatory circuit called the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. The main hormones produced by the thyroid gland are thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
What two hormones are produced by the thyroid and parathyroid?
Thyroid (function of thyroxine) and parathyroid (blood calcium regulation) glands
- The function of thyroxine in metabolism regulation. The primary function of the thyroid gland is the production of the non-steroid hormone thyroxine, a peptide molecule made from the amino acid ...
- Hypothyroidism – a disorder of an underactive thyroid. ...
- Calcitonin and Parathyroid hormone in the regulation of blood calcium levels. ...

What does the thyroid hormone do?
What does the thyroid gland do? The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate the body's metabolic rate controlling heart, muscle and digestive function, brain development and bone maintenance. Its correct functioning depends on a good supply of iodine from the diet.
What do T3 and T4 hormones do?
T3 and T4 work together to regulate how your body uses energy. These hormones also play an important role in controlling your weight, body temperature, muscle strength, and nervous system.
What happens when T3 is low?
Low T3 levels Low T3 test results can indicate an underactive thyroid, or hypothyroidism. Sometimes, low T3 can also indicate starvation. According to the ATA, a person can develop an underactive thyroid due to autoimmune disease, or as a result of radiation treatment or thyroid surgery.
What happens when T4 is high?
In general, T4 results that are higher than normal may be a sign of: Hyperthyroidism, which may be caused by Graves disease or another medical condition that causes your thyroid to make too much T4. Thyroiditis (thyroid inflammation) Toxic goiter (an enlarged thyroid with areas that make extra thyroid hormone)
What is the difference between T3 and T4 hormone?
Thyroxine (T4) is responsible for your metabolism, mood, and body temperature, among other things. T3, too, is made in the thyroid gland, and it can also be made in other tissues within the body by converting T4 (in a process called deiodination) into T3.
Is T3 or T4 more important?
Because T4 is converted into another thyroid hormone called T3 (triiodothyronine), free T4 is the more important hormone to measure. Any changes show up in T4 first. T3 and T4 help to control how your body stores and uses energy (metabolism). The thyroid hormones also help control many of your body's other processes.
What happens if T3 is high?
What happens when T3 levels are high? Higher-than-normal T3 levels typically indicate hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). Hyperthyroidism has several causes, including Graves' disease (an autoimmune condition), thyroid nodules and thyroiditis (inflammation of your thyroid gland).
Does T3 and T4 increase metabolic rate?
T4 and T3 are also well known for their in vivo association with basal metabolic rate (BMR) in homeotherms, at least in the laboratory (Nicol et al., 2000; Silvestri et al., 2005; Johnstone et al., 2005; Kim, 2008). By increasing cellular metabolism, T3 can increase BMR and promote thermoregulation.
What is the main function of thyroid hormone?
Thyroid hormones are integral in the regulation of many functions and aspects of the human body, such as temperature regulation, energy levels, wei...
What are the effects of thyroid hormone?
An imbalance in thyroid hormone can lead to a lot of health repercussions. The effects depend on the conditions, but most thyroid problems can have...
What hormones does the thyroid produce?
The thyroid gland produces two hormones – Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4)
What hormones does the thyroid produce?
The thyroid gland produces two hormones – Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4) Explore more about Thyroid hormone or other related topics by registering at BYJU’S Biology.
Where are thyroid hormones secreted?
The thyroid hormones are secreted by the thyroid gland, which is located in front of the neck. These hormones are integral in the regulation of many functions and aspects of the human body, such as temperature regulation, energy levels, weight, hair, nail growth and more.
What is the main function of thyroid hormone?
Thyroid hormones are integral in the regulation of many functions and aspects of the human body, such as temperature regulation, energy levels, weight, hair, nail growth and more.
What is the term for a condition where there is excess triiodothyronine in the?
Thyrotoxicosis is a condition where there is excess triiodothyronine in the bloodstream. Inflammation of the thyroid or a benign tumour can result in conditions such as Hyperthyroidism. Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone.
What hormones help with muscle and bone health?
Thyroid hormones help with brain development and function. It also helps with muscle control as well as bone health. Regulates the metabolic rate of the body. Also regulates the metabolism of fat, proteins and carbohydrates. Thyroid hormones also help with protein synthesis.
What are the symptoms of a thyroid imbalance?
The effects depend on the conditions, but most thyroid problems can have the following symptoms: weight gain, depression, constipation and tiredness.
Where is T3 produced?
Triiodothyronine (T3) T3 is produced by the thyroid gland as well as in other tissues, via the removal of iodine from Thyroxine (T4).
Where does thyroid hormone release?
Regulation of thyroid hormone starts at the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) into the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system to the anterior pituitary gland. TRH stimulates thyrotropin cells in the anterior pituitary to the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Why is thyroid hormone important?
In children, thyroid hormones act synergistically with growth hormone to stimulate bone growth. The impact of thyroid hormone in CNS is important. During the prenatal period, it is needed for the maturation of the brain. In adults, it can affect mood.
How to diagnose thyroid disease?
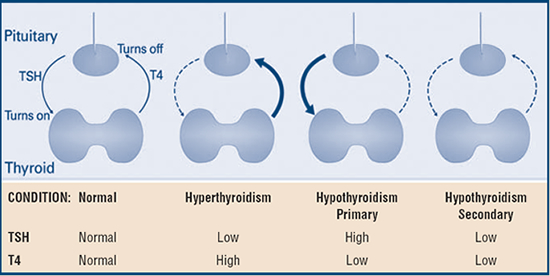
The initial tests of choice to screen for any thyroid abnormality are a TSH and free thyroxine (free T4) test. These determine whether the abnormality arises centrally from the thyroid gland (primary), peripherally from the pituitary (secondary), or hypothalamus (tertiary). In primary hypothyroidism is suspected, the thyroid gland is not releasing enough thyroid hormones. Therefore, TSH levels will be appropriately elevated, while free T4 levels will be lower. In primary hyperthyroidism, free T4 levels abnormally increased, and TSH levels will be appropriately decreased. Other lab tests such as TSH receptor antibodies or antibodies to thyroid peroxidase can help aid in diagnosing Graves disease or Hashimoto thyroiditis, respectively. [9]
What is TRH in the pituitary?
TRH stimulates thyrotropin cells in the anterior pituitary to the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TRH is a peptide hormone created by the cell bodies in the periventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus.
How does thyroid affect the body?
In general, when the thyroid hormone binds to its intranuclear receptor, it activates the genes for increasing metabolic rate and thermogenesis. Increasing metabolic rate involves increased oxygen and energy consumption.
What is the function of the thyroid gland?
The thyroid hormone is well known for controlling metabolism, growth, and many other bodily functions. The thyroid gland, anterior pituitary gland, and hypothalamus comprise a self-regulatory circuit called the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis.
Why does T4 increase in pregnancy?
In pregnant women, thyroid-binding globulin production is increased because of estrogen and beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-HCG). More free T4 will be bound to TGB, leading to increased production of T4. TSH levels and free T4 levels will normalize, and total T4 will increase.
Why is thyroid important?
Thyroid hormones are essential to the way cells and organs operate. A healthy thyroid releases the correct amount of hormones to regulate metabolism, which provides energy.
Which glands release TSH?
The thyroid gland receives signals from the brain to control the amount of hormones released. The hypothalamus in the brain alerts the nearby pituitary gland when hormone levels become too low by releasing thyroid stimulating hormones, or TSH. The pituitary then releases TSH and the thyroid responds by secreting more T3 and T4.
What are the hormones that regulate metabolism?
Thyroid hormones are essential to the way cells and organs operate. A healthy thyroid releases the correct amount of hormones to regulate metabolism, which provides energy. The major hormones the thyroid gland secretes are thyroxine, known as T4, and triiodothyronine,...
What is the treatment for underactive thyroid?
Known as hypothyroidism, an underactive thyroid is often treated with T4 medication to boost low hormone levels, according to Hormone Health Network. Doctors regularly monitor hormone levels of patients with hypothyroidism and readjust medication to maintain proper levels.
What hormones are involved in the heart?
The thyroid hormones are also involved with how fast the heart beats, body temperature, muscle strength, and the replenishment of dying cells.
What are the symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
Symptoms include anxiety, increased sweating, vision problems, muscle weakness, menstrual irregularities, and diarrhea. Medication is used to reduce the amount of hormones released by the thyroid.
What is the function of the thyroid gland?
The thyroid gland's job is to make hormones that are essential to your metabolism, growth, and development. T3 and T4 work together to regulate an array of vital functions, including: Metabolic rate. Weight loss or gain. Heart rate.
What hormones does the pituitary gland produce?
The pituitary gland constantly monitors your blood for levels of thyroid hormones, and if it detects too little, it releases TSH. That tells your thyroid gland to produce more of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) . If the pituitary detects too much T3 or T4, it slows down the production of TSH, ...
Why is my TSH level abnormal?
Several different things can cause your TSH levels to be abnormal. Often, it’s due to a medical condition that impairs the thyroid gland. Some conditions that are known to do this include: 2
What is the treatment for thyroid cancer?
Radiation treatments for cancer of or near the thyroid gland. Thyroidectomy (removal of all or part of the thyroid gland) Non-functioning thyroid gland at birth. Iodine deficiency. Taking medication that’s high in iodine. Iodine is essential for the proper production and function of the thyroid hormones.
What is the function of TSH?
Functions. Causes of Abnormal Levels. Associated Conditions. TSH Test. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) is a hormone that’s produced by the pituitary gland in your brain for the single purpose of sending a message to the thyroid gland.
What diseases affect the thyroid gland?
Autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid gland (Hashimoto’s disease, Graves’ disease, and some cases of lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjogren’s syndrome)
Where is the thyroid gland located?
The thyroid gland is front and center at the base of your neck, just below your larynx (voice box) and above your sternum. It’s shaped much like a butterfly, with two lobes that are joined in the center by a narrow strip of tissue.