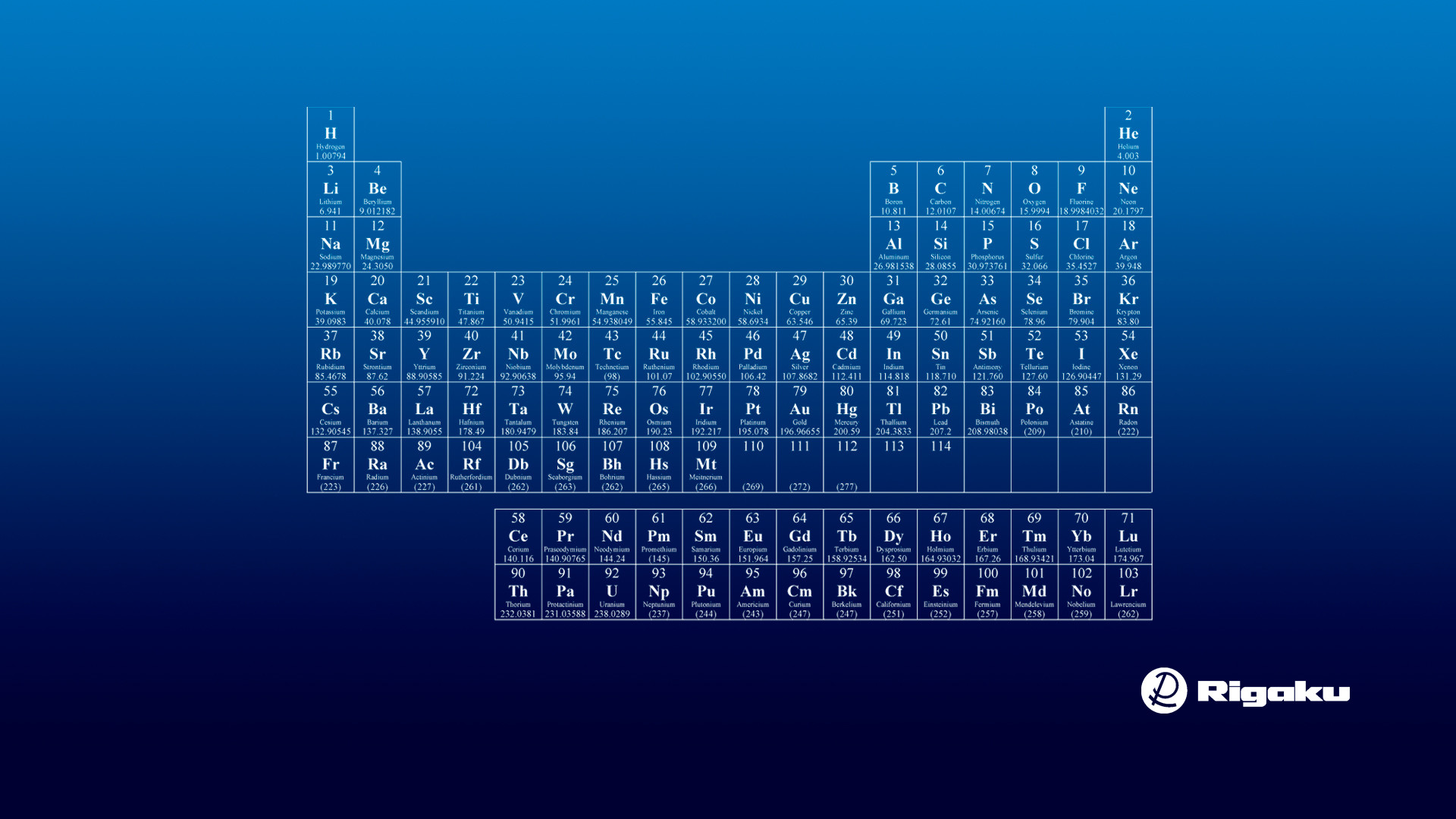
What are the first 36 elements in the periodic table?
Periodic Table: First 36 Elements STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by asen42 First 36 Elements Terms in this set (36) Hydrogen H Helium He Lithium Li
What is the periodic table of elements?
History of the periodic table of elements The periodic table of elements is an organized table of all chemical elements identified and recognized. Most fo... The periodic table of elements contains about 118 elements, and there are also many trends in the periodic table, such as ionization energy, electronegativit...
What are the 36 elements in this set?
First 36 Elements Terms in this set (36) Hydrogen H Helium He Lithium Li Beryllium Be Boron B Carbon C Nitrogen N Oxygen O Fluorine F Neon Ne Sodium Na Magnesium Mg Aluminum Al Silicon Si Phosphorus P
What is the name of Group 16 on the periodic table?
Oxygen group is the group 16 on the periodic table. The elements included in Oxygen group are;

Who created the periodic table?
The creator of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869 began collecting and sorting known properties of elements, like he was playing a game, while traveling by train.
Can periodic table games be used for grade?
The periodic table game available on this page is for entertainment purposes only, and should not be used to grade students on their knowledge of chemical elements.
Does the Modern Periodic Table Change? If So, How and Who Does That?
The periodic table as we know it today is managed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, or IUPAC (eye-you-pack).
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements.
What is the lightest element on the periodic table?
With a standard atomic weight of circa 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass.
How to determine the stability of an isotope?
To determine the stability of an isotope you can use the ratio neutron/proton (N/Z). Also to help understand this concept there is a chart of the nuclides, known as a Segre chart. This chart shows a plot of the known nuclides as a function of their atomic and neutron numbers. It can be observed from the chart that there are more neutrons than protons in nuclides with Z greater than about 20 (Calcium). These extra neutrons are necessary for stability of the heavier nuclei. The excess neutrons act somewhat like nuclear glue. Only two stable nuclides have fewer neutrons than protons: hydrogen-1 and helium-3.
How are the chemical properties of a solid, liquid, gas, and plasma determined?
The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
What is the number of neutrons in an atom?
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
What are phonons in crystals?
The quanta of the crystal vibrational field are referred to as ‘‘ phonons .’’ A phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, like solids and some liquids. Phonons play a major role in many of the physical properties of condensed matter, like thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. In fact, for crystalline, nonmetallic solids such as diamond, k ph can be quite large, exceeding values of k associated with good conductors, such as aluminum. In particular, diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity (k = 1000 W/m.K) of any bulk material.
Is metal a solid?
Metals are solids and as such they possess crystalline structure where the ions (nuclei with their surrounding shells of core electrons) occupy translationally equivalent positions in the crystal lattice. Metals in general have high electrical conductivity , high thermal conductivity, and high density. Accordingly, transport of thermal energy may be due to two effects:
What is the oxygen group on the periodic table?
Oxygen group is the group 16 on the periodic table.
Why are the elements in the bottom two rows of the periodic table included in group 3?
The elements in the two bottom rows of the periodic table are also included in these groups. They are placed in the two separate rows at the bottom because they show few different properties. Actually, the elements in the bottom rows are the extension of group 3 only. So they are included in group 3. But as these elements have few different ...
What is the first group of elements in the periodic table?
Group 1: Alkali metals group. Alkali metals group is the very first group (group 1) on the periodic table. The elements included in the Alkali metals group are; Lithium (Li)
How many groups are there in the periodic table?
Groups are the vertical columns on the periodic table. There are total 18 vertical columns on periodic table. Hence there are 18 groups. The elements lying in the same groups show similar chemical properties and they also have same number of valence electrons.
Which group is alkaline earth metals?
Alkaline earth metals are the group 2 elements on the periodic table.
Can you find every detail of an interactive periodic table?
You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table.
Do elements of the same group have the same number of valence electrons?
In this way, the elements of the same group show similar chemical properties and they also have the same number of valence electrons.
How many elements are in the periodic table?
The table below consists of 118 elements of the periodic table, sorted by atomic number, atomic weight, symbols, density, discovered year and the group.
Who created the modern periodic table?
The modern periodic table is based on the modern periodic law put forward by the English physicist Henry Moseley, which states that “the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers”.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the total number of protons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. The atomic number can provide insight into the electronic configuration of the element. For example, carbon has an electron configuration of [He] 2s 2 2p 2, since its atomic number is 6.
What is the number of protons in the nucleus called?
The number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number. The atomic number of each element is unique.
Why is the atomic number of each element unique?
While the atomic number always stays the same some elements have atoms with different atomic mass numbers. This is because some elements have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus.
How to find the mass of an element?
The number of protons and the number of neutrons shall determine the mass number of an element. Since the isotopes of an element have slightly different mass numbers, it calculates the atomic mass by obtaining the mean of the mass numbers for its isotopes.
How can periodic trends be observed?
Periodic trends in the properties of the elements can be observed down the groups and across the periods of the modern periodic table. Every chemical element has a specific atomic number, which provides insight into the number of protons present within its nucleus.
