Myocardial infarction. Myocardial infarction ( MI ), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to a part of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw.
What tests confirm a diagnosis of myocardial infarction?
You may also undergo:
- Chest X-ray. An X-ray image of your chest allows your doctor to check the size of your heart and its blood vessels and to look for fluid in your lungs.
- Echocardiogram. ...
- Coronary catheterization (angiogram). ...
- Exercise stress test. ...
- Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). ...
What is meant by myocardial infarction?
The term "myocardial infarction" focuses on the myocardium (the heart muscle) and the changes that occur in it due to the sudden deprivation of circulating blood. The main change is necrosis (death) of myocardial tissue. The word "infarction" comes from the Latin "infarcire" meaning "to plug up or cram."
What are the risk factors of myocardial infarction?
- Smoking
- Abnormal lipid profile/blood apolipoprotein (raised ApoB/ApoA1)
- Hypertension
- Diabetes mellitus
- Abdominal obesity (waist/hip ratio) (greater than 0.90 for males and greater than 0.85 for females)
What happens if myocardial infarction is not treated?
What happens if myocardial infarction is not treated? During a heart attack, blood flow to the heart stops due to a blockage in a coronary artery. These are the arteries that carry blood to the heart. If a person does not receive immediate treatment, this lack of blood flow can cause damage to the heart.

What indicates myocardial infarction on ECG?
One of the most significant findings of myocardial infarction is the presence of ST segment elevation. The ST segment is the part of the ECG tracing that starts at the end of the S wave and ends at the beginning of the T wave. The point where the end of the Q wave and the ST segment meet is called the J point.
How do you confirm myocardial infarction?
Tests available include: Cardiac Troponin I or Troponin T - which are both very sensitive and specific and are the recommended laboratory tests for the diagnosis of MI. Serial testing is recommended in order to confirm or exclude a rise or fall in troponin concentration.
What is the best indicator of a myocardial infarction?
The most sensitive early marker for myocardial infarction is myoglobin. Troponin levels should be measured at presentation and again 10-12 hours after the onset of symptoms.
What are the four signs of a possible myocardial infarction?
Chest Pain, Pressure, Fullness, or Discomfort You may also feel pressure, squeezing, or fullness. These symptoms usually start slowly, and they may go away and come back.
What are the 3 cardiac markers?
Cardiac enzymes ― also known as cardiac biomarkers ― include myoglobin, troponin and creatine kinase.
What laboratory test are positive indicators of MI?
Cardiac troponin levels (troponin-T and troponin-I) have a greater sensitivity and specificity than CK-MB levels in detecting MI. Positive troponin levels are considered virtually diagnostic of MI, as they are without equal in combined specificity and sensitivity in this diagnosis.
Does troponin or CK-MB rise first?
The CK-MB rises in the serum at 4–9 h after the onset of chest pain, peaks ~24 h and returns to baseline values at 48–72 h. The one advantage of CK-MB over the troponins is the early clearance that helps in the detection of reinfarction.
What is CK-MB and troponin?
CK and CK-MB were once the primary tests ordered to detect and monitor heart attacks, but they have now been largely replaced by the troponin test, which is more specific for damage to the heart. Sometimes, the CK test may be used if a heart attack is suspected and a troponin test is not available.
What are the three major characteristics used to diagnose a myocardial infarction?
The diagnosis of myocardial infarction requires two out of three components (history, ECG, and enzymes). When damage to the heart occurs, levels of cardiac markers rise over time, which is why blood tests for them are taken over a 24-hour period.
What is the most common symptom of myocardial ischemia and infarction quizlet?
The most common symptom of myocardial ischemia is angina (also called angina pectoris). This is chest pain (similar to indigestion or heartburn) that feels like: Chest discomfort. Heaviness.
What does troponin do in the heart?
Troponin T binds troponin proteins to muscle fibers. The heart releases troponin into the blood following an injury, such as a heart attack. Very high troponin levels usually mean that a person has recently had a heart attack. The medical term for this attack is myocardial infarction.
Which of the following blood tests is most indicative of cardiac damage?
A troponin test measures the levels of troponin T or troponin I proteins in the blood. These proteins are released when the heart muscle has been damaged, such as occurs with a heart attack. The more damage there is to the heart, the greater the amount of troponin T and I there will be in the blood.
What is an acute myocardial infarction?
What is acute myocardial infarction? Acute myocardial infarction is the medical name for a heart attack . A heart attack is a life-threatening condition that occurs when blood flow to the heart muscle is abruptly cut off, causing tissue damage. This is usually the result of a blockage in one or more of the coronary arteries.
What causes a blockage in the arteries?
Bad cholesterol. Bad cholesterol, also called low-density lipoprotein (LDL), is one of the leading causes of a blockage in the arteries. Cholesterol is a colorless substance that’s found in the food you eat. Your body also makes it naturally.
What type of fat is clogged arteries?
Another type of fat that contributes to clogged arteries is trans fat, or hydrogenated fat. Trans fat is usually artificially produced and can be found in a variety of processed foods. Trans fat is typically listed on food labels as hydrogenated oil or partially hydrogenated oil.
What age do you have a heart attack?
The risk of having a heart attack increases with age. Men are at a higher risk of a heart attack after age 45, and women are at a higher risk of a heart attack after age 55.
What does it mean when you have a tight chest?
pressure or tightness in the chest. pain in the chest, back, jaw, and other areas of the upper body that lasts more than a few minutes or that goes away and comes back. shortness of breath. sweating. nausea. vomiting. anxiety. a cough. dizziness.
Does high triglycerides cause heart attacks?
High triglyceride levels. High triglyceride levels also increase your risk for having a heart attack. Triglycerides are a type of fat that clog up your arteries. Triglycerides from the food you eat travel through your blood until they’re stored in your body, typically in your fat cells.
Is high blood pressure a risk factor for heart attack?
High blood pressure. You’re at greater risk for heart attack if you have high blood pressure. Normal blood pressure is below 120/80 mm Hg (millimeters of mercury) depending on your age. As the numbers increase, so does your risk of developing heart problems.
What is a myocardial infarction?
A myocardial infarction occurs when an atherosclerotic plaque slowly builds up in the inner lining of a coronary artery and then suddenly ruptures, causing catastrophic thrombus formation, totally occluding the artery and preventing blood flow downstream. A myocardial infarction ( MI ), commonly known as a heart attack, ...
What is the most common symptom of acute myocardial infarction?
Pain. Chest pain is the most common symptom of acute myocardial infarction and is often described as a sensation of tightness, pressure, or squeezing. Pain radiates most often to the left arm, but may also radiate to the lower jaw, neck, right arm, back, and upper abdomen.
What age does a person with ischemic heart disease have to be to get MI?
Family history of ischemic heart disease or MI, particularly if one has a male first-degree relative (father, brother) who had a myocardial infarction before age 55 years, or a female first-degree relative (mother, sister) less than age 65 increases a person's risk of MI.
What is MI in medical terms?
Terminology. Main article: Acute coronary syndrome. Myocardial infarction (MI) refers to tissue death ( infarction) of the heart muscle ( myocardium) caused by ischaemia, that is lack of oxygen delivery to myocardial tissue.
How many people have myocardial infarctions in 2015?
Worldwide, about 15.9 million myocardial infarctions occurred in 2015. More than 3 million people had an ST elevation MI, and more than 4 million had an NSTEMI. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States.
What is the treatment for non ST elevation myocardial infarction?
People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use of PCI in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty.
What is the most common symptom of a heart attack?
The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw.
What is the main cause of myocardial infarction?
In order to prevent the heart muscle from dying, intervention must be carried out as quickly as possible. Coronary heart disease is considered the main cause of myocardial infarction. Only very rarely are other causes of myocardial infarction present, for example spasms of the coronary vessels.
What is the term for a heart attack?
A heart attack (myocardial infarction) occurs when a blood vessel of the heart muscle (coronary artery) closes. The muscle is then cut off from the oxygen supply and can no longer do its work. A heart attack can be life threatening!
What is the most common complication of a fresh heart attack?
Cardiac arrhythmias are also visible in the ECG. These are by far the most common complication of a fresh heart attack. In addition, the ECG helps to distinguish an acute myocardial infarction from a heart attack that occurred a long time ago.
What happens if a clot blocks a vessel?
If this clot completely blocks the vessel in question, a heart attack occurs: the section of the heart muscle that is mainly supplied by this coronary vessel no longer receives enough oxygen. It can then die off within a few hours. In the worst case, the patient dies from the heart attack (acute cardiac death ).
How long after a heart attack can you start cardio?
Physical activity gets the circulation going again and prevents further vascular occlusion. A few weeks after a heart attack, patients can start with cardiovascular training.
How do you know if you have a swollen chest?
Typical symptoms: severe pain in the left chest area/behind the breastbone, shortness of breath, anxiety/feeling of anxiety; attention, the symptoms in women can be different (dizziness, vomiting) than in men!
What does it mean when your arm hurts?
The pain can be pressing, stabbing or burning. Sometimes they also radiate into other regions of the body. Thus, pain in the arm (especially on the left), upper abdomen, back, shoulder or jaw can also be a warning signal for heart attack. Other typical heart attack symptoms are:
What causes myocardial cell death?
Atherosclerosis is by far the most common cause of myocardial infarction. The major risk factors of atherosclerosis are hyperlipidemia, diabetes, smoking, hypertension, gender and age. Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation have ...
What is the marker of early atherosclerosis?
Another marker of early atherosclerosis is IL-6, which has a major role in the recruitment and activation of inflammatory cells in response to ischemia and further during the reperfusion of the infarcted myocardium (25). In addition, it stimulates the liver to produce the acute phase protein, CRP (26).
What is the plaque characterized by lipid accumulation in the vessel walls?
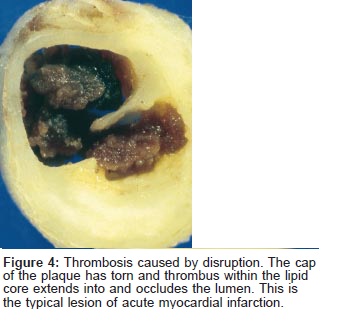
Atherosclerosis is characterized by lipid accumulation in the vessel walls leading to the formation of an atherosclerotic plaque consisting of a central lipid core surrounded by foamy macrophages and smooth muscle cells covered by a fibrous cap (7).
Is troponin C specific for myocardial injury?
As the isoforms of trop onin C is identical in the skeletal and cardiac muscle, troponin C is not extremely specific for myocardial injury (37,38). The isoforms of troponin T and troponin I differ in the skeletal and the cardiac muscle, and thus are extremely specific for cardiac tissue necrosis (39).
When was the last update for myocardial infarction?
Last Update: October 3, 2020. Introduction. According to the European Society of Cardiology, American College of Cardiology Foundation, American Heart Association, and World Health Federation Expert consensus document on the third universal definition of myocardial infarction, acute myocardial infarction can be diagnosed in several ways, ...
How long does it take for creatine kinase to be found in myocardial tissue?
CK-MB can be found in serum within 4 to 6 hours of the onset of myocardial ischemia; however, it can take up to 12 hours in some patients.
How long does it take to measure troponin?
Many recommendations based on older assays recommend repeat troponin measurement at 6 to 12 hours, but several strategies now exist with repeat measurement as soon as 2 hours.
Can acute myocardial infarction be diagnosed?
According to the European Society of Cardiology, American College of Cardiology Foundation, American Heart Association, and World Health Federation Expert consensus document on the third universal definition of myocardial infarction, acute myocardial infarction can be diagnosed in several ways, one of which depends on cardiac enzymes.
Is lactate dehydrogenase used for myocardial injury?
Previously used in conjunction with CK-MB, lactate dehydrogenase is also no longer regularly used for diagnosis of myocardial injury. Lactate dehydrogenase is found in many tissues and is therefore not specific. It also takes several hours after onset of injury for levels to become elevated. Copeptin.
Is troponin more sensitive to cardiac injury?
There are many reasons for this, but ultimately, troponin has been shown to be more specific and more sensitive to cardiac injury. Nearly all false-positive troponins are limited to situations where there is antibody cross-reactivity within the testing assay, as troponin is not released from damaged skeletal muscle.
What side of the body does myocardial ischemia occur?
When they do occur, the most common is chest pressure or pain, typically on the left side of the body (angina pectoris).
What causes myocardial ischemia?
Plaques made up mostly of cholesterol build up on your artery walls and restrict blood flow. Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of myocardial ischemia.
What are the factors that increase the risk of myocardial ischemia?
Factors that can increase your risk of developing myocardial ischemia include: Tobacco. Smoking and long-term exposure to secondhand smoke can damage the inside walls of arteries. The damage can allow deposits of cholesterol and other substances to collect and slow blood flow in the coronary arteries.
What happens if you have too much cholesterol in your blood?
If you have too many cholesterol particles in your blood, cholesterol may accumulate on your artery walls. Eventually, deposits called plaque may form. The deposits may narrow or block your arteries. The plaque can also burst, causing a blood clot.
What is the term for a heart attack caused by a plaque rupture?
If the plaques rupture, you can have a heart attack (myocardial infarction).
What happens if your heart is blocked?
If a coronary artery becomes completely blocked, the lack of blood and oxygen can lead to a heart attack that destroys part of the heart muscle. The damage can be serious and sometimes fatal. Irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia). An abnormal heart rhythm can weaken your heart and may be life-threatening.
How do you know if you have diabetes?
Other signs and symptoms — which might be experienced more commonly by women, older people and people with diabetes — include: Neck or jaw pain. Shoulder or arm pain. A fast heartbeat. Shortness of breath when you are physically active. Nausea and vomiting.
Overview
Diagnosis
A myocardial infarction, according to current consensus, is defined by elevated cardiac biomarkers with a rising or falling trend and at least one of the following:
• Symptoms relating to ischemia
• Changes on an electrocardiogram (ECG), such as ST segment changes, new left bundle branch block, or pathologic Q waves
Terminology
Myocardial infarction (MI) refers to tissue death (infarction) of the heart muscle (myocardium) caused by ischaemia, the lack of oxygen delivery to myocardial tissue. It is a type of acute coronary syndrome, which describes a sudden or short-term change in symptoms related to blood flow to the heart. Unlike the other type of acute coronary syndrome, unstable angina, a myocardial infarction occurs when there is cell death, which can be estimated by measuring by a blood test for
Signs and symptoms
Chest pain that may or may not radiate to other parts of the body is the most typical and significant symptom of myocardial infarction. It might be accompanied by other symptoms such as sweating.
Chest pain is one of the most common symptoms of acute myocardial infarction and is often described as a sensation of tightness, pressure, or squeezing. Pai…
Risk factors
The most prominent risk factors for myocardial infarction are older age, actively smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, and total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein levels. Many risk factors of myocardial infarction are shared with coronary artery disease, the primary cause of myocardial infarction, with other risk factors including male sex, low levels of physical activity, a past family history, obesity, and alcohol use. Risk factors for myocardial disease are often include…
Mechanism
The most common cause of a myocardial infarction is the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque on an artery supplying heart muscle. Plaques can become unstable, rupture, and additionally promote the formation of a blood clot that blocks the artery; this can occur in minutes. Blockage of an artery can lead to tissue death in tissue being supplied by that artery. Atherosclerotic plaques ar…
Prevention
There is a large crossover between the lifestyle and activity recommendations to prevent a myocardial infarction, and those that may be adopted as secondary prevention after an initial myocardial infarction, because of shared risk factors and an aim to reduce atherosclerosis affecting heart vessels. The influenza vaccine also appear to protect against myocardial infarction with a benefit of 15 to 45%.
Management
A myocardial infarction requires immediate medical attention. Treatment aims to preserve as much heart muscle as possible, and to prevent further complications. Treatment depends on whether the myocardial infarction is a STEMI or NSTEMI. Treatment in general aims to unblock blood vessels, reduce blood clot enlargement, reduce ischemia, and modify risk factors with the aim …