
Factors of soil formation [ edit]
- Climate [ edit] The principal climatic variables influencing soil formation are effective precipitation (i.e., precipitation minus evapotranspiration) and temperature, both of which affect the rates of chemical, physical, and biological processes. [42] ...
- Topography [ edit] ...
- Organisms [ edit] ...
What are the 5 soil forming factors?
What are the six soil forming factors?
- Parent material. Few soils weather directly from the underlying rocks.
- Climate. Soils vary, depending on the climate.
- Topography. Slope and aspect affect the moisture and temperature of soil.
- Biological factors. Plants, animals, micro-organisms, and humans affect soil formation.
- Time.
What are the five factors of soil formation?
The major soil formation factors are:
- Climate
- Relief
- Organisms
- Parent material
- Time
Which increases the rate of soil formation? Brainly?
The rate of soil formation can be accelerated by an increase in the weathering of rocks that contribute to the mineral makeup of soil. Topsoil can be increased through the increase of available organic material. Erosion can also lead to an increase in available parent material for soil formation. Even though soil formation can be accelerated, it still takes time for soil to form.
How does climate affect soil formation?
The influence of climate is due to basically two factors: temperature and rainfall. Climate indirectly affects soil formation through its influence on organisms as well. High temperatures and rainfall increase the degree of weathering and therefore the extent of soil development.
What are the factors that make up the soil?
Why is time important in soil formation?
What is the driest soil in Washington?
What are the characteristics of soil?
How many soil forming factors are there?
What are the parent materials of soil in Washington State?
How do plants affect soil?
See 4 more
About this website

What increases the rate of soil formation quizlet?
The rate of soil formation can be accelerated by an increase in the weathering of rocks that contribute to the mineral makeup of soil. Topsoil can be increased through the increase of available organic material. Erosion can also lead to an increase in available parent material for soil formation.
What are the causes of soil formation?
They are produced from rocks (parent material) through the processes of weathering and natural erosion. Water, wind, temperature change, gravity, chemical interaction, living organisms and pressure differences all help break down parent material.
What affects the rate of soil formation explain?
The amount, intensity, timing, and kind of precipitation influence soil formation. Seasonal and daily changes in temperature affect moisture effectiveness, biological activity, rates of chemical reactions, and kinds of vegetation. Topography. Slope and aspect affect the moisture and temperature of soil.
What is the rate of soil formation?
Soil development takes a very long time. It may take hundreds or even thousands of years to form the fertile upper layer of soil. Soil scientists estimate that in the very best soil forming conditions, soil forms at a rate of about 1mm/year. In poor conditions, it may take thousands of years!
How human activities affect soil formation?
Among these, the conversion from forest to agricultural land triggers one of the most severe changes: the loss of soil organic carbon. Other impacts include the use of pesticides, which decreases soil biodiversity, intensive irrigation leading to soil salinisation, and the accumulation of heavy metals in polluted soil.
How time is responsible for soil formation?
Time: The formation of the soil is not one day process but requires many years to form. Younger soils have some characteristics from their parent material, but as they age, the addition of organic matter, exposure to moisture, and other environmental factors may change its features.
What human activities affect soil?
These causes include road erosion, house construction, steep slope cultivation, tourism development, and animal trampling. These activities destroy surface vegetation and increase the potential for soil loss through exposed swallow holes (karst fissures).
What are the 5 causes of soil erosion?
Cause of Soil ErosionRainfall and Flooding. Higher intensity of rainstorms is the main cause of soil erosion. ... Agriculture. The farming practices are the major cause of soil erosion. ... Grazing. ... Logging and Mining. ... Construction. ... Rivers and Streams. ... Heavy Winds. ... Loss of Arable Land.More items...
What are the 6 main causes of soil instability?
The Causes of Unstable Soil: A Brief OverviewErosion. Erosion refers to processes in which external elements (wind, water, etc.) ... Poor Compaction. One of the most common causes of unstable soil is poor compaction. ... Freeze/Thaw. Processes of freezing and thawing essentially accelerate erosion processes. ... Decomposition.
What are the 5 types of soil formation?
Scientists attribute soil formation to the following factors: Parent material, climate, biota (organisms), topography and time.
What are the 4 soil formation processes?
Four basic processes occur in soils— additions, losses, transformations (changes), and translocation (movement).
Soil Formation and Classification | NRCS Soils - USDA
Soil Formation and Classification. The National Cooperative Soil Survey identifies and maps over 20,000 different kinds of soil in the United States.
Soil Formation: Meaning, Factors and Processes - Soil Management India
ADVERTISEMENTS: After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Soil Formation 2. Factors of Soil Formation 3. Stages 4. Processes. Meaning of Soil Formation: Soil formation is a process of two distinct phases: (i) Weathering of rocks and minerals i.e. disintegration (physical) and decomposition (chemical) of rocks and minerals; ADVERTISEMENTS: (ii) The […]
Soil formation factors and processes
Two groups Passive : i) Parent material, ii) Relief, iii) Time Active : iv) Climate, v) Vegetation & organism Passive Soil forming factors The passive soil forming factors are those which represent the source of soil forming
Formation of Soil - USDA
Formation of Soil ^ 951 stones, sucli US recent íílhiviíil and lake deposits, arc nnconsolidatod or only wcaldy cemented. Clays and shales vary exceedingly in composition. Some of tliem are highly calcareous, while others contain no lime; some have a higli
What is the Process of Soil Formation and Factors That Affect Soil ...
The soil formation process depends upon the presence of new soil material which is either acquired by denudation or deposition. Denudation is the abrasion of present rock material by the action of ice, water or wind.
What are the factors that make up the soil?
The five factors are: 1) parent material, 2) relief or topography, 3) organisms (including humans), 4) climate, and 5) time.
Why is time important in soil formation?
Time is the last of the five soil forming factors to consider. However, this does not mean that it is not important. Washington landscapes, and the soils developing on them, are products of dynamic on-going soil-forming processes. Time is just as important as each of the other soil forming factors. Time, in the way most humans think of it for soil forming processes and soil landscape development is relatively long. In geologic time, many of the soil-forming processes and landscapes that result from weathering are relatively temporary. Geologically speaking, landscapes are continually building and degrading throughout time. It takes time for all things to happen even though some things are now measured in nanoseconds.
What is the driest soil in Washington?
In Washington, it is obvious that dry soils support certain natural plants and wetter soils support different natural plants. For example, soils in the Columbia Basin (central Washington) are some of the driest in Washington. Some of these soils only receive about 7 to 10 inches of precipitation annually.
What are the characteristics of soil?
If a soil is wet, soil characteristics illustrate that fact. Soils that have a water table that moves upward and downward during different times of the year contain mottles (rusty spots) or what soil scientists call “redoximorphic features” that are similar to spots that form on a shovel that is left out in the rain. These yellowish and orange “rusty spots” help soil scientists determine where a water table occurs in a soil. Most of these wet soils in Washington are in depressions or along rivers and streams. Soil wetness is a concern for many uses unless the soil can be drained. When a soil is “too wet” there is also very little if any room for air in the soil profile. Many kinds of plants and animals are not able to live on or in these soils because of the lack of soil air. However, there are plants that have adapted to life on wet soils and these plants help a soil scientist identify wet soils.
How many soil forming factors are there?
All of the different kinds of parent material have been subjected, in varying degrees, to the other four soil forming factors. All five of the soil forming factors are acting at the same time at different rates of speed and with different degrees of efficiency.
What are the parent materials of soil in Washington State?
In more recent times, many of us are familiar with blowing dust (loess) during wind storms and volcanic ash from the eruption of Mount St. Helens in 1980. These are two of the parent materials that contribute to Washington State’s soils. Probably the most common parent material which covers almost all of the land surfaces in Washington is volcanic ash from numerous eruptions of the Cascade Mountains in the western United States. The volcanic ash is very common either by itself on the surface (volcanic ash mantles) or mixed with other material in surface horizons. Volcanic ash has very specific properties such as very light weight, capacity to hold large amounts of water, and susceptibility to compaction by vehicles when it is wet. These are some factors that influence soil genesis in Washington State.
How do plants affect soil?
The kinds of plants that grow on a soil impact the kind of plant residue that form and is incorporated into the soil. Surface soil horizons are most affected by the kinds of plants that grow on a site. Needles, twigs, leaves, stems, and roots of plants are incorporated into the soil and broken down by the different kinds of organisms that live in the soil. In Washington, soils that have darker surface horizons generally have more organic matter than do those that have a lighter- colored surface horizon. Different kinds of plants produce materials that are acidic and others produce material that is alkaline. This too changes the kind of soil that forms on a site.
How does weather affect soil formation?
The weather has a significant impact on soil formation. Water erodes rocks, wind transports sand, and freezing temperatures can create permafrost. A climate is an area in which weather patterns are consistent, and each climate can sway the soil formation process.
When will soil formation start?
April 9, 2021. June 7, 2020. The soil formation process has to start somewhere – whether it is from the erosion of rocks near a body of water or the destructive effects of an environmental disaster.
Why do microorganisms play a role in soil formation?
Microorganisms play an even greater role in soil formation because of how they guide the soil nitrogen process, which is essential for the balance of minerals and chemical reactions in the soil. Without the soil nitrogen process, the ocean and other bodies of water would become inhabitable for sea life.
What are the three stages of soil formation?
Soil formation can vary depending on what type of soil is forming – clay, sand, or silt . But generally, these are the three stages that most soils go through on their way to full formation.
What is the definition of soil formation?
Encyclopedia Britannica defines soil formation as “The evolution of soils and their properties.”
Why is it important to classify soil types?
Classifying soil types helps farmers when conducting a soil survey on their fields, or gardeners when they wish to plant only the best species of plants that will thrive in the soil.
How long does it take for soil to form?
Soil formation happens over hundreds, sometimes thousands, of years, but you can still see evidence of that formation today. You can see the soft, dark topsoil layer and every layer underneath, all the way down to the impenetrable bedrock. These layers are called soil horizons.
What are the factors that make up the soil?
The five factors are: 1) parent material, 2) relief or topography, 3) organisms (including humans), 4) climate, and 5) time.
Why is time important in soil formation?
Time is the last of the five soil forming factors to consider. However, this does not mean that it is not important. Washington landscapes, and the soils developing on them, are products of dynamic on-going soil-forming processes. Time is just as important as each of the other soil forming factors. Time, in the way most humans think of it for soil forming processes and soil landscape development is relatively long. In geologic time, many of the soil-forming processes and landscapes that result from weathering are relatively temporary. Geologically speaking, landscapes are continually building and degrading throughout time. It takes time for all things to happen even though some things are now measured in nanoseconds.
What is the driest soil in Washington?
In Washington, it is obvious that dry soils support certain natural plants and wetter soils support different natural plants. For example, soils in the Columbia Basin (central Washington) are some of the driest in Washington. Some of these soils only receive about 7 to 10 inches of precipitation annually.
What are the characteristics of soil?
If a soil is wet, soil characteristics illustrate that fact. Soils that have a water table that moves upward and downward during different times of the year contain mottles (rusty spots) or what soil scientists call “redoximorphic features” that are similar to spots that form on a shovel that is left out in the rain. These yellowish and orange “rusty spots” help soil scientists determine where a water table occurs in a soil. Most of these wet soils in Washington are in depressions or along rivers and streams. Soil wetness is a concern for many uses unless the soil can be drained. When a soil is “too wet” there is also very little if any room for air in the soil profile. Many kinds of plants and animals are not able to live on or in these soils because of the lack of soil air. However, there are plants that have adapted to life on wet soils and these plants help a soil scientist identify wet soils.
How many soil forming factors are there?
All of the different kinds of parent material have been subjected, in varying degrees, to the other four soil forming factors. All five of the soil forming factors are acting at the same time at different rates of speed and with different degrees of efficiency.
What are the parent materials of soil in Washington State?
In more recent times, many of us are familiar with blowing dust (loess) during wind storms and volcanic ash from the eruption of Mount St. Helens in 1980. These are two of the parent materials that contribute to Washington State’s soils. Probably the most common parent material which covers almost all of the land surfaces in Washington is volcanic ash from numerous eruptions of the Cascade Mountains in the western United States. The volcanic ash is very common either by itself on the surface (volcanic ash mantles) or mixed with other material in surface horizons. Volcanic ash has very specific properties such as very light weight, capacity to hold large amounts of water, and susceptibility to compaction by vehicles when it is wet. These are some factors that influence soil genesis in Washington State.
How do plants affect soil?
The kinds of plants that grow on a soil impact the kind of plant residue that form and is incorporated into the soil. Surface soil horizons are most affected by the kinds of plants that grow on a site. Needles, twigs, leaves, stems, and roots of plants are incorporated into the soil and broken down by the different kinds of organisms that live in the soil. In Washington, soils that have darker surface horizons generally have more organic matter than do those that have a lighter- colored surface horizon. Different kinds of plants produce materials that are acidic and others produce material that is alkaline. This too changes the kind of soil that forms on a site.
Formation
- Soil forms layers or horizons, roughly parallel to the earths surface, in response to five soil forming factors. The whole soil, from the surface to its lowest depths, develops naturally as a result of these five factors. The five factors are: 1) parent material, 2) relief or topography, 3) organisms (including humans), 4) climate, and 5) time. If ...
Geology
- Geologic events have provided Washington with a wide variety of parent materials. In more recent times, many of us are familiar with blowing dust (loess) during wind storms and volcanic ash from the eruption of Mount St. Helens in 1980. These are two of the parent materials that contribute to Washington States soils. Probably the most common parent material which covers almost all of …
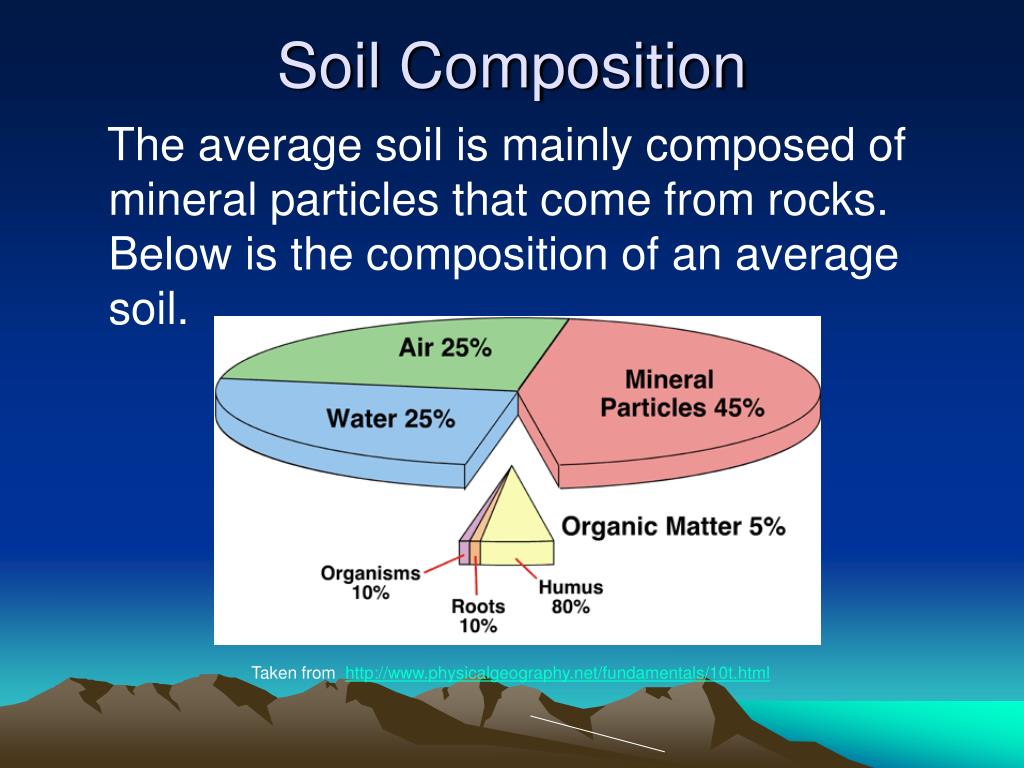
Composition
- It is thought that about 70 to 75 percent of the earths crust is made up of sedimentary rocks and the remaining 25 to 30 percent is made up of igneous rocks and glacial materials. Coarse-grained igneous rocks such as granite weather to sandy types of materials; thus soils that formed from these kinds of rocks have a sandy texture. Fine- grained sedimentary rocks such as siltstone an…
Cause
- All of the different kinds of parent material have been subjected, in varying degrees, to the other four soil forming factors. All five of the soil forming factors are acting at the same time at different rates of speed and with different degrees of efficiency.
Climate
- Washingtons climate, like its topography, varies greatly from place to place. In fact, soil climate changes quite rapidly in very short distances. Annual precipitation varies from about 7 inches in parts of the Columbia Basin to more than 300 inches in the Olympic Rainforest. Some areas in Washington receive very little snowfall and other areas receive many feet of snow in winter. Acc…
Effects
- Both living plants and animals (including humans) affect natural soil formation. The kinds of plants that grow on a soil impact the kind of plant residue that form and is incorporated into the soil. Surface soil horizons are most affected by the kinds of plants that grow on a site. Needles, twigs, leaves, stems, and roots of plants are incorporated into the soil and broken down by the di…
Other animals
- Other organisms such as worms that burrow into the soil create little channels that assist in the movement of water and air into and through soil. Burrowing animals such as voles, moles, and ground squirrels mix the soil as they dig homes which also helps to move water and air into the soil profile.
Ecology
- In Washington, it is obvious that dry soils support certain natural plants and wetter soils support different natural plants. For example, soils in the Columbia Basin (central Washington) are some of the driest in Washington. Some of these soils only receive about 7 to 10 inches of precipitation annually. Grasses such as bluebunch wheatgrass and Idaho fescue and Wyoming big sagebrus…
Symptoms
- Young soils are usually easy to recognize because they have little or weak soil horizon development and the horizons commonly are indistinct. The soil parent material and the intensity of weathering have not yet produced highly visible evidence such as clay or carbonate movement and deposition which form subsoil horizons. Normally, soil scientists think of soil development i…
Environment
- Washington State has a variable environment for soil development. Elevation ranges from 0 feet (sea level) at the shore of the Pacific Ocean to more than 14,000 feet at the summit of Mount Rainier in Pierce County and the average annual precipitation ranges from about 6 inches to more than 300 inches. Geologic formations and their rock types are also highly variable in compositio…
What Is Soil Formation?
Soil Formation Steps
- Soil formation can vary depending on what type of soil is forming – clay, sand, or silt. But generally, these are the three stages that most soils go through on their way to full formation. 1. Erode – Elements of weather cause the rocks, soil, and plant matter in an area to erode and become sediment that contains various minerals and nutrients that were in the previous materia…
Factors Affecting Soil Formation
- There are many factors in nature that influence soil formation. These factors determine what type of soil forms (sandy, loam, red clay…etc.) and its location in the world after formation. The first and most important factor affecting soil formation is the parent material. After that, various things can change the formation process, but each factor ...
Types of Soil Formation
- Clay, sand, and silt are the three textures of soil that mix to form all the different soil types. Although the soil formation process is relatively the same for all three, some variations are important to recognize.
Soil Taxonomy
- Soil taxonomy refers to the classification of soil types. Classification is necessary because of the sheer number of soil types there are. All soils can break down into three types – clay, sand, and silt – which combine to form the different variations of soils. Many elements also contribute to soil formation. Classifying soil types helps farmers when conducting a soil survey on their fields…
Soil Maps
- Soil maps are created from soil surveys. Soil scientists (pedologists) and farmers are the most common people who might need a soil survey map. Soil maps can identify the limitations and qualities of the soil in a large area of land. Landscapers can also utilize a soil survey map for aeration purposes. A soil survey mapshows the results of a soil survey mapped out on a scaled-…
Frequently Asked Questions
- How long does it take for soil to form?
According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), it can take at least 500 years for one inch of topsoil to form. Although, many soil scientists say it takes even longer. To form all the horizons in soil, it can take thousands, if not millions, of years. - Can soil be created?
Yes. Many gardeners use compost, moisture, much, and decomposing plants to create nutrient-rich topsoil, though making a soil from scratch without a parent material may prove to be difficult.