How are free radicals produced in the body?
They may be generated from normal metabolic processes in the body, or by exposure to carcinogens (cancer causing substances) in the environment. Free radicals can be produced both by carcinogens and the normal metabolic processes of cells.
How can I reduce free radicals in my body?
Develop a regular exercise routine. This can lead to higher natural antioxidant levels and decreased damage caused by oxidative stress. Minimize exposure to external causes of free radicals. This includes smoking, chemicals (including cleaning chemicals), and pesticides. Wear sunscreen. Practice stress management and coping skills.
Why are free radicals bad for You?
This in turn can lead to the production of molecules of free radicals that are unstable in high concentrations. Not all free radicals are bad. Free radical formation is crucial to the process of oxidizing nutrients from our food into chemical energy.
How do antioxidants affect free radicals?
Antioxidants and Free Radicals. Some treatments for cancer, such as radiation, create free radicals in an effort to kill cancer cells. In this setting, the use of antioxidants could, in theory, decrease the effectiveness of treatment.

What causes free radicals to increase?
Although free radicals are produced naturally in the body, lifestyle factors can accelerate their production. Those include: exposure to toxic chemicals, such as pesticides and air pollution. smoking.
What foods increase free radicals?
Cooked and Processed Meats Preservatives used in processed meats -- including sausages, bacon, ham, pepperoni, hotdogs, salami, corned beef and many deli meats -- may also create free radicals. The American Institute for Cancer Research recommends avoiding processed meats and marinating meats you intend to grill.
What kills free radicals in the body?
AntioxidantsAntioxidants are chemicals that interact with and neutralize free radicals, thus preventing them from causing damage. Antioxidants are also known as “free radical scavengers.” The body makes some of the antioxidants that it uses to neutralize free radicals. These antioxidants are called endogenous antioxidants.
How can I reduce free radicals?
Keep in mind that free radical content is high in nutrient-poor meals and those deficient of antioxidants.Avoid high glycemic foods, or foods that are rich in refined carbohydrates and sugars. ... Limit processed meats such as sausages, bacon and salami. ... Limit red meat. ... Don't reuse cooking fats and oils. ... Limit alcohol.More items...•
Does coffee cause free radicals?
Sure, they require a little extra effort since you have to grind them yourself, but research in the journal Food Chemistry shows that preground coffee contains more free radicals, which can contribute to oxidative stress and inflammation in the body.
What vitamin protects cells from free radicals?
vitamins C and EAntioxidants, such as vitamins C and E and carotenoids, may help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Does exercise increase free radicals?
Strenuous exercise actually increases the production of free-radicals but regular physical exercise protects against free radical damage by boosting the defenses to a greater extent.
Does stress cause free radicals?
Stress is also responsible for the generation of free radicals. The evidence for the involvement of free radicals and oxidative injury in producing metabolic disturbance, maladjustment and many diseases has been accumulating since long.
Does sugar increase free radicals?
Their study, published in the August issue of The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, shows that excess sugar in the bloodstream stimulates the generation of free radicals, the oxygen molecules known to damage cells lining blood vessels and many other organs.
How does vitamin C protect against free radicals?
As an antioxidant, vitamin C provides protection against oxidative stress-induced cellular damage by scavenging of reactive oxygen species, vitamin E-dependent neutralization of lipid hydroperoxyl radicals, and by protecting proteins from alkylation by electrophilic lipid peroxidation products.
What is the strongest antioxidant?
Glutathione is the most powerful and important among the antioxidants our body produces. It's a combination of three amino acids; it tackles ageing through the intestines and circulatory system.
What foods cause oxidative stress?
Diets, especially high-fat or high-carbohydrate diets, have been shown to be associated with oxidative stress by elevating the levels of protein carbonylation and lipid peroxidation products while reducing the antioxidant defense status [1].
Do eggs have free radicals?
1. Eggs can prevent macular degeneration: Eggs contain the antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin, which prevent free-radical damage to our eyes as we age. These are the same antioxidants that prevent damage to our arteries from the free radicals.
Does eating meat cause free radicals?
Meat contains fat, which can become oxidized when cooked at high temperatures. The iron in meat can also become oxidized. Preservatives used in processed meats — including sausages, bacon, ham, pepperoni, hot dogs, salami, corned beef and many deli meats — may also create free radicals.
How do free radicals damage DNA?
Free radicals can damage your cells and your DNA through a process called oxidation. The damage from these chemicals can lead to cancer and other health conditions. Some free radicals are formed as natural byproducts of your body’s processes, including eating and breathing, and you are exposed to free radicals from environmental toxins, household chemicals and cigarette smoke. Antioxidants made by your body and consumed in plant foods helps prevent free radical damage. Unfortunately, some foods contain free radicals, which add to your body’s burden.
What is the role of antioxidants in plant foods?
Antioxidants made by your body and consumed in plant foods helps prevent free radical damage. Unfortunately, some foods contain free radicals, which add to your body’s burden.
Why is meat oxidized?
Cooked and Processed Meats. Because meat contains fats, those fats can also become oxidized when cooked at high temperatures. The iron found in meat, especially red meat, can also become oxidized. Preservatives used in processed meats -- including sausages, bacon, ham, pepperoni, hotdogs, salami, corned beef and many deli meats -- may also create ...
What happens when you fry fat?
When fats or oils are heated to high temperatures, as they are with deep-frying, they can become oxidized, creating free radicals. Saturated fats are less likely than unsaturated fats to become oxidized. When cooking fats are reused, they become more oxidized and produce even more free radicals.
Is it bad to take antioxidants?
Although antioxidants from food can help combat free radical damage in your body, antioxidants may be harmful when taken out of their natural context, as is the case with antioxidant supplements. One possibility is that high doses of antioxidants may actually have a pro-oxidant effect, indicating that too much of a good thing isn’t better. The National Cancer Institute and the American Institute for Cancer Research both recommend using antioxidant supplements with caution. Consult your doctor before taking any supplements.
Why do we produce free radicals?
Our body often produces free radicals in the process of breaking down nutrients to create the energy which allows our bodies to function. The production of free radicals in normal metabolic processes such as this is one of the reasons that the risk of cancer increases with age, even when people have few exposures to cancer-causing substances.
What are the effects of free radicals?
Effects. Free Radicals and Cancer. Antioxidants. Reducing Free Radicals. Free radicals are highly reactive and unstable molecules that are produced in the body naturally as a byproduct of metabolism (oxidation), or by exposure to toxins in the environment such as tobacco smoke and ultraviolet light. Free radicals have a lifespan of only ...
How do free radicals affect DNA?
Free radicals have a lifespan of only a fraction of a second, but during that time can damage DNA, sometimes resulting in the mutations that can lead to cancer. Antioxidants in the foods we eat can neutralize the unstable molecules, reducing the risk of damage. Peter Close / Istockphoto.com / Stock Photo.
Why is oxidative stress called oxidative stress?
The reason it is named oxidative stress is that the reactions that occur which result in free radicals obtain an electron are done in the presence of oxygen. The process is actually much more complicated, and a vicious circle in essence.
Why do free radicals bind to each other?
Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons, they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselves—a process that can cause damage to DNA and other parts of human cells. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other diseases and accelerate the aging process.
What happens when a mutation in a tumor suppressor gene causes cancer?
Mutations in these genes (which are then oncogenes) result in the continuous production of proteins that promote the growth of a cell. Most often, it is a series of mutations in both tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes that leads to cancer.
What happens when a free radical steals an electron?
When one free radical "steals" an electron from a molecule, that molecule is then missing an electron (becomes a free radical), and so on. Free radicals can damage not only DNA (nucleic acids), but proteins, lipids, cell membranes, and more in the body. Damage to proteins (protein cross-linking and more) and other body components may cause disease ...
What is the body's use of free radicals?
Sometimes. The body can uses free radicals for good. This includes killing pathogens and regulating cell growth. The immune system, for example, takes advantage of free radicals’ cell-damaging qualities and uses them to destroy pathogens. Pathogens are disease-causing organisms such as bacteria and viruses.
How to reduce free radicals?
Opt for whole foods as a source of antioxidants. Studies have shown that whole fruits and vegetables may effectively help reduce your risk and symptoms related to a wide variety of chronic diseases linked to free radicals.
Why do free radicals cause oxidative stress?
Oxidative stress is caused when there’s an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants. Antioxidants stabilize free radicals and can be acquired through a nutritious and balanced diet.
What is oxidative stress?
Oxidative stress means that free radicals are triggering chain reactions in your body where proteins, lipids, and DNA are being altered. These alterations can increase your risk for a number of diseases. You may have heard how inflammation is the root cause of many diseases.
What are the causes of inflammation?
You may have heard how inflammation is the root cause of many diseases. Well, oxidative stress is behind inflammation, and that’s why it’s frequently linked to the development of different disease, including: 1 inflammatory conditions (oxidative stress has been linked to all inflammatory diseases, including arthritis) 2 cancer 3 cardiovascular disease 4 high blood pressure 5 diabetes 6 neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s 7 aging
What are the two defense mechanisms that protect cells from free radicals?
However, our body naturally has defense mechanisms in place. These defense mechanisms include antioxidants and detoxifying enzymes. Antioxidants protect both the inside and outside of cells by blocking free radicals from stealing electrons. Detoxifying enzymes protect the insides of cells from free radical damage.
How do detoxifying enzymes protect cells?
Detoxifying enzymes protect the insides of cells from free radical damage. Depending on your overall health, minimizing free radical production may be as simple as lifestyle and diet choices. For example, antioxidants are one of the best defenders of free radicals and can easily be achieved through whole foods.
Why do free radicals form?
Free radicals form because of many things in modern life, including UV light, pollution, smoking and even our diet. HowStuffWorks. The other day, I bought an expensive serum that promised to miraculously take years off my face by fighting free radicals.
What happens when a free radical is pillaged?
Free radicals typically scavenge the body to seek out a replacement for their missing electron, and all that pillaging can result in damage to cells, proteins and DNA, and a free radical chain reaction as the destabilized cell components try to regain stability.
What is the theory behind free radicals?
The theory behind free radicals is that they can lead to oxidative stress, which is the imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants.". Another mini-science lesson for you: Antioxidants are natural or man-made substances that can help prevent or delay some types of cell damage.
What are some examples of free radicals?
One well-known example of a free radical is hydroxyl radical (HO•). The molecule is one hydrogen atom short of being a water molecule, so it has one bond "dangling" from the oxygen (which is what that dot next to the O indicates). Two other examples of free radicals are the carbene molecule (: CH2), which has two dangling bonds;
Do antioxidants reduce the risk of chronic diseases?
Now That's Interesting. There may not be enough evidence to prove that antioxidants themselves reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases, but health experts still recommend eating plenty of antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables as part of a healthy diet.
Is there any long term research that shows any benefits for aging?
But, to be honest, there is no long-term research that shows any benefits for aging.". So while plenty of products and supplements tout claims about preventing or even reducing free radical damage and aging on the skin and throughout the body, the scientific evidence hasn't quite panned out to support that.
Does oxidative stress cause cancer?
Over time, oxidative stress weakens cells and tissues and can leave you more vulnerable to certain health issues, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, cancer, diabetes and more. And, as beauty marketers are keenly aware, oxidative stress can also speed up the aging process.
What causes free radical formation?
Free radicals are produced naturally in the body every day. However, certain factors can increase their production:
What are antioxidants?
Antioxidants fight the damage caused by free radicals and minimize the effects of oxidative stress on your body. These defenders can be obtained from food and play a role in repairing DNA and maintaining the health of cells.
Top What Are Free Radicals and Why Are They Bad Related Articles
Take the Alcohol (Alcoholism) Quiz to learn how your alcohol is processed by your body and your brain.
Why are oxidizing agents called electron acceptors?
Oxidizing agents are called electron acceptors, because they remove electrons from a substance, putting them in a state of loss, or oxidized. Oxidizing agents keep electrons for themselves. The oxidizing agents that have accepted electrons become free radicals if the unpaired electrons don't bind to other molecules.
What are the best ways to stop cellular damage?
Eat foods rich in antioxidants, chemicals that inhibit the oxidation of molecules by neutralizing free radicals, thereby stopping them from causing cellular damage. Antioxidants are found in a variety of plants in the form of vitamins A, C and E, selenium and certain phytonutrients and polyphenols.
Why are free radicals important?
Free radical formation is crucial to the process of oxidizing nutrients from our food into chemical energy. Free radical accumulation, however, be it atoms, ions or molecules, is harmful and can have severe consequences on our health.
What are some good foods to eat with cranberries?
Cranberries are loaded with them! Look for foods with β-carotene, lycopene and lutein, including broccoli flowers, alfalfa sprouts, Brussels sprouts, carrots, collard greens, corn, mango and tomatoes. These foods can be incorporated into several side dishes such as vegetable medleys, casseroles and salads.
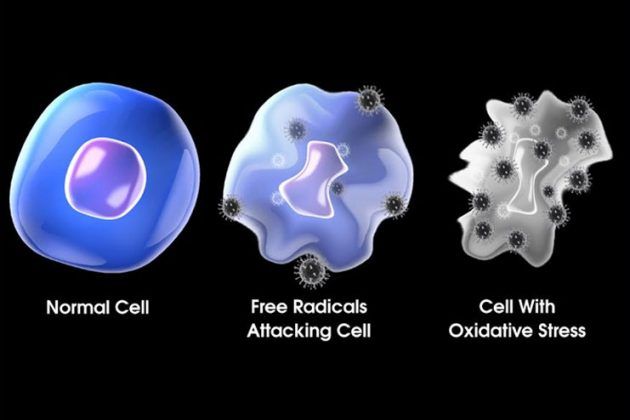
How do free radicals affect the cell?
Free radicals damage the growth, development and survival of cells in the body. Their reactive nature allows them to engage in unnecessary side reactions causing cellular impairment and eventually injury when they are present in disproportionate amounts. They directly impair cell membranes and DNA.
What are free radicals associated with?
Free radicals are frequently implicated with health problems that are experienced with age, such as hardened arteries, diabetes and even wrinkle formation. Normal molecule, left, and one missing an electron, right. Credit: www.shutterstock.com.
What is the process of nutrient metabolism?
Our mitochondria, which operate like little factories in our cells, are responsible for burning fuel from food and producing energy in each of our cells via a process called oxidative phosphorylation.