
Which male hormone inhibits the secretion of FSH?
Which Male Hormone Inhibits the Secretion of FSH? Inhibin is a protein substance, produced by men only in the testicles, which has an inhibitory role on FSH. Its low levels might indicate a blockage or another defect localized in the seminiferous tubules.
How does estrogen affect FSH levels?
The acute inhibitory effects of various doses of estrogen on FSH a … Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels are not suppressed as rapidly or to the same degree as luteinizing hormone (LH) levels in ovariectomized rats treated with either gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist or estrogen.
What stimulates the release of FSH?
GnRH stimulates FSH release. The hypothalamus produces GnRH, and it is released into the hypophyseal portal circulation to act on G-protein-coupled receptors at gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary. Those gonadotropic cells produce FSH and luteinizing hormone (LH) and release them into the peripheral circulation.
What is inhibin and how does it affect FSH?
Inhibin is a protein substance, produced by men only in the testicles, which has an inhibitory role on FSH. Its low levels might indicate a blockage or another defect localized in the seminiferous tubules. Inhibin is produced by the Sertoli cells in men and by the ovarian follicle`s granulose cells at women.
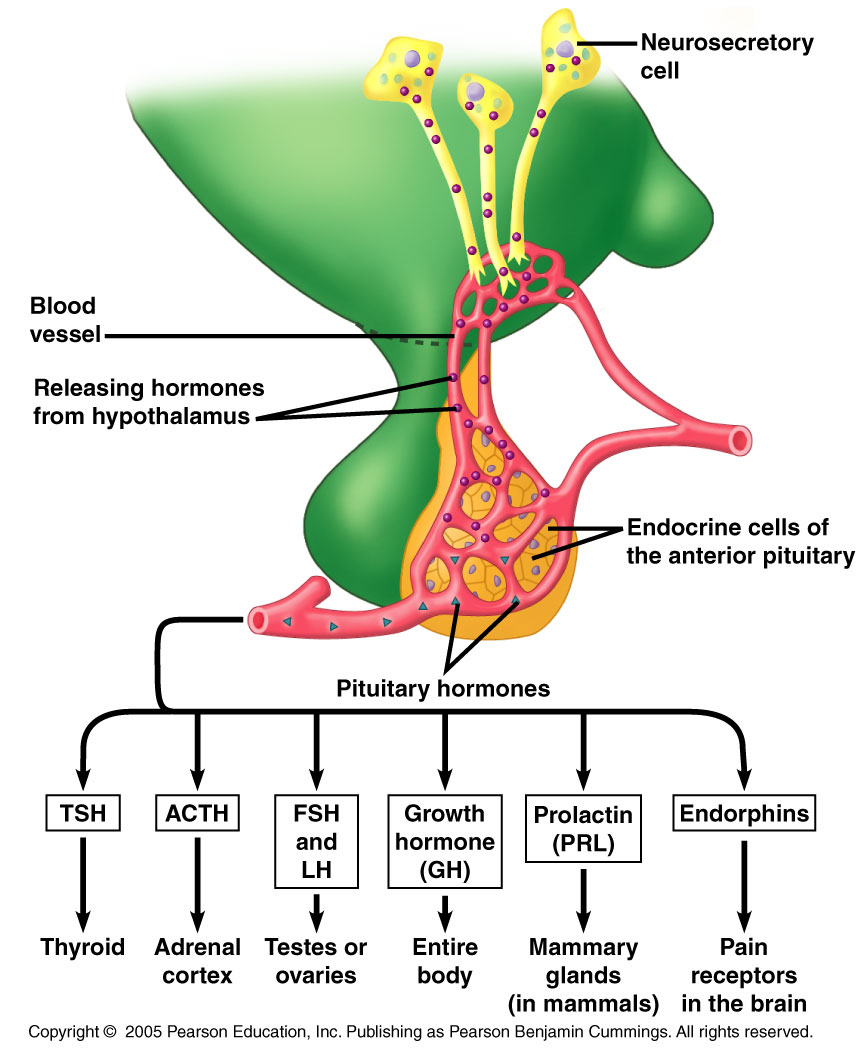
What hormones are produced by FSH?
The Sertoli cells produce an anti-mullerian hormone (AMH), which causes the involution of the Mullerian ducts, preventing the formation of female internal genitalia.
What is the role of FSH in sexual development?
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a hormone produced by the anterior pituitary in response to gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus. [1] . FSH plays a role in sexual development and reproduction in both males and females. Issues of Concern.
What hormones stimulate the hypothalamus?
When the dominant follicle produces enough estradiol to maintain levels of 200 to 300 pg/ml for 48 hours, the hypothalamus responds with a surge of GnRH which stimulates the secretion of gonadotropic hormones instead inhibiting them. FSH peaks at the same time as the LH surge that causes ovulation.
What does FSH do to ovarian follicles?
FSH stimula tes granulosa cells in the ovarian follicles to synthesize aromatase, which converts androgens produced by the thecal cells to estradiol. Follicular Development and the Menstrual Cycle. During the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, FSH stimulates the maturation of ovarian follicles.
What cells secrete inhibin B?
In men, levels of inhibin B, secreted by the Sertoli cells in response to FSH, inhibit FSH secretion via negative feedback. [5] Development. During fetal development, GnRH producing neurons develop from the epithelium of the medial olfactory pit and then migrate to the hypothalamus.[6] .
Which organ system secretes GnRH?
During puberty, the hypothalamus secretes GnRH in a pulsatile manner, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to increase secretion of LH and FSH. [6] Organ Systems Involved. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis. The hypothalamus secretes GnRH, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH.
Which subunit of FSH is unique to the hypothalamus?
The beta subunit is unique to FSH, while the alpha subunit is the same as in TSH, hCG, and LH. [2] . GnRH stimulates FSH release. The hypothalamus produces GnRH, and it is released into the hypophyseal portal circulation to act on G-protein-coupled receptors at gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary. Those gonadotropic cells produce FSH and ...
How long does FSH release?
For women of menstruating age, it’s about the most important system as anything else in the body. Anyway, these hormones work completely differently in women. In women, FSH is released for 2 weeks, LH for 2 weeks.
Why do postmenopausal women have high levels of LH and FSH?
Postmenopausal woman have VERY high levels of LH and FSH because they don’t have the negative feedback loop of the ovaries. The following is a very quick review of the menstrual cycle and how this ties into what we are learning: During the ages of 12-50, the pituitary releases FSH and LH cyclically.
What hormones are released in the pituitary gland at the age of 12?
During the ages of 12-50, the pituitary releases FSH and LH cyclically. FSH stimulates the growth of the ovarian follicle in the ovaries, and also the follicle cells around it to release estrogen. Estrogen is a feminizing hormone that affects the woman’s body, skin, breasts, bone and causes a slight thickening of endometrial lining.
What hormones do men produce at 13?
By age 13, the pituitary gland starts producing FSH and LH in guys, to promote sperm and testosterone and this process continues until the day you die. Sperm levels and testosterone levels go down with time but a 95 year old can still father a child and will try if given the chance. Negative Feedback Loop Regulation: The more LH there is, ...
Why don't we have birth control pills?
We don’t have a male birth control pill because we aren’t sure how this feedback system works. If we give a guy testosterone everyday , that primarily inhibits the release of LH which means their own testes won’t produce testosterone, but it wont stop the production of FSH that produces sperm.
What hormones affect the testes of both the male and female?
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH). Both these hormones affect the reproductive organs of both the female and the male. They are named for what they do for the ovaries of a female, although they do affect the testes of the male as well. We’ll deal with guys first, then the more complicated women.
Why is there no male birth control?
Twenty years ago it might have been a political statement to say that a male birth control pill doesn’t exist because all the physicians are males but that’s not true anymore with the majority of doctors being female.
Is FSH suppressed?
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels are not suppressed as rapidly or to the same degree as luteinizing hormone (LH) levels in ovariectomized rats treated with either gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist or estrogen.
Does estrogen inhibit LH?
Estrogen inhibition of LH and FSH secretion: effects of a GnRH antagonist. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels are not suppressed as rapidly or to the same degree as luteinizing hormone (LH) levels in ovariectomized rats treated with either gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist or estrogen.
How does LH affect FSH?
In such cases, FSH will be controlled by the hormone inhibin by sending a negative feedback signal to the pituitary gland where as LH sends a signal to the pituitary gland and to hypothalamus as well to stop testosterone production.
Why is FSH low?
certain viral infections like HIV. If the levels of FSH are low, it could be due to a problem with the pituitary gland although this is less common in occurence. Similarly, when LH levels are high in men, it means the improper functioning of the testes and if the levels are low, something is wrong with either hypothalamus or the pituitary gland.
What is the role of the hypothalamus in the production of hormones?
As discussed in our previous blog, the Hypothalamus (HPG axis) plays a major role in sending the signal to the pituitary gland to produce hormones. We all are very familiar with the pituitary gland as it is the Master Gland of the body which produces and controls many hormones throughout the body.
What hormone regulates the growth, development, pubertal maturation and reproductive functions of the body?
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) regulates the growth, development, pubertal maturation and reproductive functions of the body. FSH works together with the Luteinizing hormone (LH) to produce testosterone, which plays a major role in the development of the male reproductive organs such as testes and prostate gland and ...
What is the normal FSH level?
Normal Levels of FSH and LH. Hormone levels can be diagnosed by a simple blood test. The normal range of the FSH in adult males is 1.5 – 12.4 mIU/mL and for LH is 1.7-8.6 mIU/mL. Increase in the FSH level indicates that the testicles are not functioning well. There are various reasons for the malfunctioning of the testes.
Which gland produces the hormones related to the male reproductive system?
The pituitary gland has two parts viz anterior and posterior lobes. We are going to focus on anterior pituitary lobe, as it is responsible for the production of the hormones related to the male reproductive system. The Hypothalamus produces the GnRH Gonadotropin hormone into the blood vessels, which in turn stimulates the anterior pituitary gland ...
Which cell produces testosterone?
LH targets the Leydig cells in the seminiferous tubules and produces testosterone whereas FSH targets the Sertoli cells in the seminiferous tubules and produces protein called Androgen Binding Protein (ABP) which binds to the androgen receptor and produces the androgen testosterone and also the other hormone called Inhibin.
